Abstract
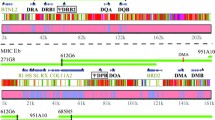
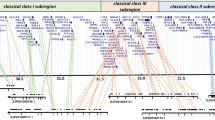
In terms of number of species, perciform (perch-like) fishes are one of the most diversified groups of modern vertebrates. Within this group, the family Cichlidae is best known for its spectacular adaptive radiation in the great lakes of East Africa. The molecular tool kit used in the study of this radiation includes the major histocompatibility complex (Mhc) genes. To refine this tool, information about the organization of the Mhc regions is badly needed. In this study, the first step was taken toward providing such information for the Mhc class one regions of Oreochromis niloticus, a representative species of the tilapiine branch of the Cichlidae, for which good bacterial artificial chromosome library is available. Screening of the library with class I gene probes led to the identification and isolation of 31 class-I-positive clones. Sequencing of one of these clones and partial characterization of the remaining clones for the presence of class I exons resulted in the construction of two contigs representing the class I region of this species as well as identification of seven additional class-I-positive singleton clones. The O. niloticus genome was shown to contain at least 28 class I genes or gene fragments. The shorter of the two contigs was approximately 330 kb long and contained eight class I genes/gene fragments; the longer contig encompassed 1,200 kb of sequence and contained minimally 17 class I genes/gene fragments; three additional class I genes were found to be borne by a clone that might be part of the shorter contig.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelrod HR, Burgess WE, Pronek N, Walls JG (1991) Dr. Axelrod’s atlas of freshwater aquarium fishes, 6th edn. TFH, Neptune City
Barlow GW (2000) The cichlid fishes. Nature’s grand experiment in evolution. Persens, Cambridge
Figueroa F, Mayer WE, Sültmann H, O’hUigin C, Tichy H, Satta Y, Takezaki N, Takahata N, Klein J (2000) Mhc class II B gene evolution in East African cichlid fishes. Immunogenetics 51:556–575
Fryer G, Iles TD (1972) The cichlid fishes of the great lakes of Africa. TFH, Neptune City
Katagiri T, Asakawa S, Minagawa S, Shimizu N, Hirono I, Aoki T (2001) Construction and characterization of BAC libraries for three fish species; rainbow trout, carp and tilapia. Anim Genet 32:200–204
Klein D, Ono H, O’hUigin C, Vincek V, Goldschmidt T, Klein J (1993) Extensive MHC variability in cichlid fishes of Lake Malawi. Nature 364:330–334
Klein J, Horejsi V (1997) Immunology. Blackwell, Oxford
Klein J, Klein D, Figueroa F, Sato A, O’hUigin C (1997) Major histocompatibility complex genes in the study of fish phylogeny. In: Kocher TD, Stepien CA (eds) Molecular systematics of fishes. Academic, New York, pp 271–283
Klein J, Sato A, Nagl S (1998) Molecular trans-species polymorphism. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 29:1–31
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Málaga-Trillo E, Zaleska-Rutczynska Z, McAndrew B, Vincek V, Figueroa F, Sültmann H, Klein J (1998) Linkage relationships and haplotype polymorphism among cichlid Mhc class II B loci. Genetics 149:1527–1537
Murray BW, Sültmann H, Klein J (1999) New family of Mhc class II A genes identified from cDNA sequences in the cichlid fish Aulonocara hansbaenschi. Immunogenetics 49:544–548
Murray BW, Shintani S, Sültmann H, Klein J (2000) Major histocompatibility complex class II A genes in cichlid fishes: identification, expression, linkage relationships, and haplotype variation. Immunogenetics 51:576–586
Nagl S, Tichy H, Mayer WE, Samonte IE, McAndrew BJ, Klein J (2001) Classification and phylogenetic relationships of African tilapiine fishes inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 20:361–374
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Nelson JS (1994) Fishes of the world. Wiley & Sons, New York
Ono H, O’hUigin C, Tichy H, Klein J (1993) Major-histocompatibility-complex variation in two species of cichlid fishes from Lake Malawi. Mol Biol Evol 10:1060–1072
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for constructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sato A, Klein D, Sültmann H, Figueroa F, O’hUigin C, Klein J (1997) Class I Mhc genes of cichlid fishes: identification, expression, and polymorphism. Immunogenetics 46:63–72
Sato A, Figueroa F, Murray BW, Málaga-Trillo E, Zaleska-Rutczynska Z, Sültmann H, Toyosawa S, Wedekind C, Steck N, Klein J (2000) Nonlinkage of the major histocompatibility complex of class I and class II loci in bony fishes. Immunogenetics 51:108–116
Sato A, Takezaki N, Tichy H, Figueroa F, Mayer WE, Klein J (2003) Origin and speciation of haplochromine fishes in East African crater lakes investigated by the analysis of their mtDNA, Mhc genes, and SINEs. Mol Biol Evol 20:1448–1462
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Trewavas E (1983) Tilapiine fishes of the genera Sarotherodon, Oreochromis and Danakilia. British Museum (Natural History), London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work had been carried out in part at the Max-Planck-Institut für Biologie, Abteilung Immungenetik, Tübingen, Germany (A.S., R.D., N.T., S.S., and J.K.).
The sequences reported in this paper have been deposited in the GenBank database (accession nos. AB270803–AB270897).
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
SFig. 1
Alignment of Mhc class I exon 2 sequences from O. niloticus. Dashes indicate identity with the simple majority consensus sequence; asterisks, alignment indels; and dots, missing information. Positions of missing nucleotides are indicated by highlighted \$ sign. Asterisks before the designation of the clone in sequence names indicate exons containing nucleotide deletions.(PDF 20 kb)
SFig. 2
Alignment of Mhc class I exon 3 sequences from O. niloticus. Dashes indicate identity with the simple majority consensus sequence; asterisks, alignment indels; and dots, missing information. P Positions of missing nucleotides are indicated by highlighted \$ sign. Asterisks before the designation of the clone in sequence names indicate exons containing nucleotide deletions.(PDF 26 kb)
SFig. 3
Alignment of Mhc class I exon 4 sequences from O. niloticus. Dashes indicate identity with the simple majority consensus sequence; asterisks, alignment indels; and dots, missing information. Positions of missing nucleotides and stop codons are indicated by highlighted \$ signs and nucleotides, respectively. Asterisks and plus signs before the designation of the clone in sequence names indicate exons containing nucleotide deletions and stop codons, respectively.(PDF 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, A., Dongak, R., Hao, L. et al. Mhc class I genes of the cichlid fish Oreochromis niloticus . Immunogenetics 58, 917–928 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-006-0151-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-006-0151-0