Abstract
Key message
This manuscript provides genome-level analysis of disease resistance genes in four maize lines, including studies of haplotype and resistance gene number as well as selection and recombination.
Abstract
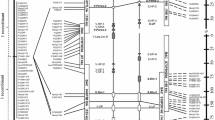
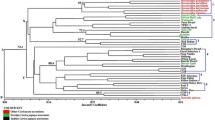
The Rp1 locus of maize is a complex resistance gene (R-gene) cluster that confers race-specific resistance to Puccinia sorghi, the causal agent of common leaf rust. Rp1 NB-LRR disease resistance genes were isolated from two Rp1 haplotypes (HRp1-B and HRp1-M) and two maize inbred lines (B73 and H95). Sixty-one Rp1 genes were isolated from Rp1-B, Rp1-M, B73 and H95 with a PCR-based approach. The four maize lines carried from 12 to 19 Rp1 genes. From 4 to 9 of the identified Rp1 genes were transcribed in the four maize lines. The Rp1 gene nucleotide diversity was higher in HRp1-B and HRp1-M than in B73 and H95. Phylogenic analysis of 69 Rp1 genes revealed that the Rp1 genes maintained in HRp1-B, HRp1-M and H95 are evolving independently of each other, while Rp1 genes in B73 and HRp1-D appear more like each other than they do genes in the other lines. The results also revealed that the analysed Rp1 R-genes were under positive selection in HRp1-M and B73. Intragenic recombination was detected in Rp1 genes maintained in the four maize lines. This demonstrates that a genetic process that has the potential to generate new resistance genes with new specificities is active at the Rp1 locus in the four analysed maize lines and that the new resistance genes may act against newly arising pathogen races that become prevalent in the pathogen population.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayliffe MA, Collins NC, Ellis JG, Pryor A (2000) The maize Rp1 rust resistance genes identifies homologues in barley that have been subject to diversifying selection. Theor Appl Genet 100:1144–1154
Ayliffe MA, Steinau M, Park RF, Rooke L, Pacheco MG et al (2004) Aberrant mRNA processing of the maize Rp1-D rust resistance gene in wheat and barley. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:853–864
Baurens FC, Bocs S, Rouard M, Matsumoto T, Miller R et al (2010) Mechanisms of haplotype divergence at the RGA08 nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat gene locus in wild banana (Musa balbisiana). BMC Plant Biol 10 PMC3017797
Bent A (1996) Plant disease resistance genes: function meets structure. Plant Cell 8:1757–1771
Chin DB, Arroyo-Garcia R, Ochoa OE, Kesseli RV, Lavelle DO et al (2001) Recombination and spontaneous mutation at the major cluster of resistance genes in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Genetics 157:831–849
Clay K, Kover P (1996) Evolution and stasis in plant-pathogen associations. Ecology 77:997–1003
Collins N, Drake J, Ayliffe M, Sun Q, Ellis J et al (1999) Molecular characterization of the maize Rp1-D rust resistance haplotype and its mutants. Plant Cell 11:1365–1376
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Dixon MS, Hatzixanthis K, Jones DA, Harrison K, Jones JDG (1998) The tomato Cf-5 disease resistance gene and six homologs show pronounced allelic variation in leucine-rich repeat copy number. Plant Cell 10:1915–1925
Ellis JG, Lawrence GJ, Luck JE, Dodds PN (1999) Identification of regions in alleles of the flax rust resistance gene L that determine differences in gene-for- gene specificity. Plant Cell 11:495–506
Ellis J, Dodds P, Pryor T (2000) The generation of plant disease resistance gene specificities. Trends Plant Sci 5:373–379
Ewing B, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 8:186–194
Hagan WL, Hooker AL (1965) Genetics of reaction to Puccinia sorghi in eleven corn inbred lines from Central and South America. Phytopathology 55:193–197
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JDG (1997) Plant disease resistance genes. Annu Rev Plant Biol 48:575–607
Hooker AL, Russell WA (1962) Inheritance of resistance to Puccinia sorghi in six corn inbred lines. Phytopathology 52:122–128
Hu G, Hulbert SH (1996) Construction of ‘compound’ rust resistance genes in maize. Euphytica 87:45–51
Hudson RR, Kreitman M, Aguade M (1987) A test of neutral molecular evolution based on nucleotide data. Genetics 116:153–159
Hulbert SH (1997) Structure and evolution of the rp1 complex conferring rust resistance in maize. Annu Rev Phytopathol 35:293–310
Hulbert SH, Drake JA (2000) Rust-resistant sh2 sweet corn populations. Hortscience 35:145–146
Hulbert SH, Pumphrey M (2014) A time for more booms and less busts? Unraveling cereal-rust interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27:207–214
Hulbert SH, Hu G, Drake JA (1997) Kansas rust-resistant sweet corn populations A and B. Hortscience 32:1130–1131
Hulbert SH, Webb CA, Smith SM, Sun Q (2001) Resistance gene complexes: evolution and utilization. Annu Rev Phytopathol 39:285–312
Hurni S, Brunner S, Buchmann G, Herren G, Jordan T, Krukowski P, Wicker T, Yahiaoui N, Mango R, Keller B (2013) Rye Pm8 and wheat Pm3 are orthologous genes and show evolutionary conservation of resistance function against powdery mildew. Plant J 76:957–969
Jiang H, Wang C, Ping L, Tian D, Yang S (2007) Pattern of LRR nucleotide variation in plant resistance genes. Plant Sci 173:253–261
Joshi RK, Nayak S (2013) Perspectives of genomic diversification and molecular recombination towards R-gene evolution in plants. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19:1–9
Jullien PE, Berger F (2009) Gamete-specific epigenetic mechanisms shape genomic imprinting. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:637–642
Kobe B, Deisenhofer J (1995) Proteins with leucine-rich repeats. Curr Opin Struct Biol 5:409–416
Lawrence GJ, Morrish BC, Ayliffe MA, Finnegan EJ, Ellis JG (1997) Inactivation of the flax rust resistance gene M associated with loss of a repeated unit within the leucine-rich repeat coding region. Plant Cell 9:641–651
Leister RT, Katagiri F (2000) A resistance gene product of the nucleotide binding site-leucine rich repeats class can form a complex with bacterial avirulence proteins in vivo. Plant J 22:345–354
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Luck JE, Lawrence GL, Dodds PN, Shepherd KW, Ellis JG (2000) Regions outside of the leucine-rich repeats of flax rust resistance proteins play a role in specificity determination. Plant Cell 12:1367–1377
Meyers BC, Dickerman AW, Michelmore RW, Sivaramakrishnan S, Cobral BW, Young ND (1999) Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding superfamily. Plant J 20:317–332
Meyers BC, Kozik A, Griego A, Kuang H, Michelmore RW (2003) Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:809–834
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC (1998) Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res 8:1113–1130
Mondragón-Palomino M, Meyers BC, Michelmore RW, Gaut BS (2002) Patterns of positive selection in the complete NBS-LRR gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Res 12:1305–1315
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nagy ED, Bennetzen JL (2008) Pathogen corruption and site-directed recombination at a plant disease resistance gene cluster. Genome Res 18:1918–1923
Nei M (1987) Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Parniske M, Hammond-Kosack KE, Golstein C, Thomas CM, Jones DA et al (1997) Novel disease resistance specificities result from sequence exchange between tandemly repeated genes at the Cf-4/9 locus of tomato. Cell 91:821–832
Pryor T (1987) The orgin and structure of fungal disease resistance genes in maize. Trends Genet 3:157–161
Ramakrishna W, Emberton J, Ogden M, SanMiguel P, Bennetzen JL (2002) Structural analysis of the maize Rp1 complex reveals numerous sites and unexpected mechanisms of local rearrangement. Plant Cell 14:3213–3223
Richter TE, Pryor TJ, Bennetzen JL, Hulbert SH (1995) New rust resistance specificities associated with recombination in the rp1 complex in maize. Genetics 141:373–381
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Saxena KMS, Hooker AL (1968) On the structure of a gene for disease resistance in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 61:1300
Sela H, Cheng J, Jun Y, Nevo E, Fahima T (2009) Divergent diversity patterns of NBS and LRR domains of resistance gene analogs in wild emmer wheat populations. Genome 52:557–565
Smith SM, Hulbert SH (2003) Evolution of disease resistance genes. In: Tsuyuma S, Leach J, Wolpert T (eds) Genomics and genetic analysis of plant parasitism and defense. APS Press
Smith S, Hulbert SH (2005) Recombination events generating a novel Rp1 race specificity. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:220–228
Smith S, Pryor A, Hulbert SH (2004) Allelic and haplotypic diversity at the Rp1 rust resistance locus of maize. Genetics 167:1939–1947
Smith SM, Steinau M, Trick H, Hulbert SH (2010) Recombinant Rp1 genes confer necrotic or nonspecific resistance phenotypes. Mol Genet Genomics 283:591–602
Song WY, Pi LY, Wang GL, Gardner J, Holsten T et al (1997) Evolution of the rice Xa21 disease resistance gene family. Plant Cell 9:1279–1287
Stirnweis D, Milani SD, Jordan T, Keller B, Brunner S (2014) Substututions of two amino acids in the nucletide-binding site domain of a resistance protein enhance the hypersensitive response and enlarge the PM3F resistance spectrum in wheat. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27:265–276
Sudupak MA, Bennetzen JL, Hulbert SH (1993) Unequal exchange and meiotic instability of Rp1 region disease resistance genes. Genetics 133:119–125
Sun Q, Collins NC, Ayliffe M, Smith SM, Drake J et al (2001) Recombination between paralogues at the rp1 rust resistance locus in maize. Genetics 158:423–438
Tajima F (1983) Evolutionary relationship of DNA sequences in finite populations. Genetics 105:437–460
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Tameling WIL, Elzinga SD, Darmin PS, Vossen JH, Takken FLW et al (2002) The tomato R gene products I-2 and Mi-1 are functional ATP binding proteins with ATPase activity. Plant Cell 14:2929–2939
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M et al (2011) MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Watterson GA (1975) On the number of segregating sites in genetical models without recombination. Theor Popul Biol 7:256–276
Wei F, Gobelman-Werner K, Morroll SM, Kurth J, Mao L et al (1999) The Mla (powdery mildew) resistance cluster is associated with three NBS-LRR gene families and suppressed recombination within a 240-kb DNA interval on chromosome 5S (1HS) of barley. Genetics 153:1929–1948
Wilkinson DR, Hooker AL (1968) Genetics of reaction to Puccinia sorghi in ten corn inbreds from Africa and Europe. Phytopathology 58:720–721
Yang Z (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci 13:555–556
Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N, Pedersen AMK (2000) Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics 155:431–449
Zhang Y, Lubberstedt T, Xu M (2013) The genetic and molecular basis of plant resistance to pathogens. J Genet Genomics 40:23–35
Acknowledgments
We thank Scot Hulbert for reviewing this manuscript and his helpful discussions regarding the Rp1 locus. This research was supported by the Georgia Commodity Commission for Corn (047461-01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The experiments comply with the current laws of the country (US) in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Xu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chavan, S., Gray, J. & Smith, S.M. Diversity and evolution of Rp1 rust resistance genes in four maize lines. Theor Appl Genet 128, 985–998 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2484-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2484-2