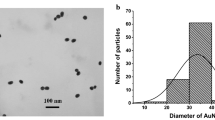
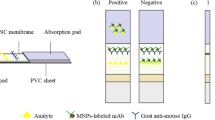
Abstract
A europium nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunoassay for highly sensitive detection of chloramphenicol residue was developed. The detection result could be either qualitatively resolved with naked eye or quantitatively analyzed with the assistance of a digital camera. In the qualitative mode, the limit of detection (LOD) was found to be 0.25 ng/mL. In the quantitative mode, the half-maximal inhibition concentration (IC50) was determined to be 0.45 ng/mL and the LOD can reach an ultralow level of 0.03 ng/mL, which is ~100 times lower than that of the conventional colloidal gold-based lateral flow immunoassay. Potential application of the established method was demonstrated by analyzing representative cow milk samples.

A europium nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunoassay for highly sensitive detection of chloramphenicol (CAP) residue was developed, of which limit of detections (LODs) can reach low levels of 0.25 and 0.03 ng/mL, respectively, in the qualitative and quantitative modes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shu XO, Gao YT, Brinton LA, Linet MS, Tu JT, Zheng W, Fraumeni JF (1988) A population-based case-control study of childhood leukemia in shanghai. Cancer 62:635–644
Jimenez JJ, Jimenez JG, Daghistani D, Yunis AA (1990) Interaction of chloramphenicol and metabolites with colony stimulating factors: possible role in chloramphenicol-induced bone marrow injury. Am J Med Sci 300:350–353
Shalit I, Marks MT (1984) Chloramphenicol in the 1980s. Drugs 28:281–291
Clark CM, Crosby NT (1986) Analysis of veterinary residues in foods. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 5:118–120
Ronning HT, Einarsen K, Asp TN (2006) Determination of chloramphenicol residues in meat, seafood, egg, honey, milk, plasma, and urine with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and the validation of the method based on 2002/657/EC. J Chromatogr A 1118:226–233
Fodey T, Murilla G, Cannavan A, Elliott C (2007) Characterization of antibodies to chloramphenicol, produced in different species by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and biosensor technologies. Anal Chim Acta 592:51–57
Posthuma-Trumpie GA, Korf J, van Amerongen A (2009) Lateral flow (immuno)assay: its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:569–582
Warsinke A (2009) Point-of-care testing of proteins. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:1393–1405
Scortichini G, Annunziata L, Haouet MN, Benedetti F, Krusteva I, Galarini R (2005) ELISA qualitative screening of chloramphenicol in muscle, eggs, honey and milk: method validation according to the Commission Decision 2002/657/EC. Anal Chim Acta 535:43–48
Xia X, Xu Y, Zhao X, Li Q (2009) Lateral flow immunoassay using europium chelate-loaded silica nanoparticles as labels. Clin Chem 55:179–182
Xu Y, Li Q (2007) Multiple fluorescent labeling of silica nanoparticles with lanthanide chelates for highly sensitive time-resolved immunofluorometric assays. Clin Chem 53:1503–1510
Shen J, Zhang Z, Yao Y, Shi W, Liu Y, Zhang S (2006) A monoclonal antibody-based time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for chloramphenicol in shrimp and chicken muscle. Anal Chim Acta 575:262–266
Armbruster DA, Tillman MD, Hubbs LM (1994) Limit of detection (LOD)/limit of quantitation (LOQ): comparison of the empirical and the statistical methods exemplified with GC-MS assays of abused drugs. Clin Chem 40:1233–1238
Li K, Liu L, Xu C, Chu X (2007) Rapid determination of chloramphenicol residues in aquaculture tissues by immunochromatographic assay. Anal Sci 23:1281–1284
Shakila RJ, Saravanakumar R, Vyla SAP, Jeyasekaran G (2007) An improved microbial assay for the detection of chloramphenicol residues in shrimp tissues. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 8:515–518
Berlina AR, Taranova NA, Zherdev AV, Vengerov YY, Dzantiev BB (2013) Quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for detection of chloramphenicol in milk. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:4997–5000
Wang L, Zhang Y, Gao X, Duan Z, Wang S (2010) Determination of chloramphenicol residues in milk by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: improvement by biotin-streptavidin-amplified system. J Agric Food Chem 58:3265–3270
Tao X, Jiang H, Zhu J, Niu L, Wu X, Shi W, Wang Z, Shen J (2012) Detection of ultratrace chloramphenicol residues in milk and chicken muscle samples using a chemiluminescent ELISA. Anal Lett 45:1254–1263
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support for this work by the Commonweal Scientific Foundation for Industry of Chinese Inspection and Quarantine (no. 201010022), the Xiamen Scientific Development Program (no. 3502Z20055008), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30500454), and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (no. 2007 J0112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiaohu Xia and Ye Xu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 9318 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, X., Xu, Y., Ke, R. et al. A highly sensitive europium nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunoassay for detection of chloramphenicol residue. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 7541–7544 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7210-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7210-9