Abstract
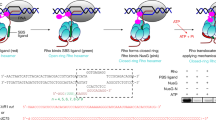
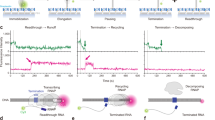
The bacterial hexameric helicase known as Rho is an archetypal sequence-specific transcription terminator that typically halts the synthesis of a defined set of transcripts, particularly those bearing cytosine-rich 3′-untranslated regions. However, under conditions of translational stress, Rho can also terminate transcription at cytosine-poor sites when assisted by the transcription factor NusG. Recent structural, biochemical, and computational studies of the Rho·NusG interaction in Escherichia coli have helped establish how NusG reprograms Rho activity. NusG is found to be an allosteric activator of Rho that directly binds to the ATPase motor domain of the helicase and facilitates closure of the Rho ring around non-ideal (purine-rich) target RNAs. The manner in which NusG acts on Rho helps to explain how the transcription terminator is excluded from acting on RNA polymerase by exogenous factors, such as the antitermination protein NusE, the NusG paralog RfaH, and RNA polymerase-coupled ribosomes. Collectively, an understanding of the link between NusG and Rho provides new insights into how transcriptional and translational fidelity are maintained during gene expression in bacteria.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artsimovitch I, Landick R (2002) The transcriptional regulator RfaH stimulates RNA chain synthesis after recruitment to elongation complexes by the exposed nontemplate DNA strand. Cell 109:193–203
Baniulyte G, Singh N, Benoit C, Johnson R, Ferguson R, Paramo M, Stringer AM, Scott A, Lapierre P, Wade JT (2017) Identification of regulatory targets for the bacterial Nus factor complex. Nat Commun 8:2027
Bidnenko E, Bidnenko V (2018) Transcription termination factor Rho and microbial phenotypic heterogeneity. Curr Genet 64:541–546
Bogden CE, Fass D, Bergman N, Nichols MD, Berger JM (1999) The structural basis for terminator recognition by the Rho transcription termination factor. Mol Cell 3:487–493
Brennan CA, Dombroski AJ, Platt T (1987) Transcription termination factor rho is an RNA-DNA helicase. Cell 48:945–952
Burmann BM, Schweimer K, Luo X, Wahl MC, Stitt BL, Gottesman ME, Rosch P (2010) A NusE:NusG complex links transcription and translation. Science 328:501–504
Burmann BM, Knauer SH, Sevostyanova A, Schweimer K, Mooney RA, Landick R, Artsimovitch I, Rosch P (2012) An alpha helix to beta barrel domain switch transforms the transcription factor RfaH into a translation factor. Cell 150:291–303
Burns CM, Richardson JP (1995) NusG is required to overcome a kinetic limitation to Rho function at an intragenic terminator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4738–4742
Cardinale CJ, Washburn RS, Tadigotla VR, Brown LM, Gottesman ME, Nudler E (2008) Termination factor Rho and its cofactors NusA and NusG silence foreign DNA in E. coli. Science 320:935–938
Chalissery J, Muteeb G, Kalarickal NC, Mohan S, Jisha V, Sen R (2011) Interaction surface of the transcription terminator Rho required to form a complex with the C-terminal domain of the antiterminator NusG. J Mol Biol 405:49–64
Dolan JW, Marshall NF, Richardson JP (1990) Transcription termination factor rho has three distinct structural domains. J Biol Chem 265:5747–5754
Downing WL, Sullivan SL, Gottesman ME, Dennis PP (1990) Sequence and transcriptional pattern of the essential Escherichia coli secE-nusG operon. J Bacteriol 172:1621–1627
Epshtein V, Cardinale CJ, Ruckenstein AE, Borukhov S, Nudler E (2007) An allosteric path to transcription termination. Mol Cell 28:991–1001
Goodson JR, Klupt S, Zhang C, Straight P, Winkler WC (2017) LoaP is a broadly conserved antiterminator protein that regulates antibiotic gene clusters in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Nat Microbiol 2:17003
Gutierrez P, Kozlov G, Gabrielli L, Elias D, Osborne MJ, Gallouzi IE, Gehring K (2007) Solution structure of YaeO, a Rho-specific inhibitor of transcription termination. J Biol Chem 282:23348–23353
Hu K, Artsimovitch I (2017) A screen for rfaH suppressors reveals a key role for a connector region of termination factor Rho. MBio 8
Kohler R, Mooney RA, Mills DJ, Landick R, Cramer P (2017) Architecture of a transcribing-translating expressome. Science 356:194–197
Lawson MR, Dyer K, Berger JM (2016) Ligand-induced and small-molecule control of substrate loading in a hexameric helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:13714–13719
Lawson MR, Ma W, Bellecourt MJ, Artsimovitch I, Martin A, Landick R, Schulten K, Berger JM (2018) Mechanism for the regulated control of bacterial transcription termination by a universal adaptor protein. Mol Cell 71:911–922.e914
Miller OL Jr, Hamkalo BA, Thomas CA Jr (1970) Visualization of bacterial genes in action. Science 169:392–395
Mitra P, Ghosh G, Hafeezunnisa M, Sen R (2017) Rho protein: roles and mechanisms. Annu Rev Microbiol 71:687–709
Miwa Y, Horiguchi T, Shigesada K (1995) Structural and functional dissections of transcription termination factor rho by random mutagenesis. J Mol Biol 254:815–837
Mooney RA, Schweimer K, Rosch P, Gottesman M, Landick R (2009) Two structurally independent domains of E. coli NusG create regulatory plasticity via distinct interactions with RNA polymerase and regulators. J Mol Biol 391:341–358
Morgan WD, Bear DG, Litchman BL, von Hippel PH (1985) RNA sequence and secondary structure requirements for rho-dependent transcription termination. Nucleic Acids Res 13:3739–3754
Nehrke KW, Zalatan F, Platt T (1993) NusG alters rho-dependent termination of transcription in vitro independent of kinetic coupling. Gene Expr 3:119–133
Pani B, Banerjee S, Chalissery J, Muralimohan A, Loganathan RM, Suganthan RB, Sen R (2006) Mechanism of inhibition of Rho-dependent transcription termination by bacteriophage P4 protein Psu. J Biol Chem 281:26491–26500
Park JS, Roberts JW (2006) Role of DNA bubble rewinding in enzymatic transcription termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:4870–4875
Pasman Z, von Hippel PH (2000) Regulation of rho-dependent transcription termination by NusG is specific to the Escherichia coli elongation complex. Biochemistry 39:5573–5585
Peters JM, Mooney RA, Kuan PF, Rowland JL, Keles S, Landick R (2009) Rho directs widespread termination of intragenic and stable RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:15406–15411
Peters JM, Vangeloff AD, Landick R (2011) Bacterial transcription terminators: the RNA 3′-end chronicles. J Mol Biol 412:793–813
Peters JM, Mooney RA, Grass JA, Jessen ED, Tran F, Landick R (2012) Rho and NusG suppress pervasive antisense transcription in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev 26:2621–2633
Rabhi M, Espeli O, Schwartz A, Cayrol B, Rahmouni AR, Arluison V, Boudvillain M (2011) The Sm-like RNA chaperone Hfq mediates transcription antitermination at Rho-dependent terminators. Embo j 30:2805–2816
Ray-Soni A, Bellecourt MJ, Landick R (2016) Mechanisms of bacterial transcription termination: all good things must end. Annu Rev Biochem 85:319–347
Richardson JP (1982) Activation of rho protein ATPase requires simultaneous interaction at two kinds of nucleic acid-binding sites. J Biol Chem 257:5760–5766
Ruteshouser EC, Richardson JP (1989) Identification and characterization of transcription termination sites in the Escherichia coli lacZ gene. J Mol Biol 208:23–43
Said N, Krupp F, Anedchenko E, Santos KF, Dybkov O, Huang YH, Lee CT, Loll B, Behrmann E, Burger J et al (2017) Structural basis for lambdaN-dependent processive transcription antitermination. Nat Microbiol 2:17062
Schwartz A, Margeat E, Rahmouni AR, Boudvillain M (2007) Transcription termination factor rho can displace streptavidin from biotinylated RNA. J Biol Chem 282:31469–31476
Sedlyarova N, Shamovsky I, Bharati BK, Epshtein V, Chen J, Gottesman S, Schroeder R, Nudler E (2016) sRNA-mediated control of transcription termination in E. coli. Cell 167:111–121.e113
Sevostyanova A, Groisman EA (2015) An RNA motif advances transcription by preventing Rho-dependent termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E6835–E6843
Skordalakes E, Berger JM (2003) Structure of the Rho transcription terminator: mechanism of mRNA recognition and helicase loading. Cell 114:135–146
Thomsen ND, Berger JM (2009) Running in reverse: the structural basis for translocation polarity in hexameric helicases. Cell 139:523–534
Thomsen ND, Lawson MR, Witkowsky LB, Qu S, Berger JM (2016) Molecular mechanisms of substrate-controlled ring dynamics and substepping in a nucleic acid-dependent hexameric motor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E7691-e7700
Tomar SK, Artsimovitch I (2013) NusG-Spt5 proteins-Universal tools for transcription modification and communication. Chem Rev 113:8604–8619
Valabhoju V, Agrawal S, Sen R (2016) Molecular basis of nusg-mediated regulation of Rho-dependent transcription termination in bacteria. J Biol Chem 291:22386–22403
Yu X, Horiguchi T, Shigesada K, Egelman EH (2000) Three-dimensional reconstruction of transcription termination factor rho: orientation of the N-terminal domain and visualization of an RNA-binding site. J Mol Biol 299:1279–1287
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by G. Harold and Leila Y. Mathers Foundation and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (R37-071747), to J.M.B. M.R.L. gratefully acknowledges support from the A.P. Giannini Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lawson, M.R., Berger, J.M. Tuning the sequence specificity of a transcription terminator. Curr Genet 65, 729–733 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-019-00939-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-019-00939-1