Abstract
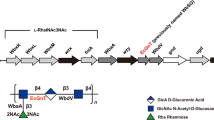
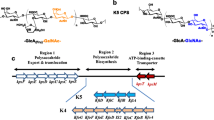
The biological activities of heparan sulfate (HS) and heparin (HP) are closely related to their molecular structures. Both Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase 2 (PmHS2) and Escherichia coli K5 KfiA have been used for enzymatic and chemoenzymatic synthesis of HS and HP oligosaccharides and their derivatives. We show here that cloning using the pET15b vector and expressing PmHS2 as an N-His6-tagged fusion protein improve its expression level in E. coli. Investigation of the donor substrate specificity of the N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activities of P. multocida heparosan synthase 2 (PmHS2) and E. coli K5 KfiA indicates the substrate promiscuities of PmHS2 and KfiA. Overall, both PmHS2 and KfiA can use uridine 5'-diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) and some of its C2'- and C6'-derivatives as donor substrates for their α1–4-GlcNAcT activities. Nevertheless, PmHS2 has a broader tolerance towards substrate modifications. Other than the UDP-sugars that can be used by KfiA, additional C6'-derivatives of UDP-GlcNAc, UDP-glucose, and UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine (UDP-GalNAc) are tolerable substrates for the α1–4-GlcNAcT activity of PmHS2. The substrate promiscuities of PmHS2 and KfiA will allow efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of diverse HS and HP oligosaccharide derivatives which may have improved or altered activities compared to their natural counterparts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellaiche Y, The I, Perrimon N (1998) Tout-velu is a Drosophila homologue of the putative tumour suppressor EXT-1 and is needed for Hh diffusion. Nature 394:85–88
Campbell JA, Davies GJ, Bulone V, Henrissat B (1997) A classification of nucleotide-diphospho-sugar glycosyltransferases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 326(Pt 3):929–939
Chavaroche AA, Springer J, Kooy F, Boeriu C, Eggink G (2010) In vitro synthesis of heparosan using recombinant Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase PmHS2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1881–1891
Chavaroche AA, van den Broek LA, Springer J, Boeriu C, Eggink G (2011) Analysis of the polymerization initiation and activity of Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase PmHS2, an enzyme with glycosyltransferase and UDP-sugar hydrolase activity. J Biol Chem 286:1777–1785
Chavaroche AA, van den Broek LA, Boeriu C, Eggink G (2012) Synthesis of heparosan oligosaccharides by Pasteurella multocida PmHS2 single-action transferases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:1199–1210
Chen M, Bridges A, Liu J (2006) Determination of the substrate specificities of N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. Biochemistry 45:12358–12365
Chen Y, Thon V, Li Y, Yu H, Ding L, Lau K, Qu J, Hie L, Chen X (2011) One-pot three-enzyme synthesis of UDP-GlcNAc derivatives. Chem Commun 47:10815–10817
Coutinho PM, Deleury E, Davies GJ, Henrissat B (2003) An evolving hierarchical family classification for glycosyltransferases. J Mol Biol 328:307–317
DeAngelis PL (2002a) Evolution of glycosaminoglycans and their glycosyltransferases: implications for the extracellular matrices of animals and the capsules of pathogenic bacteria. Anat Rec 268:317–326
DeAngelis PL (2002b) Microbial glycosaminoglycan glycosyltransferases. Glycobiology 12:9R–16R
DeAngelis PL, White CL (2002) Identification and molecular cloning of a heparosan synthase from Pasteurella multocida type D. J Biol Chem 277:7209–7213
Deangelis PL, White CL (2004) Identification of a distinct, cryptic heparosan synthase from Pasteurella multocida types A, D, and F. J Bacteriol 186:8529–8532
DeAngelis PL, Gunay NS, Toida T, Mao WJ, Linhardt RJ (2002) Identification of the capsular polysaccharides of type D and F Pasteurella multocida as unmodified heparin and chondroitin, respectively. Carbohydr Res 337:1547–1552
Dulaney SB, Huang X (2012) Strategies in synthesis of heparin/heparan sulfate oligosaccharides: 2000–present. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 67:95–136
Esko JD, Lindahl U (2001) Molecular diversity of heparan sulfate. J Clin Invest 108:169–173
Hodson N, Griffiths G, Cook N, Pourhossein M, Gottfridson E, Lind T, Lidholt K, Roberts IS (2000) Identification that KfiA, a protein essential for the biosynthesis of the Escherichia coli K5 capsular polysaccharide, is an α-UDP-GlcNAc glycosyltransferase. The formation of a membrane-associated K5 biosynthetic complex requires KfiA, KfiB, and KfiC. J Biol Chem 275:27311–27315
Izumikawa T, Egusa N, Taniguchi F, Sugahara K, Kitagawa H (2006) Heparan sulfate polymerization in Drosophila. J Biol Chem 281:1929–1934
Lindahl U (2000) 'Heparin'—from anticoagulant drug into the new biology. Glycoconj J 17:597–605
Lindahl U, Kjellen L (1991) Heparin or heparan sulfate—what is the difference? Thromb Haemost 66:44–48
Liu J, Pedersen LC (2007) Anticoagulant heparan sulfate: structural specificity and biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:263–272
Liu R, Xu Y, Chen M, Weiwer M, Zhou X, Bridges AS, DeAngelis PL, Zhang Q, Linhardt RJ, Liu J (2010) Chemoenzymatic design of heparan sulfate oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem 285:34240–34249
Muthana MM, Qu J, Li Y, Zhang L, Yu H, Ding L, Malekan H, Chen X (2012) Efficient one-pot multienzyme synthesis of UDP-sugars using a promiscuous UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase from Bifidobacterium longum (BLUSP). Chem Commun 48:2728–2730
Otto NJ, Green DE, Masuko S, Mayer A, Tanner ME, Linhardt RJ, DeAngelis PL (2012) Structure/function analysis of Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthases: toward defining enzyme specificity and engineering novel catalysts. J Biol Chem 287:7203–7212
Rimler RB (1994) Presumptive identification of Pasteurella multocida serogroups A, D and F by capsule depolymerisation with mucopolysaccharidases. Vet Rec 134:191–192
Sismey-Ragatz AE, Green DE, Otto NJ, Rejzek M, Field RA, DeAngelis PL (2007) Chemoenzymatic synthesis with distinct Pasteurella heparosan synthases: monodisperse polymers and unnatural structures. J Biol Chem 282:28321–28327
Sugahara K, Kitagawa H (2002) Heparin and heparan sulfate biosynthesis. IUBMB Life 54:163–175
Sugiura N, Baba Y, Kawaguchi Y, Iwatani T, Suzuki K, Kusakabe T, Yamagishi K, Kimata K, Kakuta Y, Watanabe H (2010) Glucuronyltransferase activity of KfiC from Escherichia coli strain K5 requires association of KfiA: KfiC and KfiA are essential enzymes for production of K5 polysaccharide, N-acetylheparosan. J Biol Chem 285:1597–1606
Vann WF, Schmidt MA, Jann B, Jann K (1981) The structure of the capsular polysaccharide (K5 antigen) of urinary-tract-infective Escherichia coli O10:K5:H4. A polymer similar to desulfo-heparin. Eur J Biochem 116:359–364
Wu JR, Chen PY, Shien JH, Shyu CL, Shieh HK, Chang F, Chang PC (2010) Analysis of the biosynthesis genes and chemical components of the capsule of Avibacterium paragallinarum. Vet Microbiol 145:90–99
Xu Y, Masuko S, Takieddin M, Xu H, Liu R, Jing J, Mousa SA, Linhardt RJ, Liu J (2011) Chemoenzymatic synthesis of homogeneous ultralow molecular weight heparins. Science 334:498–501
Yu H, Chen X (2007) Carbohydrate post-glycosylational modifications. Org Biomol Chem 5:865–872
Zak BM, Crawford BE, Esko JD (2002) Hereditary multiple exostoses and heparan sulfate polymerization. Biochim Biophys Acta 1573:346–355
Acknowledgments
This project was financially supported by NSF grants CHE0548235 and CHE1012511, NIH grant R01HD065122, the Camille Dreyfus Teacher-Scholarship, and the UC-Davis Chancellor's Fellowship. M. M. M. acknowledges UC Davis and United States Department of Education for a GAANN fellowship. X. C. is a Camille Dreyfus Teacher-Scholar and a UC-Davis Chancellor's Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 311 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yu, H., Thon, V. et al. Donor substrate promiscuity of the N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activities of Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase 2 (PmHS2) and Escherichia coli K5 KfiA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 1127–1134 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4947-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4947-1