Abstract
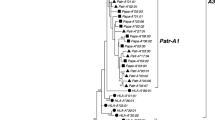
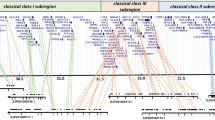
Common marmoset monkeys (Callithrix jacchus) have emerged as important animal models for biomedical research, necessitating a more extensive characterization of their major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region. However, the genomic information of the marmoset MHC (Caja) is still lacking. The MHC-B/C segment represents the most diverse MHC region among primates. Therefore, in this paper, to elucidate the detailed gene organization and evolutionary processes of the Caja class I B (Caja-B) segment, we determined two parts of the Caja-B sequences with 1,079 kb in total, ranging from H6orf15 to BAT1 and compared the structure and phylogeny with that of other primates. This segment contains 54 genes in total, nine Caja-B genes (Caja-B1 to Caja-B9), two MIC genes (MIC1 and MIC2), eight non-MHC genes, two non-coding genes, and 33 non-MHC pseudogenes that have not been observed in other primate MHC-B/C segments. Caja-B3, Caja-B4, and Caja-B7 encode proper MHC class I proteins according to amino acid structural characteristics. Phylogenetic relationships based on 48 MHC-I nucleotide sequences in primates suggested (1) species-specific divergence for Caja, Mamu, and HLA/Patr/Gogo lineages, (2) independent generation of the “seven coding exon” type MHC-B genes in Mamu and HLA/Patr/Gogo lineages from an ancestral “eight coding exon” type MHC-I gene, (3) parallel correlation with the long and short segmental duplication unit length in Caja and Mamu lineages. These findings indicate that the MHC-B/C segment has been under permanent selective pressure in the evolution of primates.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott DH, Barnett DK, Colman RJ, Yamamoto ME, Schultz-Darken NJ (2003) Aspects of common marmoset basic biology and life history important for biomedical research. Comp Med 53:339–350
Abi-Rached L, Kuhl H, Roos C, ten Hallers B, Zhu B, Carbone L, de Jong PJ, Mootnick AR, Knaust F, Reinhardt R, Parham P, Walter L (2010) A small, variable, and irregular killer cell Ig-like receptor locus accompanies the absence of MHC-C and MHC-G in gibbons. J Immunol 184:1379–1391
Adams EJ, Parham P (2001) Species-specific evolution of MHC class I genes in the higher primates. Immunol Rev 183:41–64
Adams EJ, Thomson G, Parham P (1999) Evidence for an HLA-C-like locus in the orangutan Pongo pygmaeus. Immunogenetics 49:865–871
Adams AP, Aronson JF, Tardif SD, Patterson JL, Brasky KM, Geiger R, de la Garza M, Carrion R Jr, Weaver SC (2008) Common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus) as a nonhuman primate model to assess the virulence of eastern equine encephalitis virus strains. J Virol 82:9035–9042
Anzai T, Shiina T, Kimura N, Yanagiya K, Kohara S, Shigenari A, Yamagata T, Kulski JK, Naruse TK, Fujimori Y, Fukuzumi Y, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Iwamoto C, Umehara Y, Imanishi T, Meyer A, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Bahram S, Inoko H (2003) Comparative sequencing of human and chimpanzee MHC class I regions unveils insertions/deletions as the major path to genomic divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:7708–7713
Averdam A, Seelke S, Grutzner I, Rosner C, Roos C, Westphal N, Stahl-Hennig C, Muppala V, Schrod A, Sauermann U, Dressel R, Walter L (2007) Genotyping and segregation analyses indicate the presence of only two functional MIC genes in rhesus macaques. Immunogenetics 59:247–251
Averdam A, Petersen B, Rosner C, Neff J, Roos C, Eberle M, Aujard F, Munch C, Schempp W, Carrington M, Shiina T, Inoko H, Knaust F, Coggill P, Sehra H, Beck S, Abi-Rached L, Reinhardt R, Walter L (2009) A novel system of polymorphic and diverse NK cell receptors in primates. PLoS Genet 5:e1000688
Bankiewicz KS, Sanchez-Pernaute R, Oiwa Y, Kohutnicka M, Cummins A, Eberling J (2001) Preclinical models of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Protoc Neurosci Chapter 9:Unit 9 4
Cadavid LF, Hughes AL, Watkins DI (1996) MHC class I-processed pseudogenes in New World primates provide evidence for rapid turnover of MHC class I genes. J Immunol 157:2403–2409
Cadavid LF, Shufflebotham C, Ruiz FJ, Yeager M, Hughes AL, Watkins DI (1997) Evolutionary instability of the major histocompatibility complex class I loci in New World primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14536–14541
Chang H, Wachtman LM, Pearson CB, Lee JS, Lee HR, Lee SH, Vieira J, Mansfield KG, Jung JU (2009) Non-human primate model of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000606
Daza-Vamenta R, Glusman G, Rowen L, Guthrie B, Geraghty DE (2004) Genetic divergence of the rhesus macaque major histocompatibility complex. Genome Res 14:1501–1515
Dewannieux M, Esnault C, Heidmann T (2003) LINE-mediated retrotransposition of marked Alu sequences. Nat Genet 35:41–48
Doxiadis GG, Heijmans CM, Otting N, Bontrop RE (2007) MIC gene polymorphism and haplotype diversity in rhesus macaques. Tissue Antigens 69:212–219
Ewing B, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 8:186–194
Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl MC, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res 8:175–185
Fukami-Kobayashi K, Shiina T, Anzai T, Sano K, Yamazaki M, Inoko H, Tateno Y (2005) Genomic evolution of MHC class I region in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9230–9234
Furlan R, Cuomo C, Martino G (2009) Animal models of multiple sclerosis. Methods Mol Biol 549:157–173
Gaytan F, Gaytan M, Castellano JM, Romero M, Roa J, Aparicio B, Garrido N, Sanchez-Criado JE, Millar RP, Pellicer A, Fraser HM, Tena-Sempere M (2009) KiSS-1 in the mammalian ovary: distribution of kisspeptin in human and marmoset and alterations in KiSS-1 mRNA levels in a rat model of ovulatory dysfunction. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:E520–E531
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Hattori F, Chen H, Yamashita H, Tohyama S, Satoh YS, Yuasa S, Li W, Yamakawa H, Tanaka T, Onitsuka T, Shimoji K, Ohno Y, Egashira T, Kaneda R, Murata M, Hidaka K, Morisaki T, Sasaki E, Suzuki T, Sano M, Makino S, Oikawa S, Fukuda K (2010) Nongenetic method for purifying stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Nat Methods 7:61–66
Kametani Y, Suzuki D, Kohu K, Satake M, Suemizu H, Sasaki E, Ito T, Tamaoki N, Mizushima T, Ozawa M, Tani K, Kito M, Arai H, Koyanagi A, Yagita H, Habu S (2009) Development of monoclonal antibodies for analyzing immune and hematopoietic systems of common marmoset. Exp Hematol 37:1318–1329
Kap YS, Smith P, Jagessar SA, Remarque E, Blezer E, Strijkers GJ, Laman JD, Hintzen RQ, Bauer J, Brok HP, t Hart BA (2008) Fast progression of recombinant human myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in marmosets is associated with the activation of MOG34-56-specific cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol 180:1326–1337
Knapp LA, Cadavid LF, Watkins DI (1998) The MHC-E locus is the most well conserved of all known primate class I histocompatibility genes. J Immunol 160:189–196
Layne DG, Power RA (2003) Husbandry, handling, and nutrition for marmosets. Comp Med 53:351–359
Lever MS, Stagg AJ, Nelson M, Pearce P, Stevens DJ, Scott EA, Simpson AJ, Fulop MJ (2008) Experimental respiratory anthrax infection in the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Int J Exp Pathol 89:171–179
Ludlage E, Mansfield K (2003) Clinical care and diseases of the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Comp Med 53:369–382
Mansfield K (2003) Marmoset models commonly used in biomedical research. Comp Med 53:383–392
Mizuki N, Ando H, Kimura M, Ohno S, Miyata S, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Watanabe K, Ono A, Taguchi S, Sugawara C, Fukuzumi Y, Okumura K, Goto K, Ishihara M, Nakamura S, Yonemoto J, Kikuti YY, Shiina T, Chen L, Ando A, Ikemura T, Inoko H (1997) Nucleotide sequence analysis of the HLA class I region spanning the 237-kb segment around the HLA-B and -C genes. Genomics 42:55–66
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T (1997) Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7799–7806
Nelson M, Lever MS, Savage VL, Salguero FJ, Pearce PC, Stevens DJ, Simpson AJ (2009) Establishment of lethal inhalational infection with Francisella tularensis (tularaemia) in the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Int J Exp Pathol 90:109–118
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasaki E, Hanazawa K, Kurita R, Akatsuka A, Yoshizaki T, Ishii H, Tanioka Y, Ohnishi Y, Suemizu H, Sugawara A, Tamaoki N, Izawa K, Nakazaki Y, Hamada H, Suemori H, Asano S, Nakatsuji N, Okano H, Tani K (2005) Establishment of novel embryonic stem cell lines derived from the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Stem Cells 23:1304–1313
Sasaki E, Suemizu H, Shimada A, Hanazawa K, Oiwa R, Kamioka M, Tomioka I, Sotomaru Y, Hirakawa R, Eto T, Shiozawa S, Maeda T, Ito M, Ito R, Kito C, Yagihashi C, Kawai K, Miyoshi H, Tanioka Y, Tamaoki N, Habu S, Okano H, Nomura T (2009) Generation of transgenic non-human primates with germline transmission. Nature 459:523–527
Schultz-Darken NJ (2003) Sample collection and restraint techniques used for common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus). Comp Med 53:360–363
Shiina T, Tamiya G, Oka A, Yamagata T, Yamagata N, Kikkawa E, Goto K, Mizuki N, Watanabe K, Fukuzumi Y, Taguchi S, Sugawara C, Ono A, Chen L, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Ando A, Ikemura T, Kimura M, Inoko H (1998) Nucleotide sequencing analysis of the 146-kilobase segment around the IkBL and MICA genes at the centromeric end of the HLA class I region. Genomics 47:372–382
Shiina T, Tamiya G, Oka A, Takishima N, Yamagata T, Kikkawa E, Iwata K, Tomizawa M, Okuaki N, Kuwano Y, Watanabe K, Fukuzumi Y, Itakura S, Sugawara C, Ono A, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Ando A, Ikemura T, Soeda E, Kimura M, Bahram S, Inoko H (1999) Molecular dynamics of MHC genesis unraveled by sequence analysis of the 1,796,938-bp HLA class I region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13282–13287
Shiina T, Inoko H, Kulski JK (2004) An update of the HLA genomic region, locus information and disease associations: 2004. Tissue Antigens 64:631–649
Shiina T, Ota M, Shimizu S, Katsuyama Y, Hashimoto N, Takasu M, Anzai T, Kulski JK, Kikkawa E, Naruse T, Kimura N, Yanagiya K, Watanabe A, Hosomichi K, Kohara S, Iwamoto C, Umehara Y, Meyer A, Wanner V, Sano K, Macquin C, Ikeo K, Tokunaga K, Gojobori T, Inoko H, Bahram S (2006) Rapid evolution of major histocompatibility complex class I genes in primates generates new disease alleles in humans via hitchhiking diversity. Genetics 173:1555–1570
Shiina T, Hosomichi K, Inoko H, Kulski JK (2009) The HLA genomic loci map: expression, interaction, diversity and disease. J Hum Genet 54:15–39
Specht A, DeGottardi MQ, Schindler M, Hahn B, Evans DT, Kirchhoff F (2008) Selective downmodulation of HLA-A and -B by Nef alleles from different groups of primate lentiviruses. Virology 373:229–237
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tardif SD, Smucny DA, Abbott DH, Mansfield K, Schultz-Darken N, Yamamoto ME (2003) Reproduction in captive common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus). Comp Med 53:364–368
Weatherford T, Chavez D, Brasky KM, Lanford RE (2009) The marmoset model of GB virus B infections: adaptation to host phenotypic variation. J Virol 83:5806–5814
Yaguchi M, Tabuse M, Ohta S, Ohkusu-Tsukada K, Takeuchi T, Yamane J, Katoh H, Nakamura M, Matsuzaki Y, Yamada M, Itoh T, Nomura T, Toyama Y, Okano H, Toda M (2009) Transplantation of dendritic cells promotes functional recovery from spinal cord injury in common marmoset. Neurosci Res 65:384–392
Zuhlke U, Weinbauer G (2003) The common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) as a model in toxicology. Toxicol Pathol 31(Suppl):123–127
Acknowledgments
We thank Keiko Tanaka, Kazuyo Yanagiya, and Satoko Kintou of the Department of Molecular Life Science, Division of Basic Medical Science and Molecular Medicine, Tokai University School of Medicine for the technical assistance. The work was supported by the Scientific Research on Priority Areas “Comparative Genomics” (20017023) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT) and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (21300155) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), from the program “Pakt für Forschung und Innovation” grant “Biodiversity” of the Leibniz Society and institutional support from the German Primate Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported in this paper have been submitted to the DDBJ, EMBL, and GenBank nucleotide sequence databases and have been assigned accession numbers AB600201 and AB600202.
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
PCR primer sets for the BAC contig construction (PDF 13 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Nucleotide similarities with C. jacchus draft assembly (WUGSC 3.2) (PDF 51 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
Estimated amino acid comparison among primate MHC-B and MHC-C genes. 1, 2, 3, 8, b, v, S, CHO indicate α1 domain contact site, α2 domain contact site, α3 domain contact site, CD8 contact site, beta 2 microglobulin (B2M) contact site, T cell receptor and peptide contact site, disulfide bond site, and glycosyl site, respectively. Yellow, red, orange, and blue background indicate α1, α2, α3, CD8, B2M contact sites, variable sites, both of the contact sites, and variable sites and disulfide bond and glycosyl sites, respectively. An asterisk indicates a termination codon (PDF 639 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Nucleotide sequence-based phylogenetic trees. (A1) and (A2) indicate phylogenetic trees on exon 4 to exon 8 of the MHC-I genes constructed by NJ and BI methods, respectively. (B1) and (B2) indicate phylogenetic trees on intron sequences of the MHC-I genes constructed by NJ and BI methods, respectively. Red, blue, and black gene names and boxes indicate seven exon type MHC-I genes, eight exon type MHC-B/C genes, and pseudogenes, respectively. Numbers around the branches indicate bootstrap values in NJ method and posterior probabilities in BI method (PDF 135 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Dot matrix images between the MHC-B/C segment from the POU5F1 and BAT1 versus itself such as 126 kb mouse lemur (A), 1,002 kb common marmoset (B), 1,298 kb rhesus macaque (C), 280 kb gorilla (D), 294 kb chimpanzee and 364 kb human. Red, blue, and black gene names indicate seven exon type MHC-B genes, eight exon type MHC-B and MHC-C genes and pseudogenes, respectively. Gray gene names and boxes indicate MIC and non-MHC genes (PDF 566 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiina, T., Kono, A., Westphal, N. et al. Comparative genome analysis of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I B/C segments in primates elucidated by genomic sequencing in common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Immunogenetics 63, 485–499 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-011-0526-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-011-0526-8