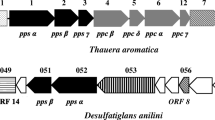
Abstract
Anaerobic phenol metabolism was studied in three facultative aerobic denitrifying bacteria, Thauera aromatica, “Aromatoleum aromaticum” strain EbN1 (Betaproteobacteria), and Magnetospirillum sp. (Alphaproteobacterium). All species formed phenylphosphate and contained phenylphosphate carboxylase but not phenol carboxylase activity. This is in contrast to direct phenol carboxylation by fermenting bacteria. Antisera raised against subunits of the Thauera phenylphosphate synthase and phenylphosphate carboxylase partly cross-reacted with the corresponding proteins in the other species. Some unsolved features of phenylphosphate carboxylase were addressed in T. aromatica. The core sub-complex of this enzyme consists of three different subunits and catalyzes the exchange of 14CO2 with the carboxyl group of 4-hydroxybenzoate, but not phenylphosphate carboxylation. It was inactivated by oxygen or by the oxidizing agent thionin and fully reactivated under reducing conditions. The purified recombinant phosphatase subunit alone had only low phenylphosphate phosphatase activity in the absence of the other components. However, activity was strongly enhanced in the presence of the core enzyme resulting in phenylphosphate carboxylation. Hence, a tight interaction of the carboxylase subunits is required for dephosphorylation of phenylphosphate, which is coupled to the concomitant carboxylation of the produced phenolate to 4-hydroxybenzoate, thus preventing a futile cycle.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders HJ, Kaetzke A, Kämpfer P, Ludwig W, Fuchs G (1995) Taxonomic position of aromatic-degrading denitrifying Pseudomonas strains K 172 and KB 740 and their description as new members of the genera Thauera, as Thauera aromatica sp. Nov., and Azoarcus, as Azoarcus evansii sp. nov., respectively, members of the beta subclass of the Proteobacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:327–333
Bak F, Widdel F (1986) Anaerobic degradation of phenol and phenol derivatives by Desulfobacterium phenolicum sp. nov. Arch Microbiol 146:177–180
Bertani G (1951) Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 62:293–300
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–252
Breinig S, Schiltz E, Fuchs G (2000) Genes involved in anaerobic metabolism of phenol in the bacterium Thauera aromatica. J Bacteriol 182:5849–5863
Chow KT, Pope MK, Davies J (1999) Characterization of a vanillic acid non-oxidative decarboxylation gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. D7. Microbiology 145:2393–2403
Fuchs G (2008) Anaerobic metabolism of aromatic compounds. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1125:82–99
Harwood CS, Parales RE (1996) The beta-ketoadipate pathway and the biology of self-identity. Annu Rev Microbiol 50:553–590
Hayaishi O (1994) Tryptophan, oxygen, and sleep. Annu Rev Biochem 63:1–24
He Z, Wiegel J (1995) Purification and characterization of an oxygen-sensitive reversible 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from Clostridium hydroxybenzoicum. Eur J Biochem 229:77–82
He Z, Wiegel J (1996) Purification and characterization of an oxygen-sensitive, reversible 3, 4-dihydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from Clostridium hydroxybenzoicum. J Bacteriol 178:3539–3543
Howard JL, Ridley SM (1990) Acetyl-CoA carboxylase: a rapid novel assay procedure used in conjunction with the preparation of enzyme from maize leaves. FEBS Lett 261:261–264
Huang J, He Z, Wiegel J (1999) Cloning, characterization, and expression of a novel gene encoding a reversible 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from Clostridium hydroxybenzoicum. J Bacteriol 181:5119–5122
Khanna P, Rajkumar B, Jothikumar N (1992) Anoxygenic degradation of aromatic substances by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Curr Microbiol 25:63–67
Kosugi Y, Imaoka Y, Gotoh F, Rahim MA, Matsui Y, Sakanishi K (2003) Carboxylations of alkali metal phenoxides with carbon dioxide. Org Biomol Chem 1:817–821
Kuever J, Kulmer J, Jannsen S, Fischer U, Blotevogel KH (1993) Isolation and characterization of a new spore-forming sulfate-reducing bacterium growing by complete oxidation of catechol. Arch Microbiol 159:282–288
Lack A, Fuchs G (1992) Carboxylation of phenylphosphate by phenol carboxylase, an enzyme system of anaerobic phenol metabolism. J Bacteriol 174:3629–3636
Lack A, Fuchs G (1994) Evidence that phenol phosphorylation to phenylphosphate is the first step in anaerobic phenol metabolism in a denitrifying Pseudomonas sp. Arch Microbiol 161:132–139
Lack A, Tommasi I, Aresta M, Fuchs G (1991) Catalytic properties of phenol carboxylase. In vitro study of CO2: 4-hydroxybenzoate isotope exchange reaction. Eur J Biochem 197:473–479
Lämmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Leppik RA, Young IG, Gibson F (1976) Membrane-associated reactions in ubiquinone biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. 3-Octaprenyl-4-hydroxybenzoate carboxy-lyase. Biochim Biophys Acta 436:800–810
Li T, Juteau P, Beaudet R, Lepine F, Villemur R, Bisaillon JG (2000) Purification and characterization of a 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from an anaerobic coculture. Can J Microbiol 46:856–859
Liu J, Zhang X, Zhou S, Tao P, Liu J (2007) Purification and characterization of a 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from Chlamydophila pneumoniae AR39. Curr Microbiol 54:102–107
Lovley DR, Lonergan DJ (1990) Anaerobic oxidation of toluene, phenol, and p-cresol by the dissimilatory iron-reducing organism, GS-15. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1858–1864
Lupa B, Lyon D, Gibbs MD, Reeves RA, Wiegel J (2005) Distribution of genes encoding the microbial non-oxidative reversible hydroxyarylic acid decarboxylases/phenol carboxylases. Genomics 86:342–351
Lupa B, Lyon D, Shaw LN, Sieprawska-Lupa M, Wiegel J (2008) Properties of the reversible nonoxidative vanillate/4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol 54:75–81
Matsui T, Yoshida T, Hayashi T, Nagasawa T (2006) Purification, characterization, and gene cloning of 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase of Enterobacter cloacae P240. Arch Microbiol 186:21–29
Meganathan R (2001) Ubiquinone biosynthesis in microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 203:131–139
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Narmandakh A, Gad’on N, Drepper F, Knapp B, Haehnel W, Fuchs G (2006) Phosphorylation of phenol by phenylphosphate synthase: role of histidine phosphate in catalysis. J Bacteriol 188:7815–7822
Rabus R, Widdel F (1995) Anaerobic degradation of ethylbenzene and other aromatic hydrocarbons by new denitrifying bacteria. Arch Microbiol 163:96–103
Rabus R, Kube M, Heider J, Beck A, Heitmann K, Widdel F, Reinhardt R (2005) The genome sequence of an anaerobic aromatic-degrading denitrifying bacterium, strain EbN1. Arch Microbiol 183:27–36
Schleinitz KM, Schmeling S, Jehmlich N, von Bergen M, Harms H, Kleinsteuber S, Vogt C, Fuchs G (2009) Phenol degradation in the strictly anaerobic iron reducing bacterium Geobacter metallireducens GS-15. Appl Envir Microbiol 75:3912–3919
Schmeling S, Narmandakh A, Schmitt O, Gad’on N, Schühle K, Fuchs G (2004) Phenylphosphate synthase: a new phosphotransferase catalyzing the first step in anaerobic phenol metabolism in Thauera aromatica. J Bacteriol 186:8044–8057
Schühle K, Fuchs G (2004) Phenylphosphate carboxylase: a new C–C lyase involved in anaerobic phenol metabolism in Thauera aromatica. J Bacteriol 186:4556–4567
Shinoda Y, Sakai Y, Ue M, Hiraishi A, Kato N (2000) Isolation and characterization of a new denitrifying spirillum capable of anaerobic degradation of phenol. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1286–1291
Solyanikova IP, Golovleva LA (1999) Phenol hydroxylases: an update. Biochemistry (Mosc) 64:365–372
Tschech A, Fuchs G (1987) Anaerobic degradation of phenol by pure cultures of newly isolated denitrifying pseudomonads. Arch Microbiol 148:213–217
Tschech A, Fuchs G (1989) Anaerobic degradation of phenol via carboxylation to 4-hydroxybenzoate: in vitro study of isotope exchange between 14CO2 and 4-hydroxybenzoate. Arch Microbiol 152:594–599
van Schie PM, Young LY (1998) Isolation and characterization of phenol-degrading denitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2432–2438
Wöhlbrand L, Kallerhoff B, Lange D, Hufnagel P, Thiermann J, Reinhardt R, Rabus R (2007) Functional proteomic view of metabolic regulation in “Aromatoleum aromaticum” strain EbN1. Proteomics 7:2222–2239
Zehr BD, Savin TJ, Hall RE (1989) A one-step, low-background Commassie staining procedure for polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 182:157–159
Zhang X, Wiegel J (1990) Sequential anaerobic degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1119–1127
Zhang X, Wiegel J (1992) The anaerobic degradation of 3-chloro-4-hydroxybenzoate in freshwater sediment proceeds via either chlorophenol or hydroxybenzoate to phenol and subsequently to benzoate. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3580–3585
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) and by the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie. Thanks are due to Karola Schühle for invaluable advices and help concerning the purification of phenylphosphate carboxylase. Magnetospirillum sp. strain CC-26 was a gift from Yoshifumi Shinoda. His advices concerning the cultivation of this strain are thankfully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Wolfgang Buckel.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmeling, S., Fuchs, G. Anaerobic metabolism of phenol in proteobacteria and further studies of phenylphosphate carboxylase. Arch Microbiol 191, 869–878 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-009-0519-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-009-0519-2