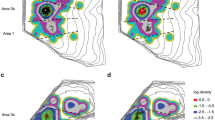
Abstract
Topographic maps and columnar structures are fundamental to cortical sensory information processing. Most of the knowledge about detailed topographic maps and columnar structure comes mainly from experiments conducted on anesthetized animals. Towards the goal of evaluating whether topographic maps change with respect to behavioral demands, we used intrinsic signal optical imaging in alert monkeys to examine the spatial specificity of cortical topographic representation. Specifically, the somatotopies of neighboring distal finger pad representation in areas 3b and 1 were examined in the same awake and anesthetized squirrel monkey. In comparison to the anesthetized animal, we found larger cortical activation sizes in the alert animal in area 3b, where activation widths were found to overlap with even non-adjacent digits. This may suggest that in the alert animal, there is less inhibition across the somatotopic map within area 3b.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahissar E, Vaadia E, Ahissar M, Bergman H, Arieli A, Abeles M (1992) Dependence of cortical plasticity on correlated activity of single neurons and on behavioral context. Science 257:1412–1415
Alloway KD, Rosenthal P, Burton H (1989) Quantitative measurements of receptive field changes during antagonism of GABAergic transmission in primary somatosensory cortex of cats. Exp Brain Res 78:514–532
Bullier J, Hupe JM, James AC, Girard P (2001) The role of feedback connections in shaping the responses of visual cortical neurons. Prog Brain Res 134:193–204
Burton H, Sinclair RJ (2000) Tactile-spatial and cross-modal attention effects in the primary somatosensory cortical areas 3b and 1–2 of rhesus monkeys. Somatosens Mot Res 17:213–228
Burton H, MacLeod AM, Videen TO, Raichle ME (1997) Multiple foci in parietal and frontal cortex activated by rubbing embossed grating patterns across fingerpads: a positron emission tomography study in humans. Cereb Cortex 7:3–17
Chapin JK, Lin CS (1984) Mapping the body representation in the SI cortex of anesthetized and awake rats. J Comp Neurol 229:199–213
Chapin JK, Woodward DJ (1981) Modulation of sensory responsiveness of single somatosensory cortical cells during movement and arousal behaviors. Exp Neurol 72:164–178
Chapman CE, Ageranioti-Belanger SA (1991) Discharge properties of neurones in the hand area of primary somatosensory cortex in monkeys in relation to the performance of an active tactile discrimination task. I. Areas 3b and 1. Exp Brain Res 87:319–339
Chen LM, Friedman RM, Ramsden BM, LaMotte RH, Roe AW (2001) Fine-scale organization of SI (area 3b) in the squirrel monkey revealed with intrinsic optical imaging. J Neurophysiol 86:3011–3029
Chen LM, Friedman RM, Roe AW (2002) Optical imaging reveals area-specific interactions between nociceptive and tactile responses in SI of squirrel monkey. In: Society for Neuroscience Annual Meeting, Orlando, pp 841–842
Chen LM, Friedman RM, Roe AW (2003) Optical imaging of a tactile illusion in area 3b of the primary somatosensory cortex. Science 302:881–885
Chen LM, Friedman RM, Roe AW (2005) Optical imaging of SI topography in anesthetized and awake squirrel monkeys. J Neurosci 25:7648–7659
Cheung SW, Nagarajan SS, Bedenbaugh PH, Schreiner CE, Wang X, Wong A (2001) Auditory cortical neuron response differences under isoflurane versus pentobarbital anesthesia. Hear Res 156:115–127
Das A, Gilbert CD (1995) Long-range horizontal connections and their role in cortical reorganization revealed by optical recording of cat primary visual cortex. Nature 375:780–784
Detsch O, Vahle-Hinz C, Kochs E, Siemers M, Bromm B (1999) Isoflurane induces dose-dependent changes of thalamic somatosensory information transfer. Brain Res 829:77–89
DiCarlo JJ, Johnson KO (2000) Spatial and temporal structure of receptive fields in primate somatosensory area 3b: effects of stimulus scanning direction and orientation. J Neurosci 20:495–510
Friedberg MH, Lee SM, Ebner FF (1999) Modulation of receptive field properties of thalamic somatosensory neurons by the depth of anesthesia. J Neurophysiol 81:2243–2252
Friedman RM, Chen LM, Roe AW (2004) Modality maps within primate somatosensory cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12724–12729
Friedman RM, Chen LM, Roe AW (2008) Responses of area 1 in anesthesized squirrel monkeys to single and dual site stimulation of the digits. J Neurophysiol 100:3185–3196
Godde B, Hilger T, von Seelen W, Berkefeld T, Dinse HR (1995) Optical imaging of rat somatosensory cortex reveals representational overlap as topographic principle. Neuroreport 7:24–28
Heider B, Roe AW (2002) Time course analyses of intrinsic optical signals in anesthetized and awake macaque monkey visual cortex. Soc Neurosci Abstr 28:658
Heider B, Jando G, Siegel RM (2005) Functional architecture of retinotopy in visual association cortex of behaving monkey. Cereb Cortex 15:460–478
Hsiao SS, O’Shaughnessy DM, Johnson KO (1993) Effects of selective attention on spatial form processing in monkey primary and secondary somatosensory cortex. J Neurophysiol 70:444–447
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1977) Ferrier lecture. Functional architecture of macaque monkey visual cortex. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 198:1–59
Iwamura Y, Tanaka M, Sakamoto M, Hikosaka O (1983) Converging patterns of finger representation and complex response properties of neurons in Area 1 of the first somatosensory cortex of the conscious monkey. Exp Brain Res 51:327–337
Iwamura Y, Tanaka M, Sakamoto M, Hikosaka O (1993) Rostrocaudal gradients in the neuronal receptive field complexity in the finger region of the alert monkey’s postcentral gyrus. Exp Brain Res 92:360–368
Jenkins WM, Merzenich MM, Ochs MT, Allard T, Guic-Robles E (1990) Functional reorganization of primary somatosensory cortex in adult owl monkeys after behaviorally controlled tactile stimulation. J Neurophysiol 63:82–104
Jiang W, Lamarre Y, Chapman CE (1990) Modulation of cutaneous cortical evoked potentials during isometric and isotonic contractions in the monkey. Brain Res 536:69–78
Jiang W, Chapman CE, Lamarre Y (1991) Modulation of the cutaneous responsiveness of neurones in the primary somatosensory cortex during conditioned arm movements in the monkey. Exp Brain Res 84:342–354
Juliano SL, Hand PJ, Whitsel BL (1981) Patterns of increased metabolic activity in somatosensory cortex of monkeys Macaca fascicularis, subjected to controlled cutaneous stimulation: a 2-deoxyglucose study. J Neurophysiol 46:1260–1284
Lipton PA, White JA, Eichenbaum H (2007) Disambiguation of overlapping experiences by neurons in the medial entorhinal cortex. J Neurosci 27:5787–5795
Liu Y, Denton JM, Nelson RJ (2005) Neuronal activity in primary motor cortex differs when monkeys perform somatosensory and visually guided wrist movements. Exp Brain Res 167:571–586
Liu Y, Denton JM, Nelson RJ (2007) Neuronal activity in monkey primary somatosensory cortex is related to expectation of somatosensory and visual go-cues. Exp Brain Res 177:540–550 (Epub 2006)
Logothetis NK, Pauls J, Augath M, Trinath T, Oeltermann A (2001) Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the fMRI signal. Nature 412:150–157
McKenna TM, Whitsel BL, Dreyer DA (1982) Anterior parietal cortical topographic organization in macaque monkey: a reevaluation. J Neurophysiol 48:289–317
Meftah el M, Shenasa J, Chapman CE (2002) Effects of a cross-modal manipulation of attention on somatosensory cortical neuronal responses to tactile stimuli in the monkey. J Neurophysiol 88:3133–3149
Nelson RJ (1987) Activity of monkey primary somatosensory cortical neurons changes prior to active movement. Brain Res 406:402–407
Nelson RJ, Sur M, Felleman DJ, Kaas JH (1980) Representations of the body surface in postcentral parietal cortex of Macaca fascicularis. J Comp Neurol 192:611–643
Panetsos F, Nunez A, Avendano C (1995) Local anaesthesia induces immediate receptive field changes in nucleus gracilis and cortex. Neuroreport 7:150–152
Pons TP, Wall JT, Garraghty PE, Cusick CG, Kaas JH (1987) Consistent features of the representation of the hand in area 3b of macaque monkeys. Somatosens Res 4:309–331
Raffi M, Siegel RM (2005) Functional architecture of spatial attention in the parietal cortex of the behaving monkey. J Neurosci 25:5171–5186
Ramsden BM, Hung CP, Roe AW (2001) Real and illusory contour processing in area V1 of the primate: a cortical balancing act. Cereb Cortex 11:648–665
Reed JL, Pouget P, Qi HX, Zhou Z, Bernard MR, Burish MJ, Haitas J, Bonds AB, Kaas JH (2008) Widespread spatial integration in primary somatosensory cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10233–10237
Ries CR, Puil E (1999) Ionic mechanism of isoflurane’s actions on thalamocortical neurons. J Neurophysiol 81:1802–1809
Roe AW, Healy FL, Friedman RM, Heider B, Chen LM (2002) Differences in SI topography between anesthetized and awake squirrel monkey as revealed by optical imaging. Soc Neurosci Abstr 28:651–653
Rojas MJ, Navas JA, Rector DM (2006) Evoked response potential markers for anesthetic and behavioral states. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291:R189–R196
Rudolph U, Antkowiak B (2004) Molecular and neuronal substrates for general anaesthetics. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:709–720
Schummers J, Marino J, Sur M (2002) Synaptic integration by V1 neurons depends on location within the orientation map. Neuron 36:969–978
Shoham D, Grinvald A (2001) The cortical representation of the hand in macaque and human area S–I: high resolution optical imaging. J Neurosci 21:6820–6835
Slovin H, Arieli A, Hildesheim R, Grinvald A (2002) Long-term voltage-sensitive dye imaging reveals cortical dynamics in behaving monkeys. J Neurophysiol 88:3421–3438
spiYamamori Y, Kishikawa K, Collins JG (1995) Halothane effects on low-threshold receptive field size of rat spinal dorsal horn neurons appear to be independent of supraspinal modulatory systems. Brain Res 702:162–168
Steinmetz PN, Roy A, Fitzgerald PJ, Hsiao SS, Johnson KO, Niebur E (2000) Attention modulates synchronized neuronal firing in primate somatosensory cortex. Nature 404:187–190
Stryker MP, Jenkins WM, Merzenich MM (1987) Anesthetic state does not affect the map of the hand representation within area 3b somatosensory cortex in owl monkey. J Comp Neurol 258:297–303
Sur M, Merzenich MM, Kaas JH (1980) Magnification, receptive-field area, and “hypercolumn” size in areas 3b and 1 of somatosensory cortex in owl monkeys. J Neurophysiol 44:295–311
Sur M, Nelson RJ, Kaas JH (1982) Representations of the body surface in cortical areas 3b and 1 of squirrel monkeys: comparisons with other primates. J Comp Neurol 211:177–192
Tommerdahl M, Whitsel B (1996) Optical imaging of intrinsic signals in somatosensory cortex. Birkhauser Verlag, Basel
Vnek N, Ramsden BM, Hung CP, Goldman-Rakic PS, Roe AW (1999) Optical imaging of functional domains in the cortex of the awake and behaving monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4057–4060
Yamakura T, Harris RA (2000) Effects of gaseous anesthetics nitrous oxide and xenon on ligand-gated ion channels. Comparison with isoflurane and ethanol. Anesthesiology 93:1095–1101
Acknowledgments
We thank Barbara Heider and Francine Healy for assistance on initial experiments. Supported by NIH NS044375 (AWR) and DE16606 (LMC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L.M., Friedman, R.M. & Roe, A.W. Optical imaging of digit topography in individual awake and anesthetized squirrel monkeys. Exp Brain Res 196, 393–401 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1861-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1861-y