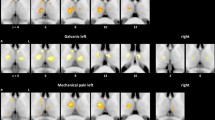
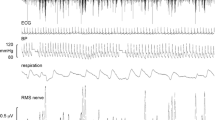
Abstract
Vestibular stimulation has been reported to alleviate central pain. Clinical and physiological studies confirm pervasive interactions between vestibular signals and somatosensory circuits, including nociception. However, the neural mechanisms underlying vestibular-induced analgesia remain unclear, and previous clinical studies cannot rule out explanations based on alternative, non-specific effects such as distraction or placebo. To investigate how vestibular inputs influence nociception, we combined caloric vestibular stimulation (CVS) with psychophysical and electrocortical responses elicited by nociceptive-specific laser stimulation in humans (laser-evoked potentials, LEPs). Cold water CVS applied to the left ear resulted in significantly lower subjective pain intensity for experimental laser pain to the left hand immediately after CVS, relative both to before CVS and to 1 h after CVS. This transient reduction in pain perception was associated with reduced amplitude of all LEP components, including the early N1 wave reflecting the first arrival of nociceptive input to primary somatosensory cortex. We conclude that cold left ear CVS elicits a modulation of both nociceptive processing and pain perception. The analgesic effect induced by CVS could be mediated either by subcortical gating of the ascending nociceptive input, or by direct modulation of the primary somatosensory cortex.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CVS:
-
Caloric vestibular stimulation
- LEPs:
-
Laser-evoked potentials
- PIVC:
-
Parietoinsular vestibular cortex
- SEPs:
-
Somatosensory-evoked potentials
- ERPs:
-
Event-related potentials
References
Alvord LS, Farmer BL (1997) Anatomy and orientation of the human external ear. J Am Acad Audiol 8:383–390
Baumgärtner U, Cruccu G, Iannetti GD, Treede RD (2005) Laser guns and hot plates. Pain 116:1–3
Bense S, Stephan T, Yousry TA, Brandt T, Dieterich M (2001) Multisensory cortical signal increases and decreases during vestibular galvanic stimulation (fMRI). J Neurophysiol 85(2):886–899
Berthoz A (1996) How does the cerebral cortex process and utilize vestibular signals? In: Baloh RW, Halmagyi GM (eds) Disorders of the vestibular system. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 113–125
Berthoz A, Israel I, Georges-Francois P, Grasso R, Tsuzuku T (1995) Spatial memory of body linear displacement: What is being stored? Science 269:95–98
Bisiach E, Rusconi ML, Vallar G (1991) Remission of somatoparaphrenic delusion through vestibular stimulation. Neuropsychologia 29(10):1029–1031
Blanke O, Ortigue S, Landis T, Seeck M (2002) Stimulating illusory own-body perceptions. Nature 419:269–270
Bottini G, Sterzi R, Paulesu E, Vallar G, Cappa SF, Erminio F et al (1994) Identification of the central vestibular projections in man: a positron emission tomography activation study. Exp Brain Res 99(1):164–169
Bottini G, Paulesu E, Sterzi R, Warburton E, Wise RJ, Vallar G, Frackowiak RS, Frith CD (1995) Modulation of conscious experience by peripheral sensory stimuli. Nature 376(6543):778–781
Bottini G, Paulesu E, Gandola M, Loffredo S, Scarpa P, Sterzi R et al (2005) Left caloric vestibular stimulation ameliorates right hemianesthesia. Neurology 65(8):1278–1283
Bromm B, Treede RD (1984) Nerve fibre discharges, cerebral potentials and sensations induced by CO2 laser stimulation. Hum Neurobiol 3(1):33–40
Coats AC, Smith SY (1967) Body position and the intensity of caloric nystagmus. Acta Otolaryngol 63:515–532
Dieterich M, Bense S, Lutz S, Drzezga A, Stephan T, Bartenstein P, Brandt T (2003) Dominance for vestibular cortical function in the non-dominant hemisphere. Cereb Cortex 13(9):994–1007
Drake RL, Drake RL, Gray H (2008) Gray’s atlas of anatomy. Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, Philadelphia
Eickhoff SB, Jbabdi S, Caspers S, Laird AR, Fox PT, Zilles K, Behrens TE (2010) Anatomical and functional connectivity of cytoarchitectonic areas within the human parietal operculum. J Neurosci 30(18):6409–6421
Fasold O, von Brevern M, Kuhberg M, Ploner CJ, Villringer A, Lempert T, Wenzel R (2002) Human vestibular cortex as identified with caloric stimulation in functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 17(3):1384–1393
Ferrè ER, Bottini G, Haggard P (2011) Vestibular modulation of somatosensory perception. Eur J Neurosci 34(8):1337–1344
Ferrè ER, Bottini G, Haggard P (2012) Vestibular inputs modulate somatosensory cortical processing. Brain Struct Funct 217(4):859–864
Ferrè ER, Bottini G, Iannetti GD, Haggard P (2013) The balance of feelings: vestibular modulation of bodily sensations. Cortex 49(3):748–758
Guldin WO, Grüsser OJ (1998) Is there a vestibular cortex? Trends Neurosci 21:256–259
Hu L, Liang M, Mouraux A, Wise RG, Hu Y, Iannetti GD (2011) Taking into account latency, amplitude, and morphology: improved estimation of single-trial ERPs by wavelet filtering and multiple linear regression. J Neurophysiol 106(6):3216–3229
Iannetti GD, Hughes NP, Lee MC, Mouraux A (2008) Determinants of laser-evoked EEG responses: Pain perception or stimulus saliency? J Neurophysiol 100(2):815–828
Janzen J, Schlindwein P, Bense S, Bauermann T, Vucurevic G, Stoeter P, Dieterich M (2008) Neural correlates of hemispheric dominance and ipsilaterality within the vestibular system. Neuroimage 42(4):1508–1518
Jauregui-Renaud K, Yarrow K, Oliver R, Gresty MA, Bronstein AM (2000) Effects of caloric stimulation on respiratory frequency and heart rate and blood pressure variability. Brain Res Bull 53(1):17–23
Jung TP, Makeig S, Westerfield M, Townsend J, Courchesne E, Sejnowski TJ (2000) Removal of eye activity artifacts from visual event-related potentials in normal and clinical subjects. Clin Neurophysiol 111:1745–1758
Jung P, Baumgärtner U, Stoeter P, Treede RD (2009) Structural and functional asymmetry in the human parietal opercular cortex. J Neurophysiol 101(6):3246–3257
Legrain V, Guérit JM, Bruyer R, Plaghki L (2002) Attentional modulation of the nociceptive processing into the human brain: selective spatial attention, probability of stimulus occurrence, and target detection effects on laser evoked potentials. Pain 99:21–39
Lenggenhager B, Hilti L, Palla A, Macauda G, Brugger P (2014) Vestibular stimulation does not diminish the desire for amputation. Cortex 54:210–212
Liu CC, Veldhuijzen DS, Ohara S, Winberry J, Greenspan JD, Lenz FA (2011) Spatial attention to thermal pain stimuli in subjects with visual spatial hemi-neglect: extinction, mislocalization and misidentification of stimulus modality. Pain 152(3):498–506
Lopez C, Blanke O, Mast FW (2012a) The human vestibular cortex revealed by coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Neuroscience 212:159–179
Lopez C, Schreyer HM, Preuss N, Mast FW (2012b) Vestibular stimulation modifies the body schema. Neuropsychologia 50(8):1830–1837
McGeoch PD, Ramachandran VS (2008) Vestibular stimulation can relieve central pain of spinal origin. Spinal Cord 46(11):756–757
McGeoch PD, Williiams LE, Lee RR, Ramachandran VS (2008) Behavioural evidence for vestibular stimulation as a treatment for central post-stroke pain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(11):1298–1301
Miller SM, Liu GB, Ngo TT, Hooper G, Riek S, Carson RG, Pettigrew JD (2000) Interhemispheric switching mediates perceptual rivalry. Curr Biol 10:383–392
Mouraux A, Iannetti GD (2008) Across-trial averaging of event-related EEG responses and beyond. Magn Reson Imaging 26:1041–1054
Mouraux A, Iannetti GD (2009) Nociceptive laser-evoked brain potentials do not reflect nociceptive-specific neural activity. J Neurophysiol 101:3258–3269
Ngo TT, Liu GB, Tilley AJ, Pettigrew JD, Miller SM (2007) Caloric vestibular stimulation reveals discrete neural mechanisms for coherence rivalry and eye rivalry: a meta-rivalry model. Vision Res 47(21):2685–2699
Ngo TT, Liu GB, Tilley AJ, Pettigrew JD, Miller SM (2008) The changing face of perceptual rivalry. Brain Res Bull 75(5):610–618
Ramachandran VS, McGeoch PD, Williams L, Arcilla G (2007) Rapid relief of thalamic pain syndrome induced by vestibular caloric stimulation. Neurocase 13(3):185–188
Ronga I, Valentini E, Mouraux A, Iannetti GD (2013) Novelty is not enough: laser-evoked potentials are determined by stimulus saliency, not absolute novelty. J Neurophysiol 109(3):692–701
Ryan MN, Gibson PG, Birring SS (2014) Arnold’s nerve cough reflex: evidence for chronic cough as a sensory vagal neuropathy. J Thorac Dis 6:S748–S752
Saunders RL, Weider D (1985) Tympanic membrane sensation. Brain 108:387–404
Scharein E, Bromm B (1998) The intracutaneous pain model in the assessment of analgesic efficacy. Pain Rev 5(4):216–246
Schlereth T, Baumgärtner U, Magerl W, Stoeter P, Treede RD (2003) Left-hemisphere dominance in early nociceptive processing in the human parasylvian cortex. Neuroimage 20(1):441–454
Suzuki M, Kitano H, Ito R, Kitanishi T, Yazawa Y, Ogawa T, Shiino A, Kitajima K (2001) Cortical and subcortical vestibular response to caloric stimulation detected by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Cogn Brain Res 12:441–449
Tarkka IM, Treede RD (1993) Equivalent electrical source analysis of pain-related somatosensory evoked potentials elicited by a CO2 laser. J Clin Neurophysiol 10:513–519
Treede RD, Meyer RA, Raja SN, Campbell JN (1995) Evidence for two different heat transduction mechanisms in nociceptive primary afferents innervating monkey skin. J Physiol 483(3):747–758
Truex RC, Carpenter MB, Strong OS (1969) Human neuroanatomy. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Uddman R, Grunditz T, Larsson A, Sundler F (1988) Sensory innervation of the ear drum and middle-ear mucosa: retrograde tracing and immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res 252:141–146
Valentini E, Hu L, Chakrabarti B, Hu Y, Aglioti SM, Iannetti GD (2012) The primary somatosensory cortex largely contributes to the early part of the cortical response elicited by nociceptive stimuli. Neuroimage 59(2):1571–1581
Valeriani M, De Tommaso M, Restuccia D, Le Pera D, Guido M, Iannetti GD et al (2003) Reduced habituation to experimental pain in migraine patients: a CO(2) laser evoked potential study. Pain 105(1):57–64
Vallar G, Sterzi R, Bottini G, Cappa S, Rusconi ML (1990) Temporary remission of left hemianesthesia after vestibular stimulation. A sensory neglect phenomenon. Cortex 26:123–131
Vallar G, Bottini G, Rusconi ML, Sterzi R (1993) Exploring somatosensory hemineglect by vestibular stimulation. Brain 116(1):71–86
Wilkinson D, Morris R, Milberg W, Sakel M (2013) Caloric vestibular stimulation in aphasic syndrome. Front Integr Neurosci 7:99
Zu Eulenburg P, Caspers S, Roski C, Eickhoff SB (2012) Meta-analytical definition and functional connectivity of the human vestibular cortex. Neuroimage 60(1):162–169
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Wellcome Trust Project Grant 094863/Z/10/Z to GDI and PH. EF was supported by a BIAL Foundation bursary. PH was additionally supported by a Major Research Fellowship from Leverhulme Trust, by EU project VERE (WP1), by ERC Advanced Grant HUMVOL, and by an ESRC Professorial Research Fellowship. GDI is University Research Fellow of The Royal Society and acknowledges the support of The Wellcome Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrè, E.R., Haggard, P., Bottini, G. et al. Caloric vestibular stimulation modulates nociceptive evoked potentials. Exp Brain Res 233, 3393–3401 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4412-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4412-8