Abstract
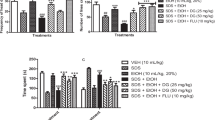
Early life stress influences adult psychopathology and is associated with an increase in the propensity for drug use/seeking throughout the lifespan. Animal models corroborate that stress exposure exacerbates maladaptive reactivity to stressful stimuli while also shifting the rewarding properties of many drugs of abuse, including nicotine (NIC), a stimulant commonly misused by adolescents. Interestingly, NIC treatment can also normalize some stress-induced behavioral deficits in adult rodents; however, little is known about NIC’s therapeutic efficacy following stress experienced during adolescence. The goal of the following experiments was to elucidate NIC’s ability to buffer the negative consequences of stress exposure, and to further assess behavioral responsivity while on the drug. Given that stress often occurs in both physical and non-physical forms, we employed the vicarious social defeat stress (VSDS) model which allows for investigation of both physical (PS) and emotional stress (ES) exposure. After 10 days, exposure to PS and ES decreased interaction with a social target in the social interaction test (SIT), confirming social avoidance. Groups were further divided and given NIC (0.0 or 160 mg/L) in their drinking water. After 1 month of NIC consumption, the mice were exposed to the SIT, elevated plus maze (EPM), and the forced swim test (FST), respectively. NIC-treated mice showed a reversal of stress-induced deficits in the EPM and FST. Surprisingly, the mice did not show improvement in the SIT regardless of treatment condition. Together, these data confirm NIC’s ability to normalize some stress-induced behavioral deficits; however, NIC’s effects on social behavior need further investigation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriani W, Laviola G (2004) Windows of vulnerability to psychopathology and therapeutic strategy in the adolescent rodent model. Behav Pharmacol 15:341–352
Alcantara LF, Warren BL, Parise EM, Iniguez SD, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2014) Effects of psychotropic drugs on second messenger signaling and preference for nicotine in juvenile male mice. Psychopharmacology 231:1479–1492
Andersen SL, Teicher MH (2008) Stress, sensitive periods and maturational events in adolescent depression. Trends Neurosci 31:183–191
Andreasen JT, Henningsen K, Bate S, Christiansen S, Wiborg O.J (2011) Nicotine reverses anhedonic-like response and cognitive impairment in the rat chronic mild stress model of depression: comparison with sertraline. J Psychopharmacology 25:1134–1141. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881110391831
Arakawa H (2018) Ethological approach to social isolation effects in behavioral studies of laboratory rodents. Behav Brain Res 341:98–108
Benowitz NL (2008) Clinical pharmacology of nicotine: implications for understanding, preventing, and treating tobacco addiction. Clin Pharmacol Ther 83:531–541
Berton O, McClung CA, Dileone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Graham D, Tsankova NM, Bolanos CA, Rios M, Monteggia LM, Self DW, Nestler EJ (2006) Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 311:864–868
Bolanos CA, Glatt SJ, Jackson D (1998) Subsensitivity to dopaminergic drugs in periadolescent rats: a behavioral and neurochemical analysis. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 111:25–33
Bolanos CA, Nestler EJ (2004) Neurotrophic mechanisms in drug addiction. NeuroMolecular Med 5:69–83
Brady KT, Sinha R (2005) Co-occurring mental and substance use disorders: the neurobiological effects of chronic stress. Am J Psychiatry 162:1483–1493
Brunzell DH, Russell DS, Picciotto MR (2003) In vivo nicotine treatment regulates mesocorticolimbic CREB and ERK signaling in C57Bl/6J mice. J Neurochem 84:1431–1441
Campos AC, Fogaça MV, Aguiar DC, Guimarães FS (2013) Animal models of anxiety disorders and stress. Braz J Psychiatry 35(Suppl 2):S101–S111
Carlezon WA Jr, Konradi C (2004) Understanding the neurobiological consequences of early exposure to psychotropic drugs: linking behavior with molecules. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):47–60
Croft AP, Brooks SP, Cole J, Little HJ (2005) Social defeat increases alcohol preference of C57BL/10 strain mice; effect prevented by a CCKB antagonist. Psychopharmacology 183:163–170
Dao JM, McQuown SC, Loughlin SE, Belluzzi JD, Leslie FM (2011) Nicotine alters limbic function in adolescent rat by a 5-HT1A receptor mechansm. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:1319–1331
Der-Avakian A, Mazei-Robison MS, Kesby JP, Nestler EJ, Markou A (2014) Enduring deficits in brain reward function after chronic social defeat in rats: susceptibility, resilience, and antidepressant response. Biol Psychiatry 76:542–549
Dube WV, Ahearn WH, Lionello-Denolf K, McIlvane WJ (2009) Behavioral momentum: translational research in intellectual and developmental disabilities. Behav Anal Today 10:238–253
Einat H, Yuan P, Gould TD, Li J, Du J, Zhang L, Manji HK, Chen G (2003) The role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in mood modulation. J Neurosci 23:7311–7316
File SE, Cheeta S, Kenny PJ (2000) Neurobiological mechanisms by which nicotine mediates different types of anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 393:231–236
File SE, Kenny PJ, Ouagazzal AM (1998) Bimodal modulation by nicotine of anxiety in the social interaction test: role of the dorsal hippocampus. Behav Neurosci 112:1423–1429
Finkelhor D, Turner HA, Shattuck A, Hamby SL (2015) Prevalence of childhood exposure to violence, crime, and abuse: results from the National Survey of Children’s Exposure to Violence. JAMA Pediatr 169:746–754
Flores RJ, Uribe KP, Swalve N, O’Dell LE (2019) Sex differences in nicotine intravenous self-administration: a meta-analytic review. Physiol Behav 203:42–50
Harris AZ, Atsak P, Bretton ZH, Holt ES, Alam R, Morton MP, Abbas AI, Leonardo ED, Bolkan SS, Hen R, Gordon JA (2018) A novel method for chronic social defeat stress in female mice. Neuropsychopharmacology (6):1276–1283
Golden SA, Covington HE, Berton O, Russo SJ (2011) A standardized protocol for repeated social defeat stress in mice. Nat Protoc 6:1183–1191
Grant BF, Hasin DS, Chou SP, Stinson FS, Dawson DA (2004) Nicotine dependence and psychiatric disorders in the United States: results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:1107–1115
Hsu HR, Chen TY, Chan MH, Chen HH (2007) Acute effects of nicotine on restraint stress-induced anxiety-like behavior, c-Fos expression, and corticosterone release in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 566:124–131
Iniguez SD, Riggs LM, Nieto SJ, Dayrit G, Zamora NN, Shawhan KL, Cruz B, Warren BL (2014) Social defeat stress induces a depression-like phenotype in adolescent male c57BL/6 mice. Stress 17:247–255
Iniguez SD, Warren BL, Neve RL, Nestler EJ, Russo SJ, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2008) Insulin receptor substrate-2 in the ventral tegmental area regulates behavioral responses to cocaine. Behav Neurosci 122:1172–1177
Iniguez SD, Warren BL, Parise EM, Alcantara LF, Schuh B, Maffeo ML, Manojlovic Z, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2009) Nicotine exposure during adolescence induces a depression-like state in adulthood. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1609–1624
Iñiguez SD, Flores-Ramirez FJ, Riggs LM, Alipio JB, Garcia-Carachure I, Hernandez MA, Sanchez DO, Lobo MK, Serrano PA, Braren SH, Castillo SA (2018) Vicarious social defeat stress induces depression-related outcomes in female mice. Biol Psychiatry 83(1):9–17
Irvine EE, Cheeta S, File SE (1999) Time-course of changes in the social interaction test of anxiety following acute and chronic administration of nicotine. Behav Pharmacol 10:691–697
Kassel JD, Stroud LR, Paronis CA (2003) Smoking, stress, and negative affect: correlation, causation, and context across stages of smoking. Psychol Bull 129:270–304
Kessler RC, McGonagle KA, Swartz M, Blazer DG, Nelson CB (1993) Sex and depression in the National Comorbidity Survey. I: lifetime prevalence, chronicity and recurrence. J Affect Disord (2–3):85–96
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE (2005) Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:593–602
Khurana A, Romer D, Betancourt LM, Brodsky NL, Giannetta JM, Hurt H (2015) Experimentation versus progression in adolescent drug use: a test of an emerging neurobehavioral imbalance model. Dev Psychopathol 27:901–913
Koob G, Kreek MJ (2007) Stress, dysregulation of drug reward pathways, and the transition to drug dependence. Am J Psychiatry 164:1149–1159
Koob GF, Ahmed SH, Boutrel B, Chen SA, Kenny PJ, Markou A, O’Dell LE, Parsons LH, Sanna PP (2004) Neurobiological mechanisms in the transition from drug use to drug dependence. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:739–749
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2016) Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 3:760–773
Lando HA, Thai DT, Murray DM, Robinson LA, Jeffery RW, Sherwood NE, Hennrikus DJ (1999) Age of initiation, smoking patterns, and risk in a population of working adults. Prev Med 29:590–598
Leao RM, Cruz FC, Vendruscolo LF, de Guglielmo G, Logrip ML, Planeta CS, Hope BT, Koob GF, George O (2015) Chronic nicotine activates stress/reward-related brain regions and facilitates the transition to compulsive alcohol drinking. J Neurosci 35:6241–6253
Lenney W, Enderby B (2008) “Blowing in the wind”: a review of teenage smoking. Arch Dis Child 93:72–75
Lewinsohn PM, Rohde P, Seeley JR, Fischer SA (1993) Age-cohort changes in the lifetime occurrence of depression and other mental disorders. J Abnorm Psychol 102:110–120
Lynch WJ, Roth ME, Carroll ME (2002) Biological basis of sex differences in drug abuse: preclinical and clinical studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2:121–137
McCormick CM, Green MR (2013) From the stressed adolescent to the anxious and depressed adult: investigations in rodent models. Neuroscience 249:242–257
McQuown SC, Belluzzi JD, Leslie FM (2007) Low dose nicotine treatment during early adolescence increases subsequent cocaine reward. Neurotoxicol Teratol 29:66–73
Meliska CJ, Bartke A, McGlacken G, Jensen RA (1995) Ethanol, nicotine, amphetamine, and aspartame consumption and preferences in C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 50:619–626
Miczek KA, Yap JJ, Covington HE 3rd (2008) Social stress, therapeutics and drug abuse: preclinical models of escalated and depressed intake. Pharmacol Ther 120:102–128
Mineur YS, Picciotto MR (2009) Biological basis for the co-morbidity between smoking and mood disorders. J Dual Diagn 5:122–130
Montgomery KC (1955) The relation between fear induced by novel stimulation and exploratory behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol 48:254–260
National Research Council (US) (2003) Committee on guidelines for the use of animals in neuroscience and behavioral research (National Academies Press (US): Washington (DC). Guidelines for the care and use of mammals in neuroscience and behavioral research. https://doi.org/10.17226/10732
Newman EL, Covington HE 3rd, Suh J, Bicakci MB, Ressler KJ, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2019) Fighting females: neural and behavioral consequences of social defeat stress in female mice. Biol Psychiatry 86(9):657–668
Pandey SC, Chartoff EH, Carlezon WA Jr, Zou J, Zhang H, Kreibich AS, Blendy JA, Crews FT (2005) CREB gene transcription factors: role in molecular mechanisms of alcohol and drug addiction. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:176–184
Parrott AC (1999) Does cigarette smoking cause stress? Am Psychol 54:817–820
Parrott AC, Murphy RS (2012) Explaining the stress-inducing effects of nicotine to cigarette smokers. Hum Psychopharmacol 27:150–155
Pekonen K, Karlsson C, Laakso I, Ahtee L (1993) Plasma nicotine and cotinine concentration in mice after chronic oral administration and challenge doses. Eur Journal Pharm Sci 1:13–18
Perry AN, Westenbroek C, Becker JB (2013) The development of a preference for cocaine over food identifies individual rats with addiction-like behaviors. PLoS One 8:e79465
Picciotto MR, Mineur YS (2014) Molecules and circuits involved in nicotine addiction: the many faces of smoking. Neuropharmacology 76 Pt B: 545-53
Pizzagalli DA (2014) Depression, stress, and anhedonia: toward a synthesis and integrated model. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 10:393–423
Polter AM, Kauer JA (2014) Stress and VTA synapses: implications for addiction and depression. Eur J Neurosci 39:1179–1188
Rao U (2006) Links between depression and substance abuse in adolescents: neurobiological mechanisms. Am J Prev Med 31:S161–S174
Reed AL, Happe HK, Petty F, Bylund DB (2008) Juvenile rats in the forced-swim test model the human response to antidepressant treatment for pediatric depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 197:433–441
Rupprecht LE, Kreisler AD, Spierling SR, de Guglielmo G, Kallupi M, George O, Donny EC, Zorrilla EP, Sved AF (2018) Self-administered nicotine increases fat metabolism and suppresses weight gain in male rats. Psychopharmacology 235:1131–1140
Saal D, Dong Y, Bonci A, Malenka RC (2003) Drugs of abuse and stress trigger a common synaptic adaptation in dopamine neurons. Neuron 37:577–582
Salin-Pascual RJ, Drucker-Colin R (1998) A novel effect of nicotine on mood and sleep in major depression. Neuroreport 9:57–60
Schiff M, Plotnikova M, Dingle K, Williams GM, Najman J, Clavarino A (2014) Does adolescent’s exposure to parental intimate partner conflict and violence predict psychological distress and substance use in young adulthood? A longitudinal study. Child Abuse Negl 38:1945–1954
Sial OK, Warren BL, Alcantara LF, Parise EM, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2016) Vicarious social defeat stress: bridging the gap between physical and emotional stress. J Neurosci Methods 258:94–103
Smith PH, Homish GG, Saddleson ML, Kozlowski LT, Giovino GA (2013) Nicotine withdrawal and dependence among smokers with a history of childhood abuse. Nicotine Tob Res 15:2016–2021
Sparks JA, Pauly JR (1999) Effects of continuous oral nicotine administration on brain nicotinic receptors and responsiveness to nicotine in C57Bl/6 mice. Psychopharmacology 141:145–153
Spear LP (2000) The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:417–463
Suemaru K, Yasuda K, Cui R, Li B, Umeda K, Amano M, Mitsuhashi H, Takeuchi N, Inoue T, Gomita Y, Araki H (2006) Antidepressant-like action of nicotine in forced swimming test and brain serotonin in mice. Physiol Behav 88:545–549
Takahashi A, Chung JR, Zhang S, Zhang H, Grossman Y, Aleyasin H, Flanigan ME, Pfau ML, Menard C, Dumitriu D, Hodes GE, McEwen BS, Nestler EJ, Han MH, RussoSJ (2017) Establishment of a repeated social defeat stress model in female mice. Sci Rep 2;7(1):128–38
Thompson AB, Mowery PD, Tebes JK, McKee SA (2018) Time trends in smoking onset by sex and race/ethnicity among adolescents and young adults: findings from the 2006-2013 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Nicotine Tob Res 20:312–320
Tizabi Y, Overstreet DH, Rezvani AH, Louis VA, Clark E Jr, Janowsky DS, Kling MA (1999) Antidepressant effects of nicotine in an animal model of depression. Psychopharmacology 142:193–199
van der Deen FS, Carter KN, Wilson N, Collings S (2011) The association between failed quit attempts and increased levels of psychological distress in smokers in a large New Zealand cohort. BMC Public Health 11:598
Vazquez-Palacios G, Bonilla-Jaime H, Velazquez-Moctezuma J (2004) Antidepressant-like effects of the acute and chronic administration of nicotine in the rat forced swimming test and its interaction with fluoxetine [correction of flouxetine]. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78:165–169
Vialou V, Robison AJ, Laplant QC, Covington HE 3rd, Dietz DM, Ohnishi YN, Mouzon E, Rush AJ 3rd, Watts EL, Wallace DL, Iniguez SD, Ohnishi YH, Steiner MA, Warren BL, Krishnan V, Bolanos CA, Neve RL, Ghose S, Berton O, Tamminga CA, Nestler EJ (2010) DeltaFosB in brain reward circuits mediates resilience to stress and antidepressant responses. Nat Neurosci 13:745–752
Vieyra-Reyes P, Picciotto MR, Mineur YS (2008) Voluntary oral nicotine intake in mice down-regulates GluR2 but does not modulate depression-like behaviors. Neurosci Lett 434:18–22
Walters CL, Cleck JN, Kuo YC, Blendy JA (2005) Mu-opioid receptor and CREB activation are required for nicotine reward. Neuron 46:933–943
Warren BL, Vialou VF, Iniguez SD, Alcantara LF, Wright KN, Feng J, Kennedy PJ, Laplant Q, Shen L, Nestler EJ, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2013) Neurobiological sequelae of witnessing stressful events in adult mice. Biol Psychiatry 73:7–14
Warren BL, Sial OK, Alcantara LF, Greenwood MA, Brewer JS, Rozofsky JP, Parise EM, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2014) Altered gene expression and spine density in nucleus accumbens of adolescent and adult male mice exposed to emotional and physical stress. Dev Neurosci 36:250–260
Watson NL, VanderVeen JW, Cohen LM, DeMarree KG, Morrell HE (2012) Examining the interrelationships between social anxiety, smoking to cope, and cigarette craving. Addict Behav 37:986–989
Xiao X, Shang X, Zhai B, Zhang H, Zhang T (2018) Nicotine alleviates chronic stress-induced anxiety and depressive-like behavior and hippocampal neuropathology via regulating autophagy signaling. Neurochem Int 114:58–70
Yap JJ, Miczek KA (2007) Social defeat stress, sensitization, and intravenous cocaine self-administration in mice. Psychopharmacology 192:261–273
Zoli M, Picciotto MR (2012) Nicotinic regulation of energy homeostasis. Nicotine Tob Res 14:1270–1290
Funding
This work was supported by Texas A&M University College of Liberal Arts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parise, L.F., Sial, O.K., Warren, B.L. et al. Nicotine treatment buffers negative behavioral consequences induced by exposure to physical and emotional stress in adolescent male mice. Psychopharmacology 237, 3125–3137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05598-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05598-6