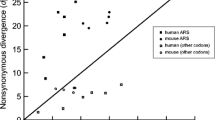
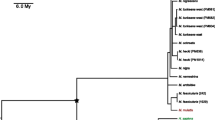
Abstract
Two related genes with potentially similar functions, one on the Y chromosome and one on the X chromosome, were examined to determine if they evolved differently because of their chromosomal positions. Six hundred fifty-seven base pairs of coding sequence of Jarid1d (Smcy) on the Y chromosome and Jarid1c (Smcx) on the X chromosome were sequenced in 13 rodent taxa. An analysis of replacement and silent substitutions, using a counting method designed for samples with small evolutionary distances, showed a significant difference between the two genes. The different patterns of replacement and silent substitutions within Jarid1d and Jarid1c may be a result of evolutionary mechanisms that are particularly strong on the Y chromosome because of its unique properties. These findings are similar to results of previous studies of Y chromosomal genes in these and other mammalian taxa, suggesting that genes on the mammalian Y evolve in a chromosome-specific manner.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agulnik AI, Mitchell MJ, Lerner JL, Woods DR, Bishop CE (1994a) A mouse Y-chromosome gene encoded by a region essential for spermatogenesis and expression of male-specific minor histocompatibility antigens. Hum Mol Genet 3: 873–878
Agulnik AI, Mitchell MJ, Mattei M-G, Borsani G, Avner PA, et al. (1994b) A novel X gene with a widely transcribed Y-linked homologue escapes X-inactivation in mouse and human. Hum Mol Genet 3: 879–884
Agulnik AI, Bishop CE, Lerner JL, Agulnik SI, Solovyev VV (1997) Analysis of mutation rates in the SMCY/SMCX genes shows that mammalian evolution is male driven. Mamm Genome 8: 134–138
Agulnik AI, Longepied G, Ty MT, Bishop CE, Mitchell M (1999) Mouse H-Y encoding Smcy gene and its X chromosomal homolog Smcx. Mamm Genome 10: 926–929
Bull JJ (1983) Evolution of sex determining mechanisms (Menlo Park, CA: Benjamin/Cummings)
Catzeflis FM, Denys C (1992) The African Nannomys (Muridae)—an early offshoot from the Mus lineage—evidence from scnDNA hybridization experiments and compared morphology. Isr J Zool 38: 219–231
Ceplitis H, Ellegren H (2004) Adaptive molecular evolution of HINTW, a female-specific gene in birds. Mol Biol Evol 21: 249–254
Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D (2000) The degeneration of Y chromosomes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355: 1563–1572
Chevret P, Granjon L, Duplantier JM, Denys C, Catzeflis FM (1994) Molecular phylogeny of the Praomys complex (Rodentia, Murinae)—a study based on DNA/DNA hybridization experiments. Zool J Linn Soc 112: 425–442
Disteche CM (1999) Escapees on the X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96: 14180–14182
Duret L, Mouchiroud D (2000) Determinants of substitution rates in mammalian genes: expression pattern affects selection intensity but not mutation rate. Mol Biol Evol 17: 68–74
Fridolfsson A-K, Cheng H, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Liu H-C, et al. (1998) Evolution of the avian sex chromosomes from an ancestral pair of autosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 8147–8152
Garcia-Moreno J, Mindell DP (2000) Rooting a phylogeny with homologous genes on opposite sex chromosomes (gametologs): a case study using avian CHD. Mol Biol Evol 17: 1826–1832
Hurst LD (1994a) Embryonic growth and the evolution of the mammalian Y chromosome I.: The Y as an attractor for selfish growth factors. Heredity 73: 223–232
Hurst LD (1994b) Embryonic growth and the evolution of the mammalian Y chromosome II: Suppression of the selfish Y-linked growth factors may explain escape from X-inactivation and rapid evolution of Sry. Heredity 73: 233–243
Jansa SA, Lundrigan BL, Tucker PK (2003) Tests for positive selection on immune and reproductive genes in closely related species of the murine genus Mus. J Mol Evol 56: 294–307
Jansa SA, Weksler M (2004) Phylogeny of muroid rodents: relationships within and among major lineages as determined by IRBP gene sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 31: 256–276
Jegalian K, Page DC (1998) A proposed path by which genes common to mammalian X and Y chromosomes evolve to become X inactivated. Nature 394: 776–780
Jensen LR, Amende M, Gurok U, Moser B, Gimmel V, et al. (2005) Mutations in the JARID1C gene, which is involved in transcriptional regulation and chromatin remodeling, cause X-linked mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 76: 227–236
Kumar S, Tamura Y, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA 2: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17: 1244–1245
Lahn BT, Page DC (1997) Functional coherence of the human Y-chromosome. Science 278: 675–680
Lahn BT, Page DC (1999) Four evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome. Science 286: 964–967
Lahn BT, Pearson NM, Jegalian K (2001) The human Y chromosome, in the light of evolution. Nat Rev Genet 2: 207–216
Lee YH, Ota T, Vacquier VD (1995) Positive selection is a general phenomenon in the evolution of abalone sperm lysin. Mol Biol Evol 12: 231–238
Lundrigan BL, Jansa SA, Tucker PK (2002) Phylogenetic relationships in the genus Mus, based on maternally, paternally, and biparentally inherited characters. Syst Biol 51: 410–431
Maddison D, Maddison W (2000) MacClade 4: Analysis of Phylogeny and Character Evolution (Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates)
Negrutiu I, Vyskot B, Barbacar N, Georgiev S, Moneger F (2001) Dioecious plants. A key to the early events of sex chromosome evolution. Plant Physiol 127: 1418–1424
Nei M, Gojobori J (1986) Simple methods for estimating the number of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3: 418–426
O’Neill MJ, O’Neill RJW (1999) Whatever happened to SRY? Cell Mol Life Sci 56: 883–893
Pamilo P, Waugh O’Neill RJ (1997) Evolution of the Sry genes. Mol Biol Evol 14: 49–55
Patsialou A, Wilsker D, Moran E (2005) DNA-binding properties of ARID family proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 33: 66–80
Rice WR (1996) Evolution of the Y sex chromosome in animals. BioScience 46: 331–343
Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F, Mullis KB, Horn GT, et al. (1985) Enzymatic amplification of β-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230: 1350–1254
Sandstedt SA, Tucker PK (2004) Evolutionary strata on the mouse X chromosome correspond to strata on the human X chromosome. Genome Res 14: 267–272
Scott DM, Ehrmann IE, Ellis PS, Agulnik AI, Bishop CE, et al. (1995) Identification of a mouse male-specific transplantation antigen, H-Y. Nature 376: 695–698
Sheardown S, Norris D, Fisher A, Brockdorff N (1996) The mouse Smcx gene exhibits developmental and tissue specific variation in degree of escape from X inactivation. Hum Mol Genet 5: 1355–1360
Steinemann M, Steinemann S (1998) Enigma of Y chromosome degeneration: neo-Y and neo-X chromosomes of Drosophila miranda a model for sex chromosome evolution. Genetica 102–103: 409–420
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP* Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods) (Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates)
Takeuchi T, Yamazaki Y, Katohfukui Y, Tsuchiya R, Kondo S, et al. (1995) Gene trap capture of a novel mouse gene, Jumonji, required for neural-tube formation. Genes Devel 9: 1211–1222
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25: 4876–4888
Toder R, Wakefield MJ, Graves JAM (2000) The minimal mammalian Y chromosome - the marsupial Y as a model system. Cytogenet Cell Genet 91: 285–292
Tucker PK, Lundrigan BL (1993) Rapid evolution of the sex determining locus in Old World mice and rats. Nature 364: 715–717
Tucker PK, Adkins RM, Rest JS (2003) Differential rates of evolution for the ZFY-related zinc finger genes, Zfy, Zfx and Zfa in the mouse genus Mus. Mol Biol Evol 20: 999–1005
Tucker PK, Sandstedt SA, Lundrigan BL (2005) Phylogenetic relationships in the subgenus Mus (genus Mus, family Muridae, subfamily Murinae): examining gene trees and species trees. Biol J Linn Soc 84: 653–662
Wang W, Meadows LR, den Haan JMM, Sherman NE, Chen Y, et al. (1995) Human H-Y: a male-specific histocompatibility antigen derived from the SMCY protein. Science 269: 1588–1590
Whitfield LS, Lovell-Badge R, Goodfellow PN (1993) Rapid sequence evolution of the mammalian sex-determining gene SRY. Nature 364: 713–715
Wu J, Ellison J, Salido E, Yen P, Mohandas T, et al. (1994a) Isolation and characterization of XE169, a novel human gene that escapes X-inactivation. Hum Mol Genet 3: 153–160
Wu J, Salido EC, Yen PH, Mohandas TK, Heng HHQ, et al. (1994b) The murine Xe169 gene escapes X-inactivation like its human homologue. Nat Genet 7: 491–496
Wyckoff GJ, Li J, Wu C-I (2002) Molecular evolution of functional genes on the mammalian Y chromosome. Mol Biol Evol 19: 1633–1636
Xu J, Burgoyne PS, Arnold AP (2002) Sex differences in sex chromosome gene expression in mouse brain. Hum Mol Genet 11: 1409–1419
Zhang J (2004) Evolution of DMY, a newly emergent male sex-determination gene of medaka fish. Genetics 166: 1887–1895
Zhang J, Nei M (1997) Accuracies of ancestral amino acid sequences inferred by the parsimony, likelihood, and distance methods. J Mol Evol 44: S139–S146
Zhang J, Kumar S, Nei M (1997) Small-sample tests of episodic adaptive evolution: A case study of primate lysozymes. Mol Biol Evol 14: 1335–1338
Zhang J, Rosenberg HF, Nei M (1998) Positive Darwinian selection after gene duplication in primate ribonuclease genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3708–3713
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jianzhi Zhang for his comments on an earlier draft of this work. This work was supported by NIH grant EY12994 and NSF grant DEB9209950.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandstedt, S.A., Tucker, P.K. Inefficient purifying selection: the mammalian Y chromosome in the rodent genus Mus. Mamm Genome 17, 14–21 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-005-0050-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-005-0050-y