Abstract
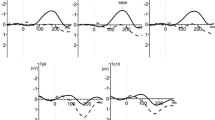
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) can systematically modify behavior by inducing changes in the underlying brain function. Objective electrophysiological evidence for tDCS-induced excitability changes has been demonstrated for the visual and somatosensory cortex, while evidence for excitability changes in the auditory cortex is lacking. In the present study, we applied tDCS over the left temporal as well as the left temporo-parietal cortex and investigated tDCS-induced effects on auditory evoked potentials after anodal, cathodal, and sham stimulation. Results show that anodal and cathodal tDCS can modify auditory cortex reactivity. Moreover, auditory evoked potentials were differentially modulated as a function of site of stimulation. While anodal tDCS over the temporal cortex increased auditory P50 amplitudes, cathodal tDCS over the temporo-parietal cortex induced larger N1 amplitudes. The results directly demonstrate excitability changes in the auditory cortex induced by active tDCS over the temporal and temporo-parietal cortex and might contribute to the understanding of mechanisms involved in the successful treatment of auditory disorders like tinnitus via tDCS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accornero N, Li Voti P, La Riccia M, Gregori B (2007) Visual evoked potentials modulation during direct current cortical polarization. Exp Brain Res 178:261–266
Ambrus GG, Zimmer M, Kincses ZT, Harza I, Kovács G, Paulus W, Antal A (2011) The enhancement of cortical excitability over the DLPFC before and during training impairs categorization in the prototype distortion task. Neuropsychologia 49:1974–1980
Annett M (1970) A classification of hand preference by association analysis. Br J Psychol 61:303–321
Antal A, Kincses TZ, Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2003) Manipulation of phosphene thresholds by transcranial direct current stimulation in man. Exp Brain Res 150:375–378
Antal A, Kincses TZ, Nitsche MA, Bartfai O, Paulus W (2004) Excitability changes induced in the human primary visual cortex by transcranial direct current stimulation: direct electrophysiological evidence. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:702–707
Antal A, Brepohl N, Poreisz C, Boros K, Csifcsak G, Paulus W (2008) Transcranial direct current stimulation over somatosensory cortex decreases experimentally induced acute pain perception. Clin J Pain 24:56–63
Been G, Ngo TT, Miller SM, Fitzgerald PB (2007) The use of tDCS and CVS as methods of non-invasive brain stimulation. Brain Res Rev 56:346–361
Bindman LJ, Lippold OC, Redfearn JW (1962) Long-lasting changes in the level of the electrical activity of the cerebral cortex produced bypolarizing currents. Nature 196:584–585
Bullard LM, Browning ES, Clark VP, Coffman BA, Garcia CM, Jung RE, van der Merwe AJ, Paulson KM, Vakhtin AA, Wootton CL, Weisend MP (2011) Transcranial direct current stimulation’s effect on novice versus experienced learning. Exp Brain Res 213:9–14
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134:9–21
Delorme A, Sejnowski T, Makeig S (2007) Enhanced detection of artifacts in EEG data using higher-order statistics and independent component analysis. Neuroimage 34:1443–1449
Dieckhofer A, Waberski TD, Nitsche M, Paulus W, Buchner H, Gobbele R (2006) Transcranial direct current stimulation applied over the somatosensory cortex—differential effect on low and high frequency SEPs. Clin Neurophysiol 117:2221–2227
Fox D (2011) Neuroscience: brain buzz. Nature 472:156–158
Fregni F, Marcondes R, Boggio PS, Marcolin MA, Rigonatti SP, Sanchez TG, Nitsche MA, Pascual-Leone A (2006) Transient tinnitus suppression induced by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation. Eur J Neurol 13:996–1001
Furubayashi T, Terao Y, Arai N, Okabe S, Mochizuki H, Hanajima R, Hamada M, Yugeta A, Inomata-Terada S, Ugawa Y (2008) Short and long duration transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) over the human hand motor area. Exp Brain Res 185:279–286
Gandiga PC, Hummel FC, Cohen LG (2006) Transcranial DC stimulation (tDCS): a tool for double-blind sham-controlled clinical studies in brain stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol 117:845–850
Garin P, Gilain C, Van Damme JP, de Fays K, Jamart J, Ossemann M, Vandermeeren Y (2011) Short- and long-lasting tinnitus relief induced by transcranial direct current stimulation. J Neurol [Epub ahead of print]
Gartside IB (1968) Mechanisms of sustained increases of firing rate of neurons in the rat cerebral cortex after polarization: reverberating circuits or modification of synaptic conductance? Nature 220:382–383
Hattori Y, Moriwaki A, Hori Y (1990) Biphasic effects of polarizing current on adenosine-sensitive generation of cyclic AMP in rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 116:320–324
Jasper HH (1958) The ten-twenty electrode system of the international federation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 10:371–375
Jeffery DT, Norton JA, Roy FD, Gorassini MA (2007) Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on the excitability of the leg motor cortex. Exp Brain Res 182:281–287
Jung TP, Makeig S, Humphries C, Lee TW, McKeown MJ, Iragui V, Sejnowski TJ (2000a) Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation. Psychophysiology 37:163–178
Jung TP, Makeig S, Westerfield M, Townsend J, Courchesne E, Sejnowski TJ (2000b) Removal of eye activity artifacts from visual event-related potentials in normal and clinical subjects. Clin Neurophysiol 111:1745–1758
Kincses TZ, Antal A, Nitsche MA, Bártfai O, Paulus W (2004) Facilitation of probabilistic classification learning by transcranial direct current stimulation of the prefrontal cortex in the human. Neuropsychologia 42:113–117
Kleinjung T, Langguth B (2009) Strategies for enhancement of transcranial magnetic stimulation effects in tinnitus patients. Int Tinnitus J 15:154–160
Kraft A, Roehmel J, Olma MC, Schmidt S, Irlbacher K, Brandt SA (2010) Transcranial direct current stimulation affects visual perception measured by threshold perimetry. Exp Brain Res 207:283–290
Liebetanz D, Nitsche MA, Tergau F, Paulus W (2002) Pharmacological approach to the mechanisms of transcranial DC-stimulation-induced after-effects of human motor cortex excitability. Brain 125:2238–2247
Loui P, Hohmann A, Schlaug G (2010) Inducing disorders in pitch perception and production: a reverse-engineering approach. Proc Meet Acoust 9:50002
Madhavan S, Weber KA 2nd, Stinear JW (2011) Non-invasive brain stimulation enhances fine motor control of the hemiparetic ankle: implications for rehabilitation. Exp Brain Res 209:9–17
Matsunaga K, Nitsche MA, Tsuji S, Rothwell JC (2004) Effect of transcranial DC sensorimotor cortex stimulation on somatosensory evoked potentials in humans. Clin Neurophysiol 115:456–460
Miranda PC, Lomarev M, Hallett M (2006) Modeling the current distribution during transcranial direct current stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol 117:1623–1629
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2000) Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J Physiol 527(3):633–639
Nitsche MA, Antal A, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Tergau F, Paulus W (2003) Modulation of cortical excitability by weak direct current stimulation: technical, safety and functional aspects. Clin Electrophysiol Suppl 56:255–276
Nitsche MA, Cohen LG, Wassermann EM, Priori A, Lang N, Antal A, Paulus W, Hummel F, Boggio PS, Fregni F, Pascual-Leone A (2008) Transcranial direct current stimulation: state of the art 2008. Brain Stimulation 1:206–223
Purpura DP, McMurtry JG (1965) Intracellular activities and evoked potential changes during polarization of motor cortex. J Neurophysiol 28:166–185
Quian Quiroga R, Garcia H (2003) Single-trial event-related potentials with wavelet denoising. Clin Neurophysiol 114:376–390
Radman T, Ramos RL, Brumberg JC, Bikson M (2009) Role of cortical cell type and morphology in subthreshold and suprathreshold uniform electric field stimulation in vitro. Brain Stimul. 2:215–228
Roth BJ (1994) Mechanisms for electrical stimulation of excitable tissue. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 22:253–305
Tanaka S, Hanakawa T, Honda M, Watanabe K (2009) Enhancement of pinch force in the lower leg by anodal transcranial direct current stimulation. Exp Brain Res 196:459–465
Vines BW, Schnider NM, Schlaug G (2006) Testing for causality with transcranial direct current stimulation: pitch memory and the left supramarginal gyrus. Neuroreport 17:1047–1050
Zaehle T, Sandmann P, Thorne JD, Jäncke L, Herrmann CS (2011) Transcranial direct current stimulation of the prefrontal cortex modulates working memory performance: combined behavioural and electrophysiological evidence. BMC Neurosci 12:2
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB/TR31-TPA9) (TZ, CSH) and the Swiss National Foundation (PBZHP3-128462) (PS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaehle, T., Beretta, M., Jäncke, L. et al. Excitability changes induced in the human auditory cortex by transcranial direct current stimulation: direct electrophysiological evidence. Exp Brain Res 215, 135–140 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2879-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2879-5