Abstract
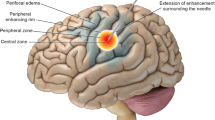
The aim of this study was to test the hypotheses that (a) MR imaging-guided radiofrequency (RF) thermal ablation is safe and feasible in porcine brain using an open C-arm-shaped low-field MR system, and that (b) induced thermal lesion size can be predicted using low-field MR imaging. Magnetic resonance-guided RF ablation was performed in the cerebral frontal lobes of six pigs. An 18-G monopolar RF electrode was inserted into the porcine brain using MR image guidance and RF was then applied for 10 min. After post-procedure imaging (T2-weighted, T1-weighted before and after gadodiamide administration), the pigs were killed and the brains were used for pathologic examination. Successful RF electrode placement was accomplished in all cases without complications; total magnet time ranged from 73 to 189 min. The thermal lesion size varied from 10 to 12 mm perpendicular to the electrode track and was easily visualized on T2-weighted and enhanced T1-weighted images. Enhanced T1-weighted imaging demonstrated the highest brain-to-RF thermal lesion contrast-to-noise ratio with an average of 1.5 ± 1.6. Enhanced T1-weighted imaging never underestimated pathologic lesion diameter with a mean difference of 2.3 ± 1.0 mm and a radiologic/pathologic correlation of 0.69. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided RF thermal ablation is feasible and safe in the porcine brain using an open MR low-field system. Induced thermal lesion size can best be monitored using enhanced T1-weighted images. In the future, RF ablation under low-field MR guidance may offer an alternative treatment option for primary and secondary brain tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 February 2000 Revised: 18 July 2000 Accepted: 19 July 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merkle, E., Shonk, J., Zheng, L. et al. MR imaging-guided radiofrequency thermal ablation in the porcine brain at 0.2 T. Eur Radiol 11, 884–892 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300000626
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300000626