Abstract.
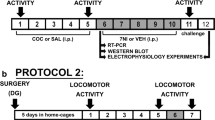
Rationale: Inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) have been shown to alter behaviors related to cocaine addiction, including its self-administration. However, previous studies have largely used mixed-action NOS inhibitors and have not examined the effects of a neuronal NOS inhibitor on cocaine self-administration. Objectives: Pretreatment with the neuronal NOS inhibitor 7-nitroindazole (7-NI) was used and its effects on cocaine self-administration were compared with those produced by pretreatment with an indirect dopamine receptor agonist (cocaine) and a D1-like dopamine receptor antagonist (SCH 23390). Methods: Rats were trained to self-administer 1 mg/kg cocaine under a second-order schedule of drug delivery, which measures drug-seeking behavior independently from drug intake. Pretreatment with various doses of 7-NI, cocaine, and SCH 23390 were tested in combination with the training dose of cocaine followed by studies examining the effects of a selected dose of each pretreatment drug in combination with a range of cocaine doses. Other rats were trained under a second-order schedule of food pellet delivery and pretreated with 7-NI, cocaine, or SCH 23390 to determine the behavioral specificity of the effects of these drugs for cocaine-maintained responding. Results: The results demonstrated that 7-NI reduced responses maintained by the cocaine training dose and produced a downward shift in the cocaine dose–response curve. Changes in drug intake were minor by comparison. Cocaine pretreatment produced effects similar to 7-NI, while the changes observed after SCH 23390 pretreatment were different from 7-NI and cocaine. The reductions in cocaine-maintained responding after 7-NI pretreatment were behaviorally specific because there was no effect of 7-NI on food-maintained responding within the dose range examined. Conclusions: By selectively reducing drug-seeking behavior, these data suggest that 7-NI may enhance the reinforcing effects of cocaine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collins, S.L., Kantak, K.M. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition decreases cocaine self-administration behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 159, 361–369 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-001-0935-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-001-0935-8