Abstract
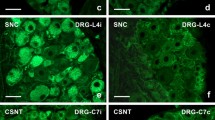
NF-κB is a ubiquitous nuclear transcription factor that regulates a number of physiological processes. NF-κB activity has been implicated in enhancing neuronal survival following CNS injury. The present study was conducted to test the hypothesis that NF-κB activity is up-regulated in neurons of the spinal cord in response to peripheral nerve transection. In this series of experiments, we used NF-κB reporter mice in which activation of NF-κB drives the expression of the lac-z gene. The response to injury of cells in the spinal cord was assessed by evaluating the number and distribution of β-galalactosidase (β-gal)-positive cells following sciatic nerve transection. The animals were randomly assigned to four groups, which were allowed to survive for one, three, five and ten days. Four mice that did not undergo sciatic nerve transection were assigned to each group to serve as controls. The total number of β-gal-positive cells in the right and left dorsal and ventral horns were compared. The numbers of β-gal-positive cells between the right and left sides were significantly different three and five days post axotomy (p<0.05). Double immunofluorescent labeling was utilized to characterize which cells showed NF-κB activity, and it revealed that all β-gal-positive cells were colocalized with MAP-2-positive neurons. The results of this study demonstrated that complete sciatic nerve transection leads to an up-regulation of NF-κB transactivation in spinal neurons ipsilateral to the side of transection. The increase in activity in the ipsilateral dorsal horn is consistent with this transcription factor acting as neuronal survival signal during this time frame in response to the peripheral nerve insult.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvidsson J, Ygge J, Grant G (1986) Cell loss in lumbar dorsal root ganglia and transganglionic degeneration after sciatic nerve resection in the rat. Brain Res 373:15–21
Baeuerle P, Henkel T (1994) Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 12:141–179
Beg A, Baltimore D (1996) An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF-α-induced cell death. Science 274:782–784
Beg A, Ruben M, Scheinman R, Haskill S, Rosen C, Baldwin A (1992) IκB interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-κB: a mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev 6:1899–1913
Bethea J, Castro M, Keane R, Lee T, Dietrich WD, Yezierski R (1998) Traumatic spinal cord injury induces nuclear factor-κB activation. J Neurosci 18:3251–3260
Bhakar A, Tannis L, Zeindler C, Russo M, Jobin C, Park D, Macpherson S, Barker P (2002) Constitutive nuclear factor-κB activity is required for central neuron survival. J Neurosci 22:8466–8475
Chiarugi A (2002) Characterization of the molecular events following impairment of NF-κB-driven transcription in neurons. Mol Brain Res 109:179–188
Choi J, Kim J, Kim D, Chun M, Gwag B, Yoon S, Joo C (2000) Failure to activate NF-κB promotes apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells following optic nerve transection. Brain Res 883:60–68
Camandola S, Mattson M (2000) Pro-apoptotic action of par-4 involves inhibition of NF-κB activity and suppression of Bcl-2 expression. J Neurosci Res 61:134–139
De Moissac D, Mustapha S, Greenberg A, Kirshenbaum L (1998) Bcl-2 activates the transcription factor NF-κB through degradation of the cytoplasmic inhibitor IκBα. J Biol Chem 273:23946–23951
Deveraux Q, Reed J (1999) IAP family proteins—suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:239–252
Doyle C, Hunt S (1997) Reduced nuclear factor κB (p65) expression in rat primary sensory neurons after peripheral nerve injury. Neuroreport 8:2937–2942
Fridmacher V, Kaltschmidt B, Goudeau B, Ndiaye D, Mattia Rossi F, Pfeiffer J, Kaltschmidt C, Israël, Mémet S (2003) Forebrain-specific neuronal inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activity leads to loss of neuroprotection. J Neurosci 23:9403–9408
Ganchi P, Sun S, Greene W, Ballard D (1992) IκB/MAD-3 masks the nuclear localization signal of NF-κB p65 and requires the transactivation domain to inhibit NF-κB p65 DNA binding. Mol Biol Cell 3:1339–1352
Gilmore S, Kane C (1998) Microglia, but not astrocytes, react to sciatic nerve injury in aging rats. Brain Res 806(1):113–116
He B, Tay S, Leong S (1997) Microglia responses in the CNS following sciatic nerve transection in C57BL/Wlds and BALB/c mice. Exp Neurol 146:587–595
Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C (2000) Constitutive NF-κB activity is modulated via neuron-astroglia interaction. Exp Brain Res 130:100–104
Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Lannes-Vieira J, Kreutzberg G, Wekerle H, Baeuerle P, Gehrmann J (1994) Transcription factor NF-κB is activated in microglia during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 55:99–106
Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Neumann H, Wekerle H, Baeuerle P (1994) Constitutive NF-κB activity in neurons. Mol Cell Biol 14:3981–3992
Kashihara Y, Kuno M, Miyata Y (1987) Cell death of axotomized motoneurons in neonatal rats, and its prevention by peripheral reinnervation. J Physiol 386:135–148
Kassed C, Butler T, Patton G, Demesquita D, Navidomskis M, Memet S, Israel A, Pennypacker K (2004) Injury-induced NF-kappaB activation in the hippocampus: implications for neuronal survival. FASEB J 18:723–724
Kassed C, Willing A, Garbouza-Davis S, Sanberg P, Pennypacker K (2002) Lack of NF-kappaB p50 exacerbates degeneration of hippocampal neurons after chemical exposure and impairs learning. Exp Neurol 176:277–288
Koulich E, Nguyen T, Johnson K, Giardina C, D’Mello S (2001) NF-κB is involved in the survival of cerebellar granule neurons: association of IκB phosphorylation with cell survival. J Neurochem 76:1188–1198
Kovács A, Chakraborty-Sett S, Ramirez S, Sniderhan L, Williamson A, Maggirwar S (2004) Mechanism of NF-κB inactivation induced by survival signal withdrawal in cerebellar granule neurons. Eur J Neurosci 20:345–352
Li L, Houenou LJ, Wu W, Lei M, Prevette D, Oppenheim R (1998) Characterization of spinal motoneuron degeneration following different types of peripheral nerve injury in neonatal and adult mice. J Comp Neurol 396:158–168
Li L, Oppenheim R, Lei M, Houenou LJ (1994) Neurotrophic agents prevent motoneuron death following sciatic nerve section in the neonatal mouse. J Neurobiol 25:759–766
Libermann T, Baltimore D (1990) Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-κB transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 10:2327–2334
Liu L, Persson J, Svensson M, Aldskogius H (1998) Glial cell responses, complement, and clusterin in the central nervous system following dorsal root transection. Glia 23:231–238
Liu L, Rudin M, Kozlova E (2000) Glial cell proliferation in the spinal cord after dorsal rhizotomy or sciatic nerve transection in the adult rat. Exp Brain Res 131:64–73
Ma W, Bisby M (1998) Increased activation of nuclear factor kappa B in rat lumbar dorsal root ganglion neurons following partial sciatic nerve injuries. Brain Res 797:243–254
Makarov S (2000) NF-κB as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation: recent advances. Mol Med Today 6:441–448
Mattson M, Culmsee C, Yu Z, Camandola S (2000) Roles of nuclear factor κB in neuronal survival and plasticity. J Neurochem 74:443–456
Mattson M, Goodman Y, Luo H, Fu W, Furukawa K (1997) Activation of NF-κB protects hippocampal neurons against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: evidence for induction of manganese superoxide dismutase and suppression of peroxynitrite production and protein tyrosine nitration. J Neurosci Res 49:681–697
Noven SV, Wallace N, Muccio D, Turtz A, Pinter MJ (1993) Adult spinal motoneurons remain viable despite prolonged absence of functional synaptic contact with muscle. Exp Neurol 123:147–156
Oliveira A, Risling M, Deckner M, Lindholm T, Langone F, Cullheim S (1997) Neonatal sciatic nerve transaction induces TUNEL labeling of neurons in the rat spinal cord and DRG. Neuroreport 8:2837–40
O’Neill L, Kaltschmidt C (1997) NF-κB: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci 20:252–258
Pahl H (1999) Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 18:6853–6866
Pennypacker K, Kassed C, Eidizadeh S, Saporta S, Sanberg P, Willing A (2001) NF-κB p50 is increased in neurons surviving hippocampal injury. Exp Neurol 172:307–319
Pollin MM, McHanwell S, Slater CR (1991) The effect of age on motor neurone death following axotomy in the mouse. Development 112:83–89
Schmidt-Ullrich R, Mémet S, Lilienbaum A, Feuillard J, Raphael M, Israël A (1996) NF-kappa B activity in transgenic mice: developmental regulation and tissue specificity. Development 122:2117–2128
Sen R, Baltimore D (1986a) Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein NF-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell 47:921–928
Sen R, Baltimore D (1986b) Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell 46:705–716
Sugimoto T, Bennett G, Kajander K (1990) Transsynaptic degeneration in the superficial dorsal horn after sciatic nerve injury: effects of a chronic constriction injury, transection, and strychnine. Pain 42:205–213
Sun S, Ganchi P, Ballard D, Greene W (1993) NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science 259:1912–1915
Tamatani M, Mitsuda N, Matsuzaki H, Okado H, Miyake S, Vitek M, Yamaguchi A, Tohyama M (2000) A pathway of neuronal apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation: roles of nuclear factor-kappaB and Bcl-2. J Neurochem 75:683–693
Van Antwerp D, Martin S, Kafri T, Green D, Verma I (1996) Suppression of TNF-α-induced apoptosis by NF-κB. Science 274:787–789
Verma I, Stevenson J, Schwartz E, Van Antwerp D, Miyamoto S (1995) Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev 9:2723–2735
Wang C, Guttridge D, Mayo M, Baldwin A (1999) NF-κB induces expression of the Bcl-2 homologue A1/Bfl-1 to preferentially suppress chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 19:5923–5929
Wang C, Mayo M, Baldwin A (1996) TNF-and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-κB. Science 274:784–787
Wang C, Mayo M, Korneluk R, Goeddel D, Baldwin A (1998) NF-κB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 281:1680–1683
Whiteside GT, Munglani R (2001) Cell death in the superficial dorsal horn in a model of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci Res 64:168–173
Wu M, Lee H, Bellas R, Schauer S, Arsura M, Katz D, Fitzgerald M, Rothstein T, Sherr D, Sonenshein G (1996) Inhibition of NF-κB/Rel induces apoptosis of murine B cells. EMBO 15:4682–4690
Zabel U, Henkel T, Silva M, Baeuerle P (1993) Nuclear uptake control of NF-κB by MAD-3, an IκB protein present in the nucleus. EMBO J 12:201–211
Zhu Y, Dulmsee C, Klumpp S, Krieglstein J (2004) Neuroprotection by transforming growth factor-β1 involves activation of nuclear factor-κB through phosphotidylinositol-3-OH kinase/AKT and mitogen activated protein kinase-extracellular-signal regulated kinase1, 2 signaling pathways. Neuroscience 123:897–906
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Lucy Colina and Dr. Cheryl Kassed for help with immunohistochemistry. This work was supported by the American Heart Association grant 0355183B (SS) and National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke NS39141-01A2 (KRP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollock, G., Pennypacker, K., Mémet, S. et al. Activation of NF-κB in the mouse spinal cord following sciatic nerve transection. Exp Brain Res 165, 470–477 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-2318-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-2318-6