Abstract
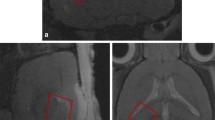
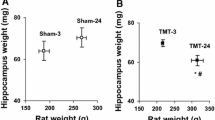
The solid-state high resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HRMAS NMR) technique was applied in this work to characterize and quantify the neurochemical changes in the rat hippocampus (CA1 or CA3) after local administration of kainic acid (KA). Intact tissue samples obtained from the KA treated and control brain samples were analyzed using HRMAS NMR. Metabolite profiles from NMR spectra of KA treated and control samples revealed the statistical significant decrease of N-acetylaspartate (NAA) and an increase of choline derivatives in the CA1 and CA3 directly receiving KA injection. Less extensive KA-induced metabolic changes were found in the hippocampi sample from the area contralateral to the site receiving KA administration. These results provided quantitative metabolic information on KA-induced neuronal loss and cell breakdown. In addition, the present study also revealed increased level of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate after KA treatment, suggesting that the cellular release of inhibitory and excitatory amino acids can be quantified using this method. KA induced microglia activation was evidenced by increased level of myo-insitol (myo-I). This study demonstrates that ex vivo HRMAS NMR is a useful tool for analyzing and quantifying changes of neurochemistry and cerebral metabolism in the intact brain.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- KA:
-
Kainic acid
- HRMAS:
-
High resolution magic angle spinning
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- MRS:
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- NAA:
-
N-acetyl-aspartate
- Cho:
-
Choline
- PC:
-
Phosphocholine
- GPC:
-
Glyocerphosphocholine
- Cre:
-
Creatine
- myo-I:
-
Myo-inositol
- Glu:
-
Glutamate
- Gln:
-
Glutamine
- GABA:
-
γ-aminobutyric acid
- DANTE:
-
Delays alternating with nutations for tailored excitation
References
Abraham H, Losonczy A, Czeh G, Lazar G (2001) Rapid activation of microglial cells by hypoxia, kainic acid, and potassium ions in slice preparations of the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 906:115–126
Ben-Ari Y, Riche D, Tremblay E, Charton G (1981) Alterations in local glucose consumption following systemic administration of kainic acid, bicuculline or metrazol. Eur Neurol 20:173–175
Ben-Ari Y, Repressa A, Tremblay E, Nitecka L (1986) Selective and non-selective seizure related brain damage produced by kainic acid. Adv Exp Med Biol 203:647–657
Bianchi L, Ballini C, Colivicchi MA, Della Corte L, Giovannini MG, Pepeu G (2003) Investigation on acetylcholine, aspartate, glutamate and GABA extracellular levels from ventral hippocampus during repeated exploratory activity in the rat. Neurochem Res 28:565–573
Bruhn T, Christensen T, Diemer NH (1997) Evidence for increased cellular uptake of glutamate and aspartate in the rat hippocampus during kainic acid seizures. A microdialysis study using the “indicator diffusion’ method. Epilepsy Res 26:363–371
Cheng LL, Ma MJ, Becerra L, Ptak T, Tracey I, Lackner A, Gonzalez RG (1997) Quantitative neuropathology by high resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6408–6413
Ding R, Asada H, Obata K (1998) Changes in extracellular glutamate and GABA levels in the hippocampal CA3 and CA1 areas and the induction of glutamic acid decarboxylase-67 in dentate granule cells of rats treated with kainic acid. Brain Res 800:105–113
Dudek FE, Hellier JL, Williams PA, Ferraro DJ, Staley KJ (2002) The course of cellular alterations associated with the development of spontaneous seizures after status epilepticus. Prog Brain Res 135:53–65
During MJ, Spencer DD (1993) Extracellular hippocampal glutamate and spontaneous seizure in the conscious human brain. Lancet 341:1607–1610
Ebisu T, Rooney WD, Graham SH, Weiner MW, Maudsley AA (1994) N-acetylaspartate as an in vivo marker of neuronal viability in kainate-induced status epilepticus: 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 14:373–382
Ermakova IV, Loseva EV, Hodges H, Sinden J (2005) Transplantation of cultured astrocytes attenuates degenerative changes in rats with kainic acid-induced brain damage. Bull Exp Biol Med 140:677–681
Griffin JL, Bollard M, Nicholson JK, Bhakoo K (2002) Spectral profiles of cultured neuronal and glial cells derived from HRMAS 1H NMR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 15:375–384
Jorgensen MB, Finsen BR, Jensen MB, CastellanoB, Diemer NH, Zimmer J (1993) Microglial and astroglial reactions to ischemic and kainic acid-induced lesions of the adult rat hippocampus. Exp Neurol 120:70–88
Liu Z, Stafstrom CE, Sarkisian MR, Yang Y, Hori A, Tandon P, Holmes GL (1997) Seizure-induced glutamate release in mature and immature animals: an in vivo microdialysis study. Neuroreport 8:2019–2023
Martinez-Bisbal MC, Marti-Bonmati L, Piquer J, Revert A, Ferrer P, Llacer JL, Piotto M, Assemat O, Celda B (2004) 1H and 13C HR-MAS spectroscopy of intact biopsy samples ex vivo and in vivo 1H MRS study of human high grade gliomas. NMR Biomed 17:191–205
Miller BL (1991) A review of chemical issues in 1H NMR spectroscopy: N-acetyl-L-aspartate, creatine and choline. NMR Biomed 4:47–52
Mitchell J, Sundstrom LE, Wheal HV (1993) Microglial and astrocytic cell responses in the rat hippocampus after an intracerebroventricular kainic acid injection. Exp Neurol 121:224–230
Morris GA, Freeman R (1978) Selective excitation in Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance. J Magn Reson 29: 433–462
Najm IM, Wang Y, Hong SC, Luders HO, Ng TC, Comair YG (1997) Temporal changes in proton MRS metabolites after kainic acid-induced seizures in rat brain. Epilepsia 38:87–94
Ross BD, Bluml S, Cowan R, Danielsen E, Farrow N, Gruetter R (1997) In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human brain: the biophysical basis of dementia. Biophys Chem 68:161–172
Ross BD, Bluml S, Cowan R (1998) In vivo MR spectroscopy of human dementia. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 8:809–822
Saransaari P, Oja SS (1998) Release of endogenous glutamate, aspartate, GABA, and taurine from hippocampal slices from adult and developing mice under cell-damaging conditions. Neurochem Res 23:563–570
Sokoloff L (1981) Localization of functional activity in the central nervous system by measurement of glucose utilization with radioactive deoxyglucose. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1:7–36
Sperk G (1994) Kainic acid seizures in the rat. Prog Neurobiol 42:1–32
Swanson MG, Vigneron DB, Tabatabai ZL, Males RG, Schmitt L, Carroll PR, James JK, Hurd RE, Kurhanewicz J (2003) Proton HR-MAS spectroscopy and quantitative pathologic analysis of MRI/3D-MRSI-targeted postsurgical prostate tissues. Magn Reson Med 50:944–954
Takeda A, Hirate M, Tamano H, Oku N (2003) Release of glutamate and GABA in the hippocampus under zinc deficiency. J Neurosci Res 72:537–542
Tanaka K, Simon RP (1994) The pattern of neuronal injury following seizures induced by intranigral kainic acid. Neurosci Lett 176:205–208
Taniwaki Y, Kato M, Araki T, Kobayashi T (1996) Microglial activation by epileptic activities through the propagation pathway of kainic acid-induced hippocampal seizures in the rat. Neurosci Lett 217:29–32
Tong Z, Yamaki T, Harada K, Houkin K (2004) In vivo quantification of the metabolites in normal brain and brain tumors by proton MR spectroscopy using water as an internal standard. Magn Reson Imaging 22:1017–1024
Tremblay E, Ottersen OP, Rovira C, Ben-Ari Y (1983) Intra-amygdaloid injections of kainic acid: regional metabolic changes and their relation to the pathological alterations. Neuroscience 8:299–315
Tsai G, Coyle JT (1995) N-acetylaspartate in neuropsychiatric disorders. Prog Neurobiol 46:531–540
Tsang TM, Griffin JL, Haselden J, Fish C, Holmes E (2005) Metabolic characterization of distinct neuroanatomical regions in rats by magic angle spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 53:1018–1024
Yager JY, Armstrong EA, Miyashita H, Wirrell EC (2002) Prolonged neonatal seizures exacerbate hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: correlation with cerebral energy metabolism and excitatory amino acid release. Dev Neurosci 24:367–381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, H., Toufexis, D., Wang, X. et al. Changes of metabolite profile in kainic acid induced hippocampal injury in rats measured by HRMAS NMR. Exp Brain Res 183, 477–485 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1061-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1061-6