Abstract
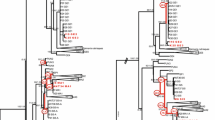
Mud crabs of the family Panopeidae are common organisms in coastal soft-bottom, vegetated, rubble, and oyster-bed communities along the temperate and tropical coastlines of the American continent. Similar morphology among many species renders their distinction and classification difficult. Here, we present phylogenies of western Atlantic Panopeidae based on DNA sequences of the mitochondrial large subunit rRNA (16S; 529 basepairs) and cytochrome oxidase I (COI; 640 basepairs) genes. Results suggest that the speciose genera Panopeus and Eurypanopeus are not monophyletic and that their taxonomy does not accurately reflect evolutionary partitions. In two cases (P. herbstii complex and E. depressus and allies), the molecular findings strongly support sister-species relationships that differ from previous morphology-based assumptions. We suggest that convergence or morphological stasis are responsible for the phenotypic similarities between divergent evolutionary lineages.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 July 1999 / Accepted: 5 April 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schubart, C., Neigel, J. & Felder, D. Molecular phylogeny of mud crabs (Brachyura: Panopeidae) from the northwestern Atlantic and the role of morphological stasis and convergence. Marine Biology 137, 11–18 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270000325
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270000325