Abstract
Rationale
Individuals vary in their susceptibility to nicotine addiction. However, there is little evidence that behavioral sensitivity to nicotine is dependent upon the functional state of nicotinic cholinergic receptors (nAChRs).
Objective
To determine the relationship between in vivo pharmacological desensitization (in other words, acute tolerance) and brain regional nAChR function.
Methods
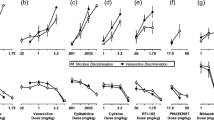
Male Sprague–Dawley rats, trained to discriminate nicotine (0.4 mg/kg free base) from saline in a two-lever drug discrimination task, were tested for the development of acute tolerance. Rats were injected with 0.4 mg/kg nicotine, tested for nicotine discrimination for 2 min, then injected with the same dose of nicotine 90 min, 180 min, and 270 min after the first injection and tested for nicotine discrimination after each injection. These subjects were separated into two groups, desensitizers (DZ) and nondesensitizers (NDZ), based upon performance in the repetitive dosing drug discrimination paradigm. The sensitivity of nAChRs in specific brain regions of these two groups was assessed by the use of an 86Rb+ efflux assay using synaptosomes prepared from the frontal cortex, hippocampus, striatum, and “thalamus,” which included the midbrain and hypothalamus as well as the thalamus.
Results
The nicotine-induced increase in 86Rb+ efflux was significantly greater in NDZ as compared to DZ in the “thalamus.” There was no statistically significant difference in the effects of nicotine in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, and striatum of these two groups. A significant correlation was observed between thalamic 86Rb+ efflux and the rate of behavioral desensitization of individual rats.
Conclusion
These findings are consistent with the concept that the production of acute tolerance by nicotine in vivo correlates directly with its ability to induce nAChR desensitization at the cellular level.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bliss CI (1967) Statistics in biology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Damaj MI, Welch SP, Martin BR (1996) Characterization and modulation of acute tolerance to nicotine in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:454–461
Dobelis P, Marks MJ, Whiteaker P, Balogh SA, Collins AC, Stitzel JA (2002) A polymorphism in the mouse neuronal α4 nicotinic receptor subunit results in an alteration in receptor function. Mol Pharmacol 62:334–342
Fenster CP, Whitworth TL, Sheffield EB, Quick MW, Lester RAJ (1999) Upregulation of surface α4β2 nicotinic receptors is initiated by receptor desensitization after chronic exposure to nicotine. J Neurosci 19:4804–4814
Hirschhorn ID, Rosecrans JA (1974) Studies on the time course and the effect of cholinergic and adrenergic receptor blockers on the stimulus effect of nicotine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl) 40:109–120
Hulihan-Giblin BA, Lumpkin MD, Kellar KJ (1990) Acute effects of nicotine on prolactin release in the rat: agonist and antagonist effects of a single injection of nicotine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:15–20
James JR, Villanueva HF, Johnson JH, Arezo S, Rosecrans JA (1994) Evidence that nicotine can acutely desensitize central nicotinic acetylcholinergic receptors. Psychopharmacology 114:456–462
Katz B, Thesleff S (1957) A study of the ‘desensitization’ produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol (Lond) 138:63–80
Marks MJ, Burch JB, Collins AC (1983) Effects of chronic nicotine infusion on tolerance development and cholinergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:806–816
Marks MJ, Farnham DA, Grady SR, Collins AC (1993a) Nicotinic receptor function determined by stimulation of rubidium efflux from mouse brain synaptosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:542–552
Marks MJ, Grady SR, Collins AC (1993b) Downregulation of nicotinic receptor function after chronic nicotine infusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:1268–1276
Marks MJ, Grady SR, Yang JM, Lippiello PM, Collins AC (1994) Desensitization of nicotine-stimulated 86Rb+ efflux from mouse brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem 63:2125–2135
Meltzer LT, Rosecrans JA (1981) Investigations on the CNS sites of action of the discriminative stimulus effects of arecoline and nicotine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:21–26
Miyata H, Ando K, Yanagita T (2002) Brain regions mediating the discriminative stimulus effects of nicotine in rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci 965:354–363
Mohammed AH (2000) Genetic dissection of nicotine-related behaviour: a review of animal studies. Behav Brain Res 113:35–41
Nishizaki T (2003) N-glycosylation sites on the nicotinic ACh receptor subunits regulate receptor channel desensitization and conductance. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 114:172–176
Nordberg A, Wahlstrom G, Arnelo U, Larsson C (1985) Effect of long-term nicotine treatment on [3H]nicotine binding sites in the rats brain. Drug Alcohol Depend 16:9–17
Ochoa ELM, Chattopadhyay A, McNamee MG (1989) Desensitization of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: molecular mechanisms and effect of modulators. Cell Mol Neurobiol 9:141–178
Perkins KA, Grobe JE, Fonte C, Goettler J, Caggiula AR, Reynolds WA, Stiller RL, Scierka A, Jacob RG (1994) Chronic and acute tolerance to subjective, behavioral and cardiovascular effects of nicotine in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:628–638
Perkins KA, Grobe JE, Mitchell SL, Goettler J, Caggiula A, Stiller RL, Scierka A (1995) Acute tolerance to nicotine in smokers: lack of dissipation within 2 hours. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 118:164–170
Pomerleau OF, Collins AC, Shiffman S, Pomerleau CS (1993) Why some people smoke and others do not: new perspectives. J Consult Clin Psychol 61:723–731
Quick MW, Lester RAJ (2002) Desensitization of neuronal nicotinic receptors. J Neurobiol 53:457–478
Rosecrans JA, Villanueva HF (1991) Discriminative stimulus properties of nicotine: mechanisms of transduction. NIDA Res Monogr 116:101–116
Rosecrans JA, Karan LD (1993) Neurobehavioral mechanisms of nicotine action: role in the initiation and maintenance of tobacco dependence. J Subst Abuse Treat 10:161–170
Rosecrans JA, Stimler CA, Hendry JS, Meltzer LT (1989) Nicotine-induced tolerance and dependence in rats and mice: studies involving schedule-controlled behavior. Prog Brain Res 79:239–248
Rosecrans JA, Wiley JL, Bass CE, Karan LD (1995) Nicotine-induced acute tolerance: studies involving schedule-controlled behavior. Brain Res Bull 37:359–362
Rowell PP, Hillebrand JA (1994) Characterization of nicotine-induced desensitization of evoked dopamine release from rat striatal synaptosomes. J Neurochem 63:561–569
Schwartz RD, Kellar KJ (1985) In vivo regulation of [3H]acetylcholine recognition sites in brain by nicotinic cholinergic drugs. J Neurochem 45:427–433
Sharp BM, Beyer HS (1986) Rapid desensitization of the acute stimulatory effects of nicotine on rat plasma adrenocorticotropin and prolactin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238:486–491
Shoaib M, Stolerman IP (1996) Brain sites mediating the discriminative stimulus effects of nicotine in rats. Behav Brain Res 78:183–188
Stolerman IP, Shoaib M (1991) The neurobiology of nicotine addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:467–473
Stolerman IP, Fink R, Jarvik ME (1973) Acute and chronic tolerance to nicotine measured by activity in rats. Psychopharmacologia 30:329–342
Tallarida RJ, Murray RB (1986) Manual of pharmacology calculations with computer programs. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Wiley JL, James JR, Rosecrans JA (1996) Discriminative stimulus properties of nicotine: approaches to evaluating potential nicotinic agonists and antagonists. Drug Dev Res 38:222–230
Zhang X, Paterson D, James R, Gong ZH, Rosecrans J, Nordberg A (2000) Rats exhibiting acute behavioral tolerance to nicotine have more [125I]alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites in brain than rats not exhibiting tolerance. Behav Brain Res 113:105–115
Zoli M, Léna C, Picciotto MR, Changeux JP (1998) Identification of four classes of brain nicotinic receptors using β2-mutant mice. J Neurosci 18:4461–4472
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Michael J. Marks for his invaluable assistance in establishing the 86Rb+ efflux assay in our laboratory. We also thank Dr. Peter Rowell for his loan of equipment for the 86Rb+ efflux assays and Dr. Forrest Smith for his assistance in the determination of ED50 values. The experiments described within this publication are all in compliance with the laws of the USA. Research described in this article was supported by Philip Morris USA Inc. and Philip Morris International.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, S.E., James, J.R., Lapp, L.N. et al. Evidence of cellular nicotinic receptor desensitization in rats exhibiting nicotine-induced acute tolerance. Psychopharmacology 184, 306–313 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0049-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0049-9