Abstract
Background
Intrathecal and intravenous chemotherapy, specifically methotrexate, might contribute to neural microstructural damage.
Objective
To assess, by diffusion tensor imaging, microstructural integrity of white matter in paediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) following intrathecal and intravenous chemotherapy.
Materials and methods
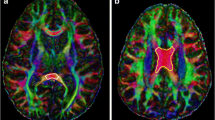
Eleven children diagnosed with de novo ALL underwent MRI scans of the brain with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) prior to commencement of chemotherapy and at 12 months after diagnosis, using a 3-tesla (T) MRI scanner. We investigated the changes in DTI parameters in white matter tracts before and after chemotherapy using tract-based spatial statistics overlaid on the International Consortium of Brain Mapping DTI-81 atlas. All of the children underwent formal neurodevelopmental assessment at the two study time points.
Results
Whole-brain DTI analysis showed significant changes between the two time points, affecting several white matter tracts. The tracts demonstrated longitudinal changes of decreasing mean and radial diffusivity. The neurodevelopment of the children was near compatible for age at the end of ALL treatment.
Conclusion
The quantification of white matter tracts changes in children undergoing chemotherapy showed improving longitudinal values in DTI metrics (stable fractional anisotropy, decreasing mean and radial diffusivity), which are incompatible with deterioration of microstructural integrity in these children.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pui C-H, Robison LL, Look AT (2008) Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 371:1030–1043
Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR et al (2009) Long-term survivors of childhood cancers in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 18:1033–1040
Hunger SP, Lu X, Devidas M et al (2012) Improved survival for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia between 1990 and 2005: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 30:1663–1669
Pui C-H, Campana D, Pei D et al (2009) Treating childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia without cranial irradiation. N Engl J Med 360:2730–2741
Hudson MM, Ness KK, Gurney JG et al (2013) Clinical ascertainment of health outcomes among adults treated for childhood cancer. JAMA 309:2371–2381
Yeoh AEJ, Tan D, Li C-K et al (2013) Management of adult and paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in Asia: resource-stratified guidelines from the Asian oncology summit 2013. Lancet Oncol 14:e508–e523
Krull KR, Brinkman TM, Li C et al (2013) Neurocognitive outcomes decades after treatment for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort Study. J Clin Oncol 31:4407–4415
Buizer AI, de Sonneville LMJ, Veerman AJP (2009) Effects of chemotherapy on neurocognitive function in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a critical review of the literature. Pediatr Blood Cancer 52:447–454
Cheung YT, Krull KR (2015) Neurocognitive outcomes in long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated on contemporary treatment protocols: a systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 53:108–120
Yeoh AEJ, Ariffin H, Chai ELL et al (2012) Minimal residual disease-guided treatment deintensification for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results from the Malaysia-Singapore acute lymphoblastic leukemia 2003 study. J Clin Oncol 30:2384–2392
Hermoye L, Saint-Martin C, Cosnard G et al (2006) Pediatric diffusion tensor imaging: normal database and observation of the white matter maturation in early childhood. Neuroimage 29:493–504
Loh KB, Ramli N, Tan LK et al (2012) Quantification of diffusion tensor imaging in normal white matter maturation of early childhood using an automated processing pipeline. Eur Radiol 22:1413–1426
Jenkinson M (2013) TBSS userguide. FMRIB (functional magnetic resonance imaging of the brain) analysis group. http://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/fslwiki/TBSS/UserGuide. Accessed 19 May 2020
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H et al (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31:1487–1505
Wong YQ, Tan LK, Seow P et al (2017) Microstructural integrity of white matter tracts amongst older fallers: a DTI study. PLoS One 12:e0179895
Veeramuthu V, Narayanan V, Kuo TL et al (2015) Diffusion tensor imaging parameters in mild traumatic brain injury and its correlation with early neuropsychological impairment: a longitudinal study. J Neurotrauma 32:1497–1509
Korkman M, Kirk U, Kemp S (2007) Test review of NEPSY-II — second edition. Buros Center for Testing, Lincoln
Yeoh AEJ, Lu Y, Chin WHN et al (2018) Intensifying treatment of childhood B-lymphoblastic leukemia with IKZF1 deletion reduces relapse and improves overall survival: results of Malaysia-Singapore ALL 2010 study. J Clin Oncol 36:2726–2735
Inglese M, Bester M (2010) Diffusion imaging in multiple sclerosis: research and clinical implications. NMR Biomed 23:865–872
Westlye LT, Walhovd KB, Dale AM et al (2010) Life-span changes of the human brain white matter: diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and volumetry. Cereb Cortex 20:2055–2068
Dellani PR, Eder S, Gawehn J et al (2008) Late structural alterations of cerebral white matter in long-term survivors of childhood leukemia. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:1250–1255
Schuitema I, Deprez S, Hecke WV et al (2013) Accelerated aging, decreased white matter integrity, and associated neuropsychological dysfunction 25 years after pediatric lymphoid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 31:3378–3388
Harila MJ, Winqvist S, Lanning M et al (2009) Progressive neurocognitive impairment in young adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 53:156–161
Morioka S, Morimoto M, Yamada K (2013) Effect of chemotherapy on the brain in childhood: diffusion tensor imaging of subtle white matter damage. Neuroradiology 55:1251–1257
Sabin ND, Cheung YT, Reddick WE et al (2018) The impact of persistent leukoencephalopathy on brain white matter microstructure in long-term survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with chemotherapy only. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 39:1919–1925
Cancelliere A, Mangano FT, Air EL et al (2013) DTI values in key white matter tracts from infancy through adolescence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:1443–1449
Krogsrud SK, Fjell AM, Tamnes CK et al (2016) Changes in white matter microstructure in the developing brain — a longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging study of children from 4 to 11 years of age. Neuroimage 124:473–486
Schneider J, Il’yasov K, Hennig J, Martin E (2004) Fast quantitative diffusion-tensor imaging of cerebral white matter from the neonatal period to adolescence. Neuroradiology 46:258–266
Duffner P (2004) Long-term effects of radiation therapy on cognitive and endocrine function in children with leukemia and brain tumors. Neurologist 10:293–310
Acknowledgements
This work was partially funded by University of Malaya (Grant no. P003A-13HTM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramli, N., Lim, C.H., Rajagopal, R. et al. Assessing changes in microstructural integrity of white matter tracts in children with leukaemia following exposure to chemotherapy. Pediatr Radiol 50, 1277–1283 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-020-04717-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-020-04717-x