Abstract
Rationale
Depression is highly prevalent in diabetes (DM). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) which is mainly regulated by the endoplasmic reticulum chaperon sigma-1 receptor (S1R) plays a relevant role in the development of depression.
Objectives
We studied the dose-dependent efficacy of S1R agonist fluvoxamine (FLU) in the prevention of DM-induced depression and investigated the significance of the S1R-BDNF pathway.
Methods
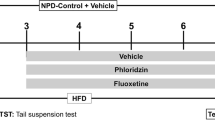
We used streptozotocin to induce DM in adult male rats that were treated for 2 weeks p.o. with either different doses of FLU (2 or 20 mg/bwkg) or FLU + S1R antagonist NE100 (1 mg/bwkg) or vehicle. Healthy controls were also enrolled. Metabolic, behaviour, and neuroendocrine changes were determined, and S1R and BDNF levels were measured in the different brain regions.
Results
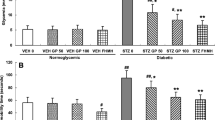
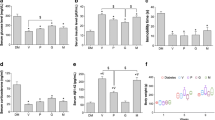
In DM rats, immobility time was increased, adrenal glands were enlarged, and thymuses were involuted. FLU in 20 mg/bwkg, but not in 2 mg/bwkg dosage, ameliorated depression-like behaviour. S1R and BDNF protein levels were decreased in DM, while FLU induced SIR-BDNF production. NE100 suspended all effects of FLU.
Conclusions
We suggest that disturbed S1R-BDNF signaling in the brain plays a relevant role in DM-induced depression. The activation of this cascade serves as an additional target in the prevention of DM-associated depression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Autry AE, Monteggia LM (2012) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol Rev 64:238–258
Bronikowski AM, Carter PA, Swallow JG, Girard IA, Rhodes JS, Garland T (2001) Open-field behavior of house mice selectively bred for high voluntary wheel-running. Behav Genet 31:309–316
Chan O, Inouye K, Riddell MC, Vranic M, Matthews SG (2003) Diabetes and the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Minerva Endocrinol 28:87–102
Chen PC, Chan YT, Chen HF, Ko MC, Li CY (2013) Population-based cohort analyses of the bidirectional relationship between type 2 diabetes and depression. Diabetes Care 36:376–382
Coplan JD, Gopinath S, Abdallah CG, Berry BR (2014) A neurobiological hypothesis of treatment-resistant depression - mechanisms for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor non-efficacy. Front Behav Neurosci 8:189
Cunha AB, Frey BN, Andreazza AC, Goi JD, Rosa AR, Goncalves CA, Santin A, Kapczinski F (2006) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor is decreased in bipolar disorder during depressive and manic episodes. Neurosci Lett 398:215–219
de Zwaan M, Nutzinger DO (1996) Effect of fluvoxamine on total serum cholesterol levels during weight reduction. J Clin Psychiatry 57:346–348
Duman RS, Monteggia LM (2006) A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 59:1116–1127
Durany N, Michel T, Kurt J, Cruz-Sanchez FF, Cervas-Navarro J, Riederer P (2000) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 levels in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Int J Dev Neurosci 18:807–813
Etemad A, Sheikhzadeh F, Asl NA (2015) Evaluation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in diabetic rats. Neurol Res 37:217–222
Federation ID (2013) International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas, 6th edn. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, 2013.
Fishback JA, Robson MJ, Xu YT, Matsumoto RR (2010) Sigma receptors: potential targets for a new class of antidepressant drug. Pharmacol Ther 127:271–282
Fujimoto M, Hayashi T, Urfer R, Mita S, Su TP (2012) Sigma-1 receptor chaperones regulate the secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Synapse 66:630–639
Golden SH, Lazo M, Carnethon M, Bertoni AG, Schreiner PJ, Diez Roux AV, Lee HB, Lyketsos C (2008) Examining a bidirectional association between depressive symptoms and diabetes. JAMA 299:2751–2759
Hashimoto K (2015) Activation of sigma-1 receptor chaperone in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases and its clinical implication. J Pharmacol Sci 127:6–9
Hayashi T, Su TP (2004) Sigma-1 receptor ligands: potential in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. CNS drugs 18:269–284
Hayashi T, Su TP (2007) Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca(2+) signaling and cell survival. Cell 131:596–610
Hayashi T, Tsai SY, Mori T, Fujimoto M, Su TP (2011) Targeting ligand-operated chaperone sigma-1 receptors in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets 15:557–577
Katon W, Fan MY, Unutzer J, Taylor J, Pincus H, Schoenbaum M (2008) Depression and diabetes: a potentially lethal combination. J Gen Intern Med 23:1571–1575
Korczak DJ, Pereira S, Koulajian K, Matejcek A, Giacca A (2011) Type 1 diabetes mellitus and major depressive disorder: evidence for a biological link. Diabetologia 54:2483–2493
Kourrich S, Su TP, Fujimoto M, Bonci A (2012) The sigma-1 receptor: roles in neuronal plasticity and disease. Trends Neurosci 35:762–771
Mardon K, Kassiou M, Donald A (1999) Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on neuronal sigma receptors in the rat brain. Life Sci 65:PL 281–PL 286
Markowitz SM, Gonzalez JS, Wilkinson JL, Safren SA (2011) A review of treating depression in diabetes: emerging findings. Psychosomatics 52:1–18
Mizoguchi H, Nakade J, Tachibana M, Ibi D, Someya E, Koike H, Kamei H, Nabeshima T, Itohara S, Takuma K, Sawada M, Sato J, Yamada K (2011) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to kindled seizure development in pentylenetetrazole-treated mice by converting pro-BDNF to mature BDNF in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 31:12963–12971
Narita N, Hashimoto K, Tomitaka S, Minabe Y (1996) Interactions of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors with subtypes of sigma receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 307:117–119
Niitsu T, Ishima T, Yoshida T, Hashimoto T, Matsuzawa D, Shirayama Y, Nakazato M, Shimizu E, Hashimoto K, Iyo M (2014) A positive correlation between serum levels of mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 215:268–273
Noble EE, Billington CJ, Kotz CM, Wang C (2011) The lighter side of BDNF. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300:R1053–R1069
Oswald P, Souery D, Mendlewicz J (2003) Fluvoxamine-induced hyperglycaemia in a diabetic patient with comorbid depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 6:85–87
Palomino A, Vallejo-Illarramendi A, Gonzalez-Pinto A, Aldama A, Gonzalez-Gomez C, Mosquera F, Gonzalez-Garcia G, Matute C (2006) Decreased levels of plasma BDNF in first-episode schizophrenia and bipolar disorder patients. Schizophr Res 86:321–322
Pandey GN, Ren X, Rizavi HS, Conley RR, Roberts RC, Dwivedi Y (2008) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tyrosine kinase B receptor signalling in post-mortem brain of teenage suicide victims. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:1047–1061
Park M, Katon WJ, Wolf FM (2013) Depression and risk of mortality in individuals with diabetes: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 35:217–225
Perovic M, Tesic V, Mladenovic Djordjevic A, Smiljanic K, Loncarevic-Vasiljkovic N, Ruzdijic S, Kanazir S (2013) BDNF transcripts, proBDNF and proNGF, in the cortex and hippocampus throughout the life span of the rat. Age 35:2057–2070
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47:379–391
Reddy VS, Bui QT, Jacobs JR, Begelman SM, Miller DP, French WJ, Investigators of National Registry of Myocardial Infarction b (2015) Relationship between serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and in-hospital mortality following acute myocardial infarction (the lipid paradox). Am J Cardiol 115:557–562
Reus GZ, Abelaira HM, Stringari RB, Fries GR, Kapczinski F, Quevedo J (2012) Memantine treatment reverses anhedonia, normalizes corticosterone levels and increases BDNF levels in the prefrontal cortex induced by chronic mild stress in rats. Metab Brain Dis 27:175–182
Roy T, Lloyd CE (2012) Epidemiology of depression and diabetes: a systematic review. J Affect Disord 142(Suppl):S8–S21
Sanchez C, Meier E (1997) Behavioral profiles of SSRIs in animal models of depression, anxiety and aggression. Are they all alike? Psychopharmacology 129:197–205
Sen S, Duman R, Sanacora G (2008) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, and antidepressant medications: meta-analyses and implications. Biol Psychiatry 64:527–532
Shrestha SS, Zhang P, Li R, Thompson TJ, Chapman DP, Barker L (2013) Medical expenditures associated with major depressive disorder among privately insured working-age adults with diagnosed diabetes in the United States, 2008. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 100:102–110
Slattery DA, Cryan JF (2012) Using the rat forced swim test to assess antidepressant-like activity in rodents. Nat Protoc 7:1009–1014
Sugimoto Y, Tagawa N, Kobayashi Y, Mitsui-Saito K, Hotta Y, Yamada J (2012) Involvement of the sigma1 receptor in the antidepressant-like effects of fluvoxamine in the forced swimming test in comparison with the effects elicited by paroxetine. Eur J Pharmacol 696:96–100
Thompson Ray M, Weickert CS, Wyatt E, Webster MJ (2011) Decreased BDNF, trkB-TK+ and GAD67 mRNA expression in the hippocampus of individuals with schizophrenia and mood disorders. J Psychiatry Neurosci : JPN 36:195–203
Tse L, Procyshyn RM, Fredrikson DH, Boyda HN, Honer WG, Barr AM (2014) Pharmacological treatment of antipsychotic-induced dyslipidemia and hypertension. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 29:125–137
Varga J, Domokos A, Barna I, Jankord R, Bagdy G, Zelena D (2011) Lack of vasopressin does not prevent the behavioural and endocrine changes induced by chronic unpredictable stress. Brain Res Bull 84:45–52
Voican CS, Corruble E, Naveau S, Perlemuter G (2014) Antidepressant-induced liver injury: a review for clinicians. Am J Psychiatry 171:404–415
Wetsel WC, Rodriguiz RM, Guillemot J, Rousselet E, Essalmani R, Kim IH, Bryant JC, Marcinkiewicz J, Desjardins R, Day R, Constam DB, Prat A, Seidah NG (2013) Disruption of the expression of the proprotein convertase PC7 reduces BDNF production and affects learning and memory in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:17362–17367
Willner P (1984) The validity of animal models of depression. Psychopharmacology 83:1–16
World Health Organization, pp Facts sheet No 369 - Depression. Accessed on the 18th of May 2014, Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/.
Yagasaki Y, Numakawa T, Kumamaru E, Hayashi T, Su TP, Kunugi H (2006) Chronic antidepressants potentiate via sigma-1 receptors the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced signaling for glutamate release. J Biol Chem 281:12941–12949
Yamada J, Sugimoto Y, Inoue K (1999) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors fluoxetine and fluvoxamine induce hyperglycemia by different mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 382:211–215
Yoshimura R, Kishi T, Hori H, Atake K, Katsuki A, Nakano-Umene W, Ikenouchi-Sugita A, Iwata N, Nakamura J (2014) Serum proBDNF/BDNF and response to fluvoxamine in drug-naive first-episode major depressive disorder patients. Ann Gen Psychiatry 13:19
Zelena D, Barna I, Mlynarik M, Gupta OP, Jezova D, Makara GB (2005) Stress symptoms induced by repeated morphine withdrawal in comparison to other chronic stress models in mice. Neuroendocrinology 81:205–215
Zelena D, Filaretova L, Mergl Z, Barna I, Tóth ZE, Makara GB (2006) Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus, but not vasopressin, participates in chronic hyperactivity of the HPA axis in diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E243–E250
Zelena D, Domokos A, Barna I, Csabail K, Bagdy G, Makara GB (2007) The role of vasopressin in chronic stress studied in a chronic mild stress model of depression. Ideggyogy Sz 60:196–200
Zhang X, Norris SL, Gregg EW, Cheng YJ, Beckles G, Kahn HS (2005) Depressive symptoms and mortality among persons with and without diabetes. Am J Epidemiol 161:652–660
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by grants of OTKA K112629-K116928-K108688-PD105361-NN114607. It was also supported by MTA-SE “Lendület” Research Grant (LP-008/2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lenart, L., Hodrea, J., Hosszu, A. et al. The role of sigma-1 receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the development of diabetes and comorbid depression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Psychopharmacology 233, 1269–1278 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4209-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4209-x