Abstract
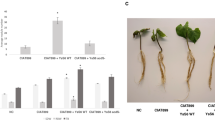
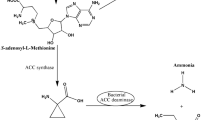
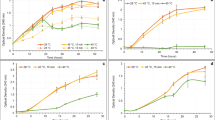
Several rhizobial strains possess the ability to modulate leguminous plants ethylene levels by producing the enzyme 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase. While the effect of ACC deaminase has been studied in several rhizobia belonging to the Alphaproteobacteria class, not much is understood about its impact in the nodulation abilities of rhizobia belonging to the Betaproteobacteria class, which are common symbionts of Mimosa species. In this work, we report the impact of ACC deaminase production by the Betaproteobacterium, Cupriavidus taiwanensis STM894, and its role in the nodulation of Mimosa pudica. C. taiwanensis STM894 was studied following its transformation with the plasmid pRKACC, containing an ACC deaminase gene. The expression of the exogenous ACC deaminase led to increased nodulation and M. pudica growth promotion by C. taiwanensis STM894. These results indicate that ACC deaminase plays an important role in modulating ethylene levels that inhibit the nodulation process induced by both rhizobia belonging to the Alpha and Betaproteobacteria class.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guinel FC (2015) Ethylene, a hormone at the center-stage of nodulation. Front Plant Sci 6:1121–1121
Van de Poel B, Van Der Straeten D (2014) 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) in plants: more than just the precursor of ethylene! Front Plant Sci 5:1–11
Ma W, Guinel FC, Glick BR (2003) Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase promotes nodulation of pea plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4396–4402
Uchiumi T, Ohwada T, Itakura M et al (2004) Expression islands clustered on the symbiosis island of the Mesorhizobium loti genome. J Bacteriol 186:2439–2448
Nascimento FX, Rossi MJ, Soares CRFS. et al (2014) New insights into 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase phylogeny, evolution and ecological significance. PLoS One 9:e99168
Nascimento FX, Brígido C, Glick BR, Rossi MJ (2016) The role of rhizobial acc deaminase in the nodulation process of leguminous plants. Int J Agron 2016:1–9
Ma W, Charles TC, Glick BR (2004) Expression of an exogenous 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase gene in Sinorhizobium meliloti increases its ability to nodulate alfalfa. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5891–5897
Conforte V, Echeverria M, Sánchez C et al (2010) Engineered ACC deaminase-expressing free-living cells of Mesorhizobium loti show increased nodulation efficiency and competitiveness on Lotus spp. J Gen Appl Microbiol 56:331–338
Nascimento F, Brígido C, Alho L et al (2012) Enhanced chickpea growth-promotion ability of a Mesorhizobium strain expressing an exogenous ACC deaminase gene. Plant Soil 353:221–230
Nascimento FX, Brígido C, Glick BR et al (2012) Mesorhizobium ciceri LMS-1 expressing an exogenous 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase increases its nodulation abilities and chickpea plant resistance to soil constraints. Lett Appl Microbiol 55:15–21
Brígido C, Nascimento FX, Duan J et al (2013) Expression of an exogenous 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase gene in Mesorhizobium spp. reduces the negative effects of salt stress in chickpea. FEMS Microbiol Lett 349:46–53
Kong Z, Glick BR, Duan J et al (2015) Effects of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase-overproducing Sinorhizobium meliloti on plant growth and copper tolerance of Medicago lupulina. Plant Soil 391:383–398
Chen W-M, James EK, Prescott AR et al (2003) Nodulation of Mimosa spp. by the β-proteobacterium Ralstonia taiwanensis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:1051–1061
Gyaneshwar P, Hirsch AM, Moulin L et al (2011) Legume-nodulating Betaproteobacteria: diversity, host range, and future prospects. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24:1276–1288
Chen WM, Laevens S, Lee TM et al (2001) Ralstonia taiwanensis sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Mimosa species and sputum of a cystic fibrosis patient. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1729–1735
Amadou C, Pascal G, Mangenot S et al (2008) Genome sequence of the β-rhizobium Cupriavidus taiwanensis and comparative genomics of rhizobia. Genome Res 18:1472–1483
Shah S, Li J, Moffatt BA, Glick BR (1998) Isolation and characterization of ACC deaminase genes from two different plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Can J Microbiol 44:833–843
Duan J, Jiang W, Cheng Z et al (2013) The complete genome sequence of the plant growth-promoting bacterium Pseudomonas sp. UW4. PLoS One 8:e58640
Dworkin M, Foster J (1958) Experiments with some microorganisms which utilize ethane and hydrogen. J Bacteriol 75:592–603
Penrose DM, Glick BR (2003) Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol Plant 118:10–15
Broughton WJ, Dilworth MJ (1971) Control of leghaemoglobin synthesis in snake beans. Biochem J 125:1075–1080
Glick BR, Todorovic B, Czarny J et al (2007) Promotion of plant growth by bacterial ACC deaminase. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 26:227–242
Onofre-Lemus J, Hernández-Lucas I, Girard L, Caballero-Mellado J (2009) ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate) deaminase activity, a widespread trait in Burkholderia species, and its growth-promoting effect on tomato plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6581–6590
Acknowledgements
Francisco X. Nascimento acknowledges receiving a Ph.D. fellowship (SFRH/BD/86954/2012) from Fundação de Ciência e Tecnologia, Portugal. We thank Dr. Lionel Moulin for gently ceding the Cupriavidus taiwanensis STM894 strain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nascimento, F.X., Tavares, M.J., Glick, B.R. et al. Improvement of Cupriavidus taiwanensis Nodulation and Plant Growth Promoting Abilities by the Expression of an Exogenous ACC Deaminase Gene. Curr Microbiol 75, 961–965 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-018-1474-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-018-1474-4