Abstract
Key message
Two novel QTLs conferring aphid resistance were mapped and validated on soybean chromosomes 8 and 16, respectively. Closely linked markers were developed to assist breeding for aphid resistance.
Abstract
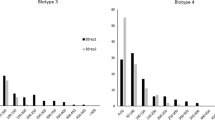
Soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura, is a highly destructive pest for soybean production. E08934, a soybean advanced breeding line derived from the wild soybean Glycine soja 85-32, has shown strong resistance to aphids. To dissect the genetic basis of aphid resistance in E08934, a mapping population (070020) consisting of 140 F3-derived lines was developed by crossing E08934 with an aphid-susceptible line E00003. This mapping population was evaluated for aphid resistance in a greenhouse trial in 2010 and three field trials in 2009, 2010, and 2011, respectively. The broad-sense heritability across the field trials was 0.84. In the mapping population 070020, two major quantitative trait loci (QTL) were detected as significantly associated with aphid resistance, and designated as Rag6 and Rag3c, respectively. Rag6 was mapped to a 10.5 centiMorgan (cM) interval between markers MSUSNP08-2 and Satt209 on chromosome 8, explaining 19.5–46.4% of the phenotypic variance in different trials. Rag3c was located at a 7.5 cM interval between markers MSUSNP16-10 and Sat_370 on chromosome 16, explaining 12.5–22.9% of the phenotypic variance in different trials. Rag3c had less resistance effect than Rag6 across all the trials. Furthermore, Rag6 and Rag3c were confirmed in two validation populations with different genetic backgrounds. No significant interaction was detected between Rag6 and Rag3c in either the mapping population or the validation populations. Both Rag6 and Rag3c were indicated as conferring antibiosis resistance to aphids by a no-choice test. The new aphid-resistance gene(s) derived from the wild germplasm G. soja 85-32 are valuable in improving soybeans for aphid resistance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akond M, Liu S, Schoener L, Anderson JA, Kantartzi SK, Meksem K, Song Q, Wang D, Wen Z, Lightfoot DA, Kassem MA (2013) A SNP-based genetic linkage map of soybean using the SoySNP6K Illumina Infinium BeadChip genotyping array. J Plant Genome Sci 1:80–89
Alt J, Ryan-Mahmutagic M (2013) Soybean aphid biotype 4 identified. Crop Sci 53(4):1491–1495
Bales C (2013) Fine mapping of aphid resistance genes in soybean plant introduction (PI) 567598B. Dissertation, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI
Bales C, Zhang G, Liu M, Mensah C, Gu C, Song Q, Hyten D, Cregan P, Wang D (2013) Mapping soybean aphid resistance genes in PI 567598B. Theor Appl Genet 126:2081–2091
Clark AJ, Perry KL (2002) Transmissibility of field isolates of soybean viruses by Aphis glycines. Plant Dis 86(11):1219–1222
Cooper SG, Concibido V, Estes R, Hunt D, Jiang GL, Krupke C, McCornack B, Mian R, O’Neal M, Poysa V, Prischmann-Voldseth D (2015) Geographic distribution of soybean aphid biotypes in the US and Canada during 2008–2010. Crop Sci 55(6):2598–2608
Development Core Team R (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Fehr WR (1987) Principles of cultivar development. Theory and technique, vol I. Iowa State University, Iowa
Fehr WR, Cavinese CE (1977) Stages of soybean development. Special Report, Agriculture and Home Economics Experiment Station, Iowa State University, issue 80:11
Grant D, Nelson RT, Cannon SB, Shoemaker RC (2010) SoyBase, the USDA-ARS soybean genetics and genomics database. Nucl Acids Res 38:D843–D846. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp798
Hartman GL, Domier LL, Wax LM, Helm CG, Onstad DW, Shaw JT, Solter LF, Voegtlin DJ, d’Arcy CJ, Gray ME, Steffey KL (2001) Occurrence and distribution of Aphis glycines on soybeans in Illinois in 2000 and its potential control. Plant Health Progr. doi:10.1094/PHP-2001-0205-01-HN
Hill JH, Alleman R, Hogg DB, Grau CR (2001) First report of transmission of Soybean mosaic virus and Alfalfa mosaic virus by Aphis glycines in the New World. Plant Dis 85(5):561
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2004a) Resistance to the soybean aphid in soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 44(1):98–106
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2004b) Resistance of Glycine species and various cultivated legumes to the soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 97:1071–1077
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2006a) A single dominant gene for resistance to the soybean aphid in the soybean cultivar Dowling. Crop Sci 46(4):1601–1605
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2006b) Soybean aphid resistance in soybean Jackson is controlled by a single dominant gene. Crop Sci 46(4):1606–1608
Hill CB, Kim KS, Crull L, Diers BW, Hartman GL (2009) Inheritance of resistance to the soybean aphid in soybean PI 200538. Crop Sci 49(4):1193–1200
Hill CB, Crull L, Herman TK, Voegtlin DJ, Hartman GL (2010) A new soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) biotype identified. J Econ Entomol 103:509–515
Huynh BL, Ehlers JD, Ndeve A, Wanamaker S, Lucas MR, Close TJ, Roberts PA (2015) Genetic mapping and legume synteny of aphid resistance in African cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) grown in California. Mol Breed 35(1):36
Jun TH, Mian MAR, Michel AP (2012) Genetic mapping revealed two loci for soybean aphid resistance in PI 567301B. Theor Appl Genet 124:13–22
Kang ST, Mian MAR, Hammond RB (2008) Soybean aphid resistance in PI 243540 is controlled by a single dominant gene. Crop Sci 48(5):1744–1748
Kim KS, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Mian MA, Diers BW (2008) Discovery of soybean aphid biotypes. Crop Sci 48(3):923–928
Kim KS, Bellendir S, Hudson KA, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Hyten DL, Hudson ME, Diers BW (2010a) Fine mapping the soybean aphid resistance gene Rag1 in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 120:1063–1071
Kim KS, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Hyten DL, Hudson ME, Diers BW (2010b) Fine mapping of the soybean aphid-resistance gene Rag2 in soybean PI 200538. Theor Appl Genet 121:599–610
Kisha TJ, Sneller CH, Diers BW (1997) Relationship between genetic distance among parents and genetic variance in populations of soybean. Crop Sci 37(4):1317–1325
Li Y, Hill CB, Carlson SR, Diers BW, Hartman GL (2007) Soybean aphid resistance genes in the soybean cultivars Dowling and Jackson map to linkage group M. Mol Breed 19:25–34
Marone D, Russo MA, Laidò G, De Leonardis AM, Mastrangelo AM (2013) Plant nucleotide binding site—leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes: active guardians in host defense responses. Int J Mol Sci 14(4):7302–7326
Meng F, Han Y, Teng W, Li Y, Li W (2011) QTL underlying the resistance to soybean aphid (Aphis glycines Matsumura) through isoflavone-mediated antibiosis in soybean cultivar “Zhongdou 27”. Theor Appl Genet 123:1459–1465
Mensah C, DiFonzo C, Nelson RL, Wang D (2005) Resistance to soybean aphid in early maturing soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 45:2228–2233
Mensah C, DiFonzo C, Wang D (2008) Inheritance of soybean aphid resistance in PI 567541B and PI 567598B. Crop Sci 48:1759–1763
Mian MA, Hammond RB, St Martin SK (2008a) New plant introductions with resistance to the soybean aphid. Crop Sci 48(3):1055–1061
Mian MAR, Kang ST, Beil SE, Hammond RB (2008b) Genetic linkage mapping of the soybean aphid resistance gene in PI243540. Theor Appl Genet 117:955–962
Michel AP, Mian MR, Davila-Olivas NH, Cañas LA (2010) Detached leaf and whole plant assays for soybean aphid resistance: differential responses among resistance sources and biotypes. J Econ Entomol 103(3):949–957
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis—a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88:9828–9832
Ohnesorg WJ, Johnson KD, O’Neal ME (2009) Impact of reduced risk insecticides on soybean aphid and their natural enemies. J Econ Entomol 102:1816–1826
Painter RH (1951) Insect resistance in crop plants. Macmillan, New York
Ragsdale DW, McCornack BP, Venette RC, Potter BD, MacRae IV, Hodgson EW, O’Neal ME, Johnson KD, O’neil RJ, DiFonzo CD, Hunt TE (2007) Economic threshold for soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 100:1258–1267
Ragsdale DW, Landis DA, Brodeur J, Heimpel GE, Desneux N (2011) Ecology and management of the soybean aphid in North America. Annu Rev Entomol 56:375–399
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song Q, Thelen JJ, Cheng J, Xu D, Hellsten U, May GD, Yu Y, Sakurai T, Umezawa T, Bhattacharyya MK, Sandhu D, Valliyodan B, Lindquist E, Peto M, Grant D, Shu S, Goodstein D, Barry K, Futrell-Griggs M, Abernathy B, Du J, Tian Z, Zhu L, Gill N, Joshi T, Libault M, Sethuraman A, Zhang X, Shinozaki K, Nguyen HT, Wing RA, Cregan P, Specht J, Grimwood J, Rokhsar D, Stacey G, Shoemaker RC, Jackson SA (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Singh RJ (ed) (2006) Genetic resources, chromosome engineering, and crop improvement: vegetable crops, vol 3. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Song Q, Jia G, Zhu Y, Grant D, Nelson RT, Hwang EY, Hyten DL, Cregan PB (2010) Abundance of SSR motifs and development of candidate polymorphic SSR markers (BARCSOYSSR_1. 0) in soybean. Crop Sci 50(5):1950–1960
Song Q, Hyten DL, Jia G, Quigley CV, Fickus EW, Nelson RL, Cregan PB (2013) Development and evaluation of SoySNP50K, a high-density genotyping array for soybean. PLoS One 8(1):E54985. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054985
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap® 4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Heredity 93(1):77–78
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Dept of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm. Assessed Aug 2012
Wu Z, Schenk-Hamlin D, Zhan W, Ragsdale DW, Heimpel GE (2004) The soybean aphid in China: a historical review. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97(2):209–218
Xiao L, Hu Y, Wang B, Wu T (2013) Genetic mapping of a novel gene for soybean aphid resistance in soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) line P203 from China. Theor Appl Genet 126:2279–2287
Yang Z, Honda K, Wang S, Ma X (2004) Re-evaluation of Glycine soja germplasm from north eastern China for aphid resistance. J Jilin Agric Sci 29(5):3–6
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2009) Molecular mapping of soybean aphid resistance genes in PI 567541B. Theor Appl Genet 118:473–482
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2010) A novel locus for soybean aphid resistance. Theor Appl Genet 120:1183–1191
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2013) Mapping and validation of a gene for soybean aphid resistance in PI 567537. Mol Breed 32:131–138
Zhang Z, Hao J, Yuan J, Song Q, Hyten DL, Cregan PB, Zhang G, Gu C, Li M, Wang D (2014) Phytophthora root rot resistance in soybean E00003. Crop Sci 54(2):492–499
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by United Soybean Board and Michigan Soybean Promotion Committee. We thank Paul Collins, Zixiang Wen, Feng Lin, Shair Wani, Ruijuan Tan and Sean Biehn for critical review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
This work complies with the current laws of the USA.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest for this study.
Additional information
Communicated by Matthew N Nelson.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2017_2935_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 1 Average damage indices (DI, %) of four indicator lines and two parental lines of the mapping population 070020 in a 2009 field trial; b 2010 field trial; c 2011 field trial. Bars with the same letter are not significantly different at P < 0.05 (TIFF 82 kb)
122_2017_2935_MOESM4_ESM.tif
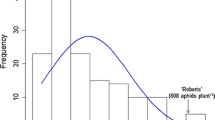
Supplementary Fig. 2 Phenotypic distribution of soybean aphid rating score of individual plants from the validation population 110193 (a-b) and the validation population 110201(c-d). Average rating scores of parents are indicated by arrows. a 3-week rating of population 110193; b 4-week rating of population 110193; c 3-week rating of population 110201; d 4-week rating of population 110201 (TIFF 72 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhang, Z., Bales, C. et al. Mapping novel aphid resistance QTL from wild soybean, Glycine soja 85-32. Theor Appl Genet 130, 1941–1952 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2935-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2935-z