Abstract
Rationale
NMDA antagonists consistently produce social inhibition in adult animals, although effects of these manipulations on social behavior of adolescents are relatively unknown.
Objectives
The aim of this study was to assess potential age differences in the socially inhibitory effects of the non-competitive NMDA antagonist, MK-801, as well as NR2 subunit selective effects, given the regional and developmental differences that exist for the NR2 subunit during ontogeny.
Methods
In separate experiments, adolescent and adult male Sprague–Dawley rats were treated acutely with MK-801 (0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2 mg/kg, i.p.), the NR2A antagonist, PEAQX (2.5, 5, 10, 20 mg/kg, s.c.), or the NR2B antagonist, ifenprodil (1.5, 3, 6, 12 mg/kg, i.p.), 10 min prior to a social interaction test.
Results
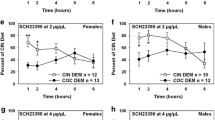
Adolescents required higher doses of MK-801 (0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg) to induce social suppression, whereas adults demonstrated reductions in social activity after all doses. Likewise, adolescents required higher doses of ifenprodil (6 and 12 mg/kg) to produce social inhibitory effects relative to adults (all doses). In contrast, adults were less sensitive to PEAQX than adolescents, with adults showing social inhibition after 20 mg/kg whereas adolescents showed this effect following 10 and 20 mg/kg. Although locomotor activity was generally reduced at both ages by all drugs tested, ANCOVAs using locomotor activity as a covariate revealed similar patterns of social inhibitory effects.
Conclusions
Adolescents are less sensitive than adults to the disruption of social behavior by NMDA and NR2B-selective receptor antagonism, but not by an NR2A antagonist—age differences that may be related to different subunit expression patterns during development.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allgaier C (2002) Ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptors. Neurochem Int 41:377–382
Anderson RI, Spear LP (2012) NMDA 2A and 2B receptor involvement in the discriminative stimulus properties of ethanol in adult male rats. Society for Neuroscience, New Orleans
Anderson RI, Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2010) Ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion in male Sprague–Dawley rats: impact of age and stress. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:2106–2115
Audet MC, Goulet S, Dore FY (2009) Impaired social motivation and increased aggression in rats subchronically exposed to phencyclidine. Physiol Behav 96:394–398
Berberich S, Punnakkal P, Jensen V, Pawlak V, Seeburg PH, Hvalby O, Kohr G (2005) Lack of NMDA receptor subtype selectivity for hippocampal long-term potentiation. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 25:6907–6910
Berndt TJ (1982) The features and effects of friendship in early adolescence. Child Dev 53:1447–1460
Bortolato M, Godar SC, Melis M, Soggiu A, Roncada P, Casu A, Flore G, Chen K, Frau R, Urbani A, Castelli MP, Devoto P, Shih JC (2012) NMDARs mediate the role of monoamine oxidase A in pathological aggression. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 32:8574–8582
Burton CL, Fletcher PJ (2012) Age and sex differences in impulsive action in rats: the role of dopamine and glutamate. Behav Brain Res 230:21–33
Carter CS (1998) Neuroendocrine perspectives on social attachment and love. Psychoneuroendocrinology 23:779–818
Csikszentmihalyi M, Larson R, Prescott S (1977) The ecology of adolescent activity and experience. J Youth Adolesc 6:281–294
de Moura Linck V, Herrmann AP, Goerck GC, Iwu MM, Okunji CO, Leal MB, Elisabetsky E (2008) The putative antipsychotic alstonine reverses social interaction withdrawal in mice. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1449–1452
Deutsch SI, Burket JA, Jacome LF, Cannon WR, Herndon AL (2011) d-Cycloserine improves the impaired sociability of the Balb/c mouse. Brain Res Bull 84:8–11
Domes G, Heinrichs M, Glascher J, Buchel C, Braus DF, Herpertz SC (2007) Oxytocin attenuates amygdala responses to emotional faces regardless of valence. Biol Psychiatry 62:1187–1190
Donaldson ZR, Young LJ (2008) Oxytocin, vasopressin, and the neurogenetics of sociality. Science 322:900–904
Eckardt MJ, File SE, Gessa GL, Grant KA, Guerri C, Hoffman PL, Kalant H, Koob GF, Li TK, Tabakoff B (1998) Effects of moderate alcohol consumption on the central nervous system. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:998–1040
File SE (1980) The use of social interaction as a method for detecting anxiolytic activity of chlordiazepoxide-like drugs. J Neurosci Methods 2:219–238
File SE, Hyde JR (1978) Can social interaction be used to measure anxiety? Br J Pharmacol 62:19–24
File SE, Seth P (2003) A review of 25 years of the social interaction test. Eur J Pharmacol 463:35–53
Frantz K, Van Hartesveldt C (1999) Locomotion elicited by MK801 in developing and adult rats: temporal, environmental, and gender effects. Eur J Pharmacol 369:145–157
Frizelle PA, Chen PE, Wyllie DJ (2006) Equilibrium constants for (R)-[(S)-1-(4-bromo-phenyl)-ethylamino]-(2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxalin-5 -yl)-methyl]-phosphonic acid (NVP-AAM077) acting at recombinant NR1/NR2A and NR1/NR2B N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors: implications for studies of synaptic transmission. Mol Pharmacol 70:1022–1032
Gururajan A, Taylor DA, Malone DT (2011) Effect of cannabidiol in a MK-801-rodent model of aspects of schizophrenia. Behav Brain Res 222:299–308
Haberny KA, Paule MG, Scallet AC, Sistare FD, Lester DS, Hanig JP, Slikker W Jr (2002) Ontogeny of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor system and susceptibility to neurotoxicity. Toxicol Sci Off J Soc Toxicol 68:9–17
Holstein SE, Spanos M, Hodge CW (2011) Adolescent C57BL/6J mice show elevated alcohol intake, but reduced taste aversion, as compared to adult mice: a potential behavioral mechanism for binge drinking. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:1842–1851
Jacobs SA, Tsien JZ (2012) Genetic overexpression of NR2B subunit enhances social recognition memory for different strains and species. PloS one 7:e36387
Jacome LF, Burket JA, Herndon AL, Deutsch SI (2011) d-Cycloserine enhances social exploration in the Balb/c mouse. Brain Res Bull 85:141–144
Kavaliers M, Choleris E (1997) Sex differences in N-methyl-d-aspartate involvement in kappa opioid and non-opioid predator-induced analgesia in mice. Brain Res 768:30–36
Knapp DJ, Overstreet DH, Moy SS, Breese GR (2004) SB242084, flumazenil, and CRA1000 block ethanol withdrawal-induced anxiety in rats. Alcohol 32:101–111
Kornhuber J, Retz W, Riederer P, Heinsen H, Fritze J (1988) Effect of antemortem and postmortem factors on [3H]glutamate binding in the human brain. Neurosci Lett 93:312–317
Labrie V, Lipina T, Roder JC (2008) Mice with reduced NMDA receptor glycine affinity model some of the negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 200:217–230
Liu XB, Murray KD, Jones EG (2004) Switching of NMDA receptor 2A and 2B subunits at thalamic and cortical synapses during early postnatal development. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 24:8885–8895
Lopez de Armentia M, Sah P (2003) Development and subunit composition of synaptic NMDA receptors in the amygdala: NR2B synapses in the adult central amygdala. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 23:6876–6883
Ma YY, Guo CY, Yu P, Lee DY, Han JS, Cui CL (2006) The role of NR2B containing NMDA receptor in place preference conditioned with morphine and natural reinforcers in rats. Exp Neurol 200:343–355
McDonald JW, Johnston MV (1990) Physiological and pathophysiological roles of excitatory amino acids during central nervous system development. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 15:41–70
Mirshahi T, Woodward JJ (1995) Ethanol sensitivity of heteromeric NMDA receptors: effects of subunit assembly, glycine and NMDAR1 Mg(2+)-insensitive mutants. Neuropharmacology 34:347–355
Montemayor R (1982) The relationship between parent-adolescent conflict and the amount of time adolescents spend alone and with parents and peers. Child Dev 53:1512–1519
Monyer H, Burnashev N, Laurie DJ, Sakmann B, Seeburg PH (1994) Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron 12:529–540
Morales M, Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2011) Age differences in the expression of acute and chronic tolerance to ethanol in male and female rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:1614–1624
Morales M, Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2013) Low doses of the NMDA receptor antagonists, MK-801, PEAQX, and ifenprodil, induces social facilitation in adolescent male rats. Behav Brain Res 250:18–22
Moy SS, Nonneman RJ, Shafer GO, Nikolova VD, Riddick NV, Agster KL, Baker LK, Knapp DJ (2012) Disruption of social approach by MK-801, amphetamine, and fluoxetine in adolescent C57BL/6J mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 36:36-46
Neyton J, Paoletti P (2006) Relating NMDA receptor function to receptor subunit composition: limitations of the pharmacological approach. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 26:1331–1333
Pellow S, File SE (1984) Multiple sites of action for anxiogenic drugs: behavioural, electrophysiological and biochemical correlations. Psychopharmacology 83:304–315
Ramirez RL, Spear LP (2010) Ontogeny of ethanol-induced motor impairment following acute ethanol: assessment via the negative geotaxis reflex in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 95:242–248
Ramirez RL, Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2011) Effect of the selective NMDA NR2B antagonist, ifenprodil, on acute tolerance to ethanol-induced motor impairment in adolescent and adult rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:1149–1159
Rung JP, Carlsson A, Ryden Markinhuhta K, Carlsson ML (2005) (+)-MK-801 induced social withdrawal in rats; a model for negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:827–832
Sanders SK, Shekhar A (1995a) Anxiolytic effects of chlordiazepoxide blocked by injection of GABAA and benzodiazepine receptor antagonists in the region of the anterior basolateral amygdala of rats. Biol Psychiatry 37:473–476
Sanders SK, Shekhar A (1995b) Regulation of anxiety by GABAA receptors in the rat amygdala. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 52:701–706
Schramm-Sapyta NL, DiFeliceantonio AG, Foscue E, Glowacz S, Haseeb N, Wang N, Zhou C, Kuhn CM (2010) Aversive effects of ethanol in adolescent versus adult rats: potential causes and implication for future drinking. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:2061–2069
Sheng M, Cummings J, Roldan LA, Jan YN, Jan LY (1994) Changing subunit composition of heteromeric NMDA receptors during development of rat cortex. Nature 368:144–147
Silveri MM, Spear LP (2002) The effects of NMDA and GABAA pharmacological manipulations on ethanol sensitivity in immature and mature animals. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:449–456
Silvestre JS, Nadal R, Pallares M, Ferre N (1997) Acute effects of ketamine in the holeboard, the elevated-plus maze, and the social interaction test in Wistar rats. Depress Anxiety 5:29–33
Siviy SM, Line BS, Darcy EA (1995) Effects of MK-801 on rough-and-tumble play in juvenile rats. Physiol Behav 57:843–847
Snigdha S, Neill JC (2008) Improvement of phencyclidine-induced social behaviour deficits in rats: involvement of 5-HT1A receptors. Behav Brain Res 191:26–31
Spear LP (2000) The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:417–463
Spear LP (2010) The behavioral neuroscience of adolescence. W. W. Norton & Company, New York
Sukhotina I, Dravolina O, Bespalov A (1998) Place conditioning of mice with the NMDA receptor antagonists, eliprodil and dizocilpine. Eur J Pharmacol 362:103–110
Trezza V, Damsteegt R, Achterberg EJ, Vanderschuren LJ (2011) Nucleus accumbens mu-opioid receptors mediate social reward. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 31:6362–6370
Turnock-Jones JJ, Jennings CA, Robbins MJ, Cluderay JE, Cilia J, Reid JL, Taylor A, Jones DN, Emson PC, Southam E (2009) Increased expression of the NR2A NMDA receptor subunit in the prefrontal cortex of rats reared in isolation. Synapse 63:836–846
Vanderschuren LJ, Niesink RJ, Spruijt BM, Van Ree JM (1995) Mu- and kappa-opioid receptor-mediated opioid effects on social play in juvenile rats. Eur J Pharmacol 276:257–266
Vanderschuren LJ, Niesink RJ, Van Ree JM (1997) The neurobiology of social play behavior in rats. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:309–326
Varlinskaya EI, Doremus-Fitzwater TL, Spear LP (2010) Repeated restraint stress alters sensitivity to the social consequences of ethanol in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96:228–235
Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2002) Acute effects of ethanol on social behavior of adolescent and adult rats: role of familiarity of the test situation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:1502–1511
Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2006) Differences in the social consequences of ethanol emerge during the course of adolescence in rats: social facilitation, social inhibition, and anxiolysis. Dev Psychobiol 48:146–161
Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2008) Social interactions in adolescent and adult Sprague–Dawley rats: impact of social deprivation and test context familiarity. Behav Brain Res 188:398–405
Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2009) Ethanol-induced social facilitation in adolescent rats: role of endogenous activity at mu opioid receptors. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:991–1000
Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2012) Increases in anxiety-like behavior induced by acute stress are reversed by ethanol in adolescent but not adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100:440–450
Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP, Spear NE (1999) Social behavior and social motivation in adolescent rats: role of housing conditions and partner's activity. Physiol Behav 67:475–482
Wenzel A, Fritschy JM, Mohler H, Benke D (1997) NMDA receptor heterogeneity during postnatal development of the rat brain: differential expression of the NR2A, NR2B, and NR2C subunit proteins. J Neurochem 68:469–478
Willey AR, Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2009) Social interactions and 50 kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in adolescent and adult rats. Behav Brain Res 202:122–129
Zhao X, Sun L, Jia H, Meng Q, Wu S, Li N, He S (2009) Isolation rearing induces social and emotional function abnormalities and alters glutamate and neurodevelopment-related gene expression in rats. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:1173–1177
Acknowledgements
The work presented in this manuscript was funded by grant P50-AA017823 to LPS
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morales, M., Spear, L.P. The effects of an acute challenge with the NMDA receptor antagonists, MK-801, PEAQX, and ifenprodil, on social inhibition in adolescent and adult male rats. Psychopharmacology 231, 1797–1807 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3278-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3278-3