Abstract
Rationale
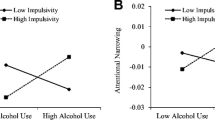
Past research has found that exposure to alcohol cues causes a narrowing of attentional scope and enhances the neural responses associated with approach motivation.
Objective
The current research sought to determine if a manipulated broadened (global) attentional scope would reduce approach-motivated neural reactivity to alcohol pictures.
Methods
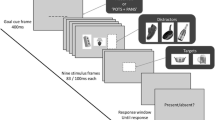
In the current study, participants (n = 82) were exposed to alcohol and neutral pictures following either a global or local attentional scope manipulation. Early motivated attentional processing was assessed using the N1 event-related potential (ERP), a neurophysiological marker of rapid motivated attention.
Results
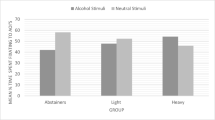
A global attentional scope reduced N1 amplitudes to alcohol pictures as compared to a local attentional scope. Self-reported binge drinking related to larger N1 amplitudes to alcohol pictures, but not to neutral pictures. Individuals with greater binge drinking experience demonstrated increased rapid motivated attentional processing to alcohol pictures.
Conclusions
These results suggest that enhancing a global (vs. local) attentional scope attenuates rapid motivated attentional processing of alcohol pictures in comparison to neutral pictures.

ᅟ




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldauf D, Deubel H (2009) Attentional selection of multiple goal positions before rapid hand movement sequences: an event-related potential study. J Cogn Neurosci 21(1):18–29
Bartholow BD, Henry EA, Lust SA (2007) Effects of alcohol sensitivity on P3 event-related potential reactivity to alcohol cues. Psychol Addict Behav 21(4):555
Bartholow BD, Lust SA, Tragesser SL (2010) Specificity of P3 event-related potential reactivity to alcohol cues in individuals low in alcohol sensitivity. Psychol Addict Behav 24(2):220
Carretié L, Hinojosa JA, Martín-Loeches M, Mercado F, Tapia M (2004) Automatic attention to emotional stimuli: neural correlates. Hum Brain Mapp 22(4):290–299
Carter BL, Tiffany ST (1999) Meta-analysis of cue-reactivity in addiction research. Addiction 94(3):327–340
Crego A, Holguín SR, Parada M, Mota N, Corral M, Cadaveira F (2009) Binge drinking affects attentional and visual working memory processing in young university students. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33(11):1870–1879
Dickter CL, Forestell CA, Hammett PJ, Young CM (2014) Relationship between alcohol dependence, escape drinking, and early neural attention to alcohol-related cues. Psychopharmacology 231(9):2031–2040
Esposito F, Mulert C, Goebel R (2009) Combined distributed source and single-trial EEG–fMRI modeling: application to effortful decision making processes. NeuroImage 47(1):112–121
Fabiani M, Gratton G, Federmeier KD (2007) Event-related brain potentials: methods, theory, and appliucations. In: Cacioppo JT, Tassinary LG, Berntson G (eds) Handbook of psychophysiology. Cambridge University Press, pp 53–84
Fadardi JS, Cox WM (2009) Reversing the sequence: reducing alcohol consumption by overcoming alcohol attentional bias. Drug Alcohol Depend 101(3):137–145
Field M, Cox WM (2008) Attentional bias in addictive behaviors: a review of its development, causes, and consequences. Drug Alcohol Depend 97(1):1–20
Field M, Eastwood B (2005) Experimental manipulation of attentional bias increases the motivation to drink alcohol. Psychopharmacology 183(3):350–357
Forestell CA, Dickter CL, Young CM (2012) Take me away: the relationship between escape drinking and attentional bias for alcohol-related cues. Alcohol 46(6):543–549
Foti D, Hajcak G, Dien J (2009) Differentiating neural responses to emotional pictures: evidence from temporal-spatial PCA. Psychophysiology 46(3):521–530
Gable PA, Harmon-Jones E (2010) Late positive potential to appetitive stimuli and local attentional bias. Emotion 10(3):441–446
Gable PA, Harmon-Jones E (2011) Attentional states influence early neural responses associated with motivational processes: local vs. global attentional scope and N1 amplitude to appetitive stimuli. Biol Psychol 87:303–305
Gable PA, Harmon-Jones E (2012) Trait behavioral approach sensitivity (BAS) relates to early (<150 ms) electrocortical responses to appetitive stimuli. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 8(7):795–798
Gable PA, Mechin NC, Neal LB (2016) Booze cues and attentional narrowing: neural correlates of virtual alcohol myopia. Psychol Addict Behav 30(3):377–382
Gray JR (2001) Emotional modulation of cognitive control: approach–withdrawal states double-dissociate spatial from verbal two-back task performance. J Exp Psychol Gen 130(3):436
Harmon-Jones E, Gable PA, Price TF (2012) The influence of affective states varying in motivational intensity on cognitive scope. Front Integr Neurosci 6. doi:10.3389/fnint.2012.00073
Hicks JA, Friedman RS, Gable PA, Davis WE (2012) Interactive effects of approach motivational intensity and alcohol cues on the scope of perceptual attention. Addiction 107(6):1074–1080
Hicks JA, Fields S, Davis WE, Gable PA (2015) Heavy drinking, impulsivity and attentional narrowing following alcohol cue exposure. Psychopharmacology 232(15):2773–2779
Keil A, Müller MM, Gruber T, Wienbruch C, Stolarova M, Elbert T (2001) Effects of emotional arousal in the cerebral hemispheres: a study of oscillatory brain activity and event-related potentials. Clin Neurophysiol 112(11):2057–2068
King AC, Houle T, de Wit H, Holdstock L, Schuster A (2002) Biphasic alcohol response differs in heavy versus light drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:827–835
Lee S, Lee JH (2015) The effect of automatic attentional bias modification on alcohol ambivalence. Addict Behav 46:58–64
MacDonald TK, MacDonald G, Zanna MP, Fong G (2000) Alcohol, sexual arousal, and intentions to use condoms in young men: applying alcohol myopia theory to risky sexual behavior. Health Psychol 19(3):290–298
Maurage P, Joassin F, Speth A, Modave J, Philippot P, Campanella S (2012) Cerebral effects of binge drinking: respective influences of global alcohol intake and consumption pattern. Clin Neurophysiol 123(5):892–901
Mechin N, Gable PA, Hicks JA (2016) Frontal asymmetry and alcohol cue reactivity: influence of core personality systems. Psychophysiology 53(8):1224–1231
Medina EL (1970) The role of alcohol in accidents and violence. In: Popham RE (ed) Alcohol and alcoholism. Toronto, University of Toronto Press, pp 350–355
Moskowitz H, DePry D (1968) Differential effect of alcohol on auditory vigilance and divided attention. Q J Stud Alcohol 29:54–67
Namkoong K, Lee E, Lee CH, Lee BO, An SK (2004) Increased P3 amplitudes induced by alcohol-related pictures in patients with alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28(9):1317–1323
Navon D (1977) Forest before trees: the precedence of global features in visual perception. Cogn Psychol 9:353–383
Olofsson JK, Nordin S, Sequeira H, Polich J (2008) Affective picture processing: an integrative review of ERP findings. Biol Psychol 77(3):247–265
Petit G, Kornreich C, Dan B, Verbanck P, Campanella S (2014) Electrophysiological correlates of alcohol-and non-alcohol-related stimuli processing in binge drinkers: a follow-up study. J Psychopharmacol 28(11):1041–1052
Plihal W, Haenschel C, Hachl P, Born J, Pietrowsky R (2001) The effect of food deprivation on ERP during identification of tachistoscopically presented food-related words. J Psychophysiol 15(3):163
Polich J (2007) Updating P300: an integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin Neurophysiol 118(10):2128–2148
Semlitsch HV, Anderer P, Schuster P, Presslich O (1986) A solution for reliable and valid reduction of ocular artifacts, applied to the P300 ERP. Psychophysiology 23(6):695–703
Steele CM, Josephs RA (1990) Alcohol myopia: its prized and dangerous effects. Am Psychol 45(8):921
Steele CM, Critchlow B, Liu TJ (1985) Alcohol and social behavior: II. The helpful drunkard. J Pers Soc Psychol 48(1):35–46
Vogel EK, Luck SJ (2000) The visual N1 component as an index of a discrimination process. Psychophysiology 37(02):190–203
Washburne C (1956) Alcohol, self, and the group. Q J Stud Alcohol 17:108–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 460 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryerson, N.C., Neal, L.B. & Gable, P.A. Attenuating the alcohol allure: attentional broadening reduces rapid motivational response to alcohol pictures. Psychopharmacology 234, 1247–1254 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4557-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4557-1