Abstract
Rationale
Carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia is a widely used pain model in rodents. However, characteristics of carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia and effects of analgesic drugs under these conditions are unknown in nonhuman primates.
Objective
The aims of this study were to develop carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia in rhesus monkeys and determine the efficacy and potency of agonists selective for the four opioid receptor subtypes in this model versus acute pain, as compared to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Results
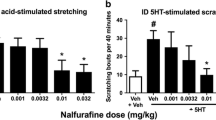
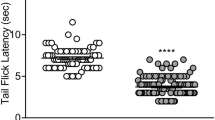
Tail injection of carrageenan produced long-lasting thermal hyperalgesia in monkeys. Systemically administered agonists selective for opioid receptor subtypes, i.e., fentanyl (mu/MOP), U-50488H (kappa/KOP), SNC80 (delta/DOP) and Ro 64-6198 (nociceptin/orphanin FQ/NOP) dose-dependently attenuated carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia with different potencies. In absence of carrageenan, these agonists, except SNC80, blocked acute thermal nociception. Opioid-related ligands, especially Ro 64-6198, were much more potent for their antihyperalgesic than antinociceptive effects. Both effects were mediated by the corresponding receptor mechanisms. Only fentanyl produced scratching at antihyperalgesic and antinociceptive doses consistent with its pruritic effects in humans, illustrating a translational profile of MOP agonists in nonhuman primates. Similar to SNC80, systemically administered NSAIDs ketorolac and naproxen dose-dependently attenuated carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia but not acute nociception.
Conclusion
Using two different pain modalities in nonhuman primates, effectiveness of clinically available analgesics like fentanyl, ketorolac and naproxen was distinguished and their efficacies and potencies were compared with the selective KOP, DOP, and NOP agonists. The opioid-related ligands displayed differential pharmacological properties in regulating hyperalgesia and acute nociception in the same subjects. Such preclinical primate models can be used to investigate novel analgesic agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber A, Bartoszyk GD, Bender HM, Gottschlich R, Greiner HE, Harting J, Mauler F, Minck KO, Murray RD, Simon M et al (1994) A pharmacological profile of the novel, peripherally-selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist, EMD 61753. Br J Pharmacol 113:1317–1327
Basbaum AI, Fields HL (1984) Endogenous pain control systems: brainstem spinal pathways and endorphin circuitry. Annu Rev Neurosci 7:309–338
Bianchi BR, Zhang XF, Reilly RM, Kym PR, Yao BB, Chen J (2012) Species comparison and pharmacological characterization of human, monkey, rat, and mouse TRPA1 channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 341:360–368
Brandt MR, Furness MS, Mello NK, Rice KC, Negus SS (2001) Antinociceptive effects of delta-opioid agonists in Rhesus monkeys: effects on chemically induced thermal hypersensitivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:939–946
Buckley MM, Brogden RN (1990) Ketorolac. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential. Drugs 39:86–109
Butelman ER, Negus SS, Ai Y, de Costa BR, Woods JH (1993) Kappa opioid antagonist effects of systemically administered nor-binaltorphimine in a thermal antinociception assay in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:1269–1276
Butelman ER, Negus SS, Gatch MB, Chang KJ, Woods JH (1995) BW373U86, a delta-opioid receptor agonist, reverses bradykinin-induced thermal allodynia in rhesus monkeys. Eur J Pharmacol 277:285–287
Butelman ER, Ko MC, Traynor JR, Vivian JA, Kreek MJ, Woods JH (2001) GR89,696: a potent kappa-opioid agonist with subtype selectivity in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:1049–1059
Butelman ER, Ball JW, Harris TJ, Kreek MJ (2003) Topical capsaicin-induced allodynia in unanesthetized primates: pharmacological modulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:1106–1114
Cahill CM, Morinville A, Hoffert C, O’Donnell D, Beaudet A (2003) Up-regulation and trafficking of delta opioid receptor in a model of chronic inflammation: implications for pain control. Pain 101:199–208
Calo G, Guerrini R (2013) Medicinal chemistry, pharmacology, and biological actions of peptide ligands selective for the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor. In: Ko M-C, Husbands SM (eds) Research and development of opioid-related ligands. ACS, pp 275–325
Castellsague J, Riera-Guardia N, Calingaert B, Varas-Lorenzo C, Fourrier-Reglat A, Nicotra F, Sturkenboom M, Perez-Gutthann S, Safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs P (2012) Individual NSAIDs and upper gastrointestinal complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies (the SOS project). Drug Saf: Int J Med Toxicol Drug Exp 35:1127–1146
Chen Y, Sommer C (2006) Nociceptin and its receptor in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons in neuropathic and inflammatory pain models: implications on pain processing. J Peripher Nerv Syst: JPNS 11:232–240
Comer SD, Hoenicke EM, Sable AI, McNutt RW, Chang KJ, De Costa BR, Mosberg HI, Woods JH (1993) Convulsive effects of systemic administration of the delta opioid agonist BW373U86 in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:888–895
Correa JD, Paiva-Lima P, Rezende RM, Dos Reis WG, Ferreira-Alves DL, Bakhle YS, Francischi JN (2010) Peripheral mu-, kappa- and delta-opioid receptors mediate the hypoalgesic effect of celecoxib in a rat model of thermal hyperalgesia. Life Sci 86:951–956
Dirig DM, Isakson PC, Yaksh TL (1998) Effect of COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition on induction and maintenance of carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:1031–1038
Dykstra LA, Schoenbaum GM, Yarbrough J, McNutt R, Chang KJ (1993) A novel delta opioid agonist, BW373U86, in squirrel monkeys responding under a schedule of shock titration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:875–882
Ellis DJ, Millar WL, Reisner LS (1990) A randomized double-blind comparison of epidural versus intravenous fentanyl infusion for analgesia after cesarean section. Anesthesiology 72:981–986
Fraser GL, Gaudreau GA, Clarke PB, Menard DP, Perkins MN (2000) Antihyperalgesic effects of delta opioid agonists in a rat model of chronic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 129:1668–1672
Hameed H, Hameed M, Christo PJ (2010) The effect of morphine on glial cells as a potential therapeutic target for pharmacological development of analgesic drugs. Curr Pain Headache Rep 14:96–104
Hawkinson JE, Szoke BG, Garofalo AW, Hom DS, Zhang H, Dreyer M, Fukuda JY, Chen L, Samant B, Simmonds S, Zeitz KP, Wadsworth A, Liao A, Chavez RA, Zmolek W, Ruslim L, Bova MP, Holcomb R, Butelman ER, Ko MC, Malmberg AB (2007) Pharmacological, pharmacokinetic, and primate analgesic efficacy profile of the novel bradykinin B1 Receptor antagonist ELN441958. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322:619–630
Herrero JF, Headley PM (1996) Reversal by naloxone of the spinal antinociceptive actions of a systemically-administered NSAID. Br J Pharmacol 118:968–972
Hill R (2000) NK1 (substance P) receptor antagonists—why are they not analgesic in humans? Trends Pharmacol Sci 21:244–246
Hu E, Calo G, Guerrini R, Ko MC (2010) Long-lasting antinociceptive spinal effects in primates of the novel nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor agonist UFP-112. Pain 148:107–113
Hutchinson MR, Bland ST, Johnson KW, Rice KC, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2007) Opioid-induced glial activation: mechanisms of activation and implications for opioid analgesia, dependence, and reward. Sci World J 7:98–111
Ikoma A, Steinhoff M, Stander S, Yosipovitch G, Schmelz M (2006) The neurobiology of itch. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:535–547
Itoh M, Takasaki I, Andoh T, Nojima H, Tominaga M, Kuraishi Y (2001) Induction by carrageenan inflammation of prepronociceptin mRNA in VR1-immunoreactive neurons in rat dorsal root ganglia. Neurosci Res 40:227–233
Ji RR, Zhang Q, Law PY, Low HH, Elde R, Hokfelt T (1995) Expression of mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptor-like immunoreactivities in rat dorsal root ganglia after carrageenan-induced inflammation. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 15:8156–8166
Jia Y, Linden DR, Serie JR, Seybold VS (1998) Nociceptin/orphanin FQ binding increases in superficial laminae of the rat spinal cord during persistent peripheral inflammation. Neurosci Lett 250:21–24
Joris JL, Dubner R, Hargreaves KM (1987) Opioid analgesia at peripheral sites: a target for opioids released during stress and inflammation? Anesth Analg 66:1277–1281
Ko MC, Husbands SM (2009) Effects of atypical kappa-opioid receptor agonists on intrathecal morphine-induced itch and analgesia in primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:193–200
Ko MC, Naughton NN (2009) Antinociceptive effects of nociceptin/orphanin FQ administered intrathecally in monkeys. J Pain: Off J Am Pain Soc 10:509–516
Ko MC, Butelman ER, Traynor JR, Woods JH (1998) Differentiation of kappa opioid agonist-induced antinociception by naltrexone apparent pA2 analysis in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:518–526
Ko MC, Naughton NN, Traynor JR, Song MS, Woods JH, Rice KC, McKnight AT (2002) Orphanin FQ inhibits capsaicin-induced thermal nociception in monkeys by activation of peripheral ORL1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 135:943–950
Ko MC, Song MS, Edwards T, Lee H, Naughton NN (2004) The role of central mu opioid receptors in opioid-induced itch in primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:169–176
Krekels EH, Angesjo M, Sjogren I, Moller KA, Berge OG, Visser SA (2011) Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modeling of the inhibitory effects of naproxen on the time-courses of inflammatory pain, fever, and the ex vivo synthesis of TXB2 and PGE2 in rats. Pharm Res 28:1561–1576
Kumagai H, Ebata T, Takamori K, Muramatsu T, Nakamoto H, Suzuki H (2010) Effect of a novel kappa-receptor agonist, nalfurafine hydrochloride, on severe itch in 337 haemodialysis patients: a Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nephrol, Dial, Transplant: Off Publ Eur Dial Transplant Assoc - Eur Ren Assoc 25:1251–1257
Kupers RC, Chen CC, Bushnell MC (1997) A model of transient hyperalgesia in the behaving monkey induced by topical application of capsaicin. Pain 72:269–275
Lin AP, Ko MC (2013) The therapeutic potential of nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor agonists as analgesics without abuse liability. ACS Chem Neurosci 4:214–224
Negus SS, Butelman ER, Al Y, Woods JH (1993) Prostaglandin E2-induced thermal hyperalgesia and its reversal by morphine in the warm-water tail-withdrawal procedure in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:1355–1363
Negus SS, Butelman ER, Gatch MB, Woods JH (1995) Effects of morphine and ketorolac on thermal allodynia induced by prostaglandin E2 and bradykinin in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:805–814
Negus SS, Gatch MB, Mello NK, Zhang X, Rice K (1998) Behavioral effects of the delta-selective opioid agonist SNC80 and related compounds in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:362–375
Obara I, Przewlocki R, Przewlocka B (2005) Spinal and local peripheral antiallodynic activity of Ro64-6198 in neuropathic pain in the rat. Pain 116:17–25
Raghavendra V, Tanga FY, DeLeo JA (2004) Attenuation of morphine tolerance, withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia, and associated spinal inflammatory immune responses by propentofylline in rats. Neuropsychopharmacol: Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 29:327–334
Reich A, Szepietowski JC (2010) Opioid-induced pruritus: an update. Clin Exp Dermatol 35:2–6
Sawynok J (2003) Topical and peripherally acting analgesics. Pharmacol Rev 55:1–20
Stanfa LC, Sullivan AF, Dickenson AH (1992) Alterations in neuronal excitability and the potency of spinal mu, delta and kappa opioids after carrageenan-induced inflammation. Pain 50:345–354
Stein C, Lang LJ (2009) Peripheral mechanisms of opioid analgesia. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:3–8
Stein C, Clark JD, Oh U, Vasko MR, Wilcox GL, Overland AC, Vanderah TW, Spencer RH (2009) Peripheral mechanisms of pain and analgesia. Brain Res Rev 60:90–113
Sukhtankar DD, Ko M-C (2013) Pharmacological investigation of NOP-related ligands as analgesics without abuse liability. In: Ko M-C, Husbands SM (eds) Research and development of opioid-related ligands. ACS, pp 393–416
Sukhtankar DD, Zaveri NT, Husbands SM, Ko MC (2013) Effects of spinally administered bifunctional nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide receptor/mu-opioid receptor ligands in mouse models of neuropathic and inflammatory pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 346:11–22
Wallace MS, Rowbotham M, Bennett GJ, Jensen TS, Pladna R, Quessy S (2002a) A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled crossover evaluation of a short course of 4030W92 in patients with chronic neuropathic pain. J Pain: Off J Am Pain Soc 3:227–233
Wallace MS, Rowbotham MC, Katz NP, Dworkin RH, Dotson RM, Galer BS, Rauck RL, Backonja MM, Quessy SN, Meisner PD (2002b) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a glycine antagonist in neuropathic pain. Neurology 59:1694–1700
Warner EA (2012) Opioids for the treatment of chronic noncancer pain. Am J Med 125:1155–1161
Watkins LR, Maier SF (2003) Glia: a novel drug discovery target for clinical pain. Nat Rev Drug Disc 2:973–985
Whiteside GT, Boulet JM, Walker K (2005) The role of central and peripheral mu opioid receptors in inflammatory pain and edema: a study using morphine and DiPOA ([8-(3,3-diphenyl-propyl)-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,3,8-triaza-spiro[4.5]dec-3-yl]-acetic acid). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314:1234–1240
Zhang X, Bao L, Arvidsson U, Elde R, Hokfelt T (1998) Localization and regulation of the delta-opioid receptor in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord of the rat and monkey: evidence for association with the membrane of large dense-core vesicles. Neuroscience 82:1225–1242
Acknowledgments
We thank Tristan Edwards and John Busenbark for technical assistance of data collection. Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases under Award number R01-AR-059193, and the National Institute on Drug Abuse under Award number R01-DA-032568. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Ethical Statement
The authors declare that the experiments comply with the current laws of the United States of America.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukhtankar, D.D., Lee, H., Rice, K.C. et al. Differential effects of opioid-related ligands and NSAIDs in nonhuman primate models of acute and inflammatory pain. Psychopharmacology 231, 1377–1387 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3341-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3341-0