Abstract
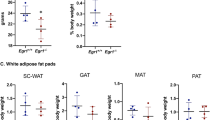
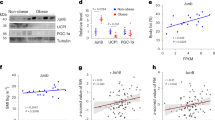
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in adipose tissue is known to promote obesity. We hypothesized that HIF-1α interferes with brown fat thermogenesis, thus decreasing energy expenditure. To test this hypothesis, we compared transgenic mice constitutively expressing HIF-1α in adipose tissues (HIF-1α++) at usual temperature (22 °C), where brown fat is somewhat active, or at thermoneutrality (30 °C), where brown fat is minimally active. HIF-1α++ mice or control litter mates were separated into room temperature (22 °C) or thermoneutrality (30 °C) groups. We assessed weight gain, food intake, calorimetry, activity, and oxygen consumption and transcriptional changes in isolated white and brown adipocytes. At 22 °C, HIF-1α++ mice exhibited accelerated weight gain, cold and glucose intolerance, hyperglycemia, and decreased energy expenditure without changes in food intake or activity. These changes were absent or minimal at thermoneutrality. In brown adipocytes of HIF-1α++ mice, oxygen consumption decreased ~50 % in association with reduced mitochondrial content, uncoupling protein 2, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 (PGC-1α). In conclusion, adipose HIF-1α overexpression inhibits thermogenesis and cellular respiration in brown adipose tissue, promoting obesity in the setting of reduced ambient temperature.
Key message
-
Constitutive HIF-1α activation in adipose tissue promotes weight gain in mice.
-
The weight gain is associated with reduced brown adipose tissue function and oxygen consumption.
-
Reduced oxygen consumption may be mediated by reductions in mitochondria.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Semenza GL, Shimoda LA, Prabhakar NR (2006) Regulation of gene expression by HIF-1. Novartis Found Symp 272:2–8
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL (1995) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:5510–5514
Semenza GL (1996) Transcriptional regulation by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 molecular mechanisms of oxygen homeostasis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 6:151–157
Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW, Laughner E, Wenger RH, Gassmann M, Gearhart JD, Lawler AM, Yu AY et al (1998) Cellular and developmental control of O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev 12:149–162
Krishnan J, Danzer C, Simka T, Ukropec J, Walter KM, Kumpf S, Mirtschink P, Ukropcova B, Gasperikova D, Pedrazzini T et al (2012) Dietary obesity-associated HIF1alpha activation in adipocytes restricts fatty acid oxidation and energy expenditure via suppression of the Sirt2-NAD+ system. Genes Dev 26:259–270
He Q, Gao Z, Yin J, Zhang J, Yun Z, Ye J (2011) Regulation of HIF-1{alpha} activity in adipose tissue by obesity-associated factors: adipogenesis, insulin, and hypoxia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 300:E877–E885
Sun K, Halberg N, Khan M, Magalang UJ, Scherer PE (2013) Selective inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha ameliorates adipose tissue dysfunction. Mol Cell Biol 33:904–917
Lee YS, Kim JW, Osborne O, Oh da Y, Sasik R, Schenk S, Chen A, Chung H, Murphy A, Watkins SM et al (2014) Increased adipocyte O2 consumption triggers HIF-1alpha, causing inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Cell 157:1339–1352
Shin MK, Drager LF, Yao Q, Bevans-Fonti S, Yoo DY, Jun JC, Aja S, Bhanot S, Polotsky VY (2012) Metabolic consequences of high-fat diet are attenuated by suppression of HIF-1alpha. PLoS One 7:e46562
Halberg N, Khan T, Trujillo ME, Wernstedt-Asterholm I, Attie AD, Sherwani S, Wang ZV, Landskroner-Eiger S, Dineen S, Magalang UJ et al (2009) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha induces fibrosis and insulin resistance in white adipose tissue. Mol Cell Biol 29:4467–4483
Drager LF, Yao Q, Hernandez KL, Shin MK, Bevans-Fonti S, Gay J, Sussan TE, Jun JC, Myers AC, Olivecrona G et al (2013) Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces atherosclerosis via activation of adipose angiopoietin-like 4. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 188:240–248
Maloney SK, Fuller A, Mitchell D, Gordon C, Overton JM (2014) Translating animal model research: does it matter that our rodents are cold? Physiology (Bethesda) 29:413–420
Uchida K, Shiuchi T, Inada H, Minokoshi Y, Tominaga M (2010) Metabolic adaptation of mice in a cool environment. Pflugers Arch 459:765–774
Cannon B, Nedergaard J (2011) Nonshivering thermogenesis and its adequate measurement in metabolic studies. JExpBiol 214:242–253
Jun JC, Shin MK, Yao Q, Devera R, Fonti-Bevans S, Polotsky VY (2013) Thermoneutrality modifies the impact of hypoxia on lipid metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 304:E424–E435
Zhang H, Bosch-Marce M, Shimoda LA, Tan YS, Baek JH, Wesley JB, Gonzalez FJ, Semenza GL (2008) Mitochondrial autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem 283:10892–10903
Hao Q, Yadav R, Basse AL, Petersen S, Sonne SB, Rasmussen S, Zhu Q, Lu Z, Wang J, Audouze K et al (2015) Transcriptome profiling of brown adipose tissue during cold exposure reveals extensive regulation of glucose metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 308:E380–E392
Carey HV, Andrews MT, Martin SL (2003) Mammalian hibernation: cellular and molecular responses to depressed metabolism and low temperature. Physiol Rev 83:1153–1181
Bowker-Kinley MM, Davis WI, Wu P, Harris RA, Popov KM (1998) Evidence for existence of tissue-specific regulation of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem J 329(Pt 1):191–196
Hosogai N, Fukuhara A, Oshima K, Miyata Y, Tanaka S, Segawa K, Furukawa S, Tochino Y, Komuro R, Matsuda M et al (2007) Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 56:901–911
Rausch ME, Weisberg S, Vardhana P, Tortoriello DV (2008) Obesity in C57BL/6J mice is characterized by adipose tissue hypoxia and cytotoxic T-cell infiltration. Int J Obes 32:451–463
Ye J, Gao Z, Yin J, He Q (2007) Hypoxia is a potential risk factor for chronic inflammation and adiponectin reduction in adipose tissue of ob/ob and dietary obese mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E1118–E1128
Jiang C, Qu A, Matsubara T, Chanturiya T, Jou W, Gavrilova O, Shah YM, Gonzalez FJ (2011) Disruption of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in adipocytes improves insulin sensitivity and decreases adiposity in high-fat diet-fed mice. Diabetes 60:2484–2495
Zhang X, Lam KS, Ye H, Chung SK, Zhou M, Wang Y, Xu A (2010) Adipose tissue-specific inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1{alpha} induces obesity and glucose intolerance by impeding energy expenditure in mice. J Biol Chem 285:32869–32877
Semenza GL (2011) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulator of mitochondrial metabolism and mediator of ischemic preconditioning. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:1263–1268
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL, Denko NC (2006) HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metab 3:187–197
Nikami H, Nedergaard J, Fredriksson JM (2005) Norepinephrine but not hypoxia stimulates HIF-1alpha gene expression in brown adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 337:121–126
Klingenspor M (2003) Cold-induced recruitment of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. Exp Physiol 88:141–148
Enerback S, Jacobsson A, Simpson EM, Guerra C, Yamashita H, Harper ME, Kozak LP (1997) Mice lacking mitochondrial uncoupling protein are cold-sensitive but not obese. Nature 387:90–94
Arsenijevic D, Onuma H, Pecqueur C, Raimbault S, Manning BS, Miroux B, Couplan E, Alves-Guerra MC, Goubern M, Surwit R et al (2000) Disruption of the uncoupling protein-2 gene in mice reveals a role in immunity and reactive oxygen species production. Nat Genet 26:435–439
Yamazaki N, Yamanaka Y, Hashimoto Y, Shinohara Y, Shima A, Terada H (1997) Structural features of the gene encoding human muscle type carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. FEBS Lett 409:401–406
Eddy SF, Morin P Jr, Storey KB (2006) Differential expression of selected mitochondrial genes in hibernating little brown bats, Myotis lucifugus. J Exp Zool A Comp Exp Biol 305:620–630
Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R, Wright M, Spiegelman BM (1998) A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell 92:829–839
Finck BN, Kelly DP (2006) PGC-1 coactivators: inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J Clin Invest 116:615–622
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL, Dang CV (2006) HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab 3:177–185
Mason SD, Rundqvist H, Papandreou I, Duh R, McNulty WJ, Howlett RA, Olfert IM, Sundberg CJ, Denko NC, Poellinger L et al (2007) HIF-1alpha in endurance training: suppression of oxidative metabolism. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R2059–R2069
Zhang H, Gao P, Fukuda R, Kumar G, Krishnamachary B, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Semenza GL (2007) HIF-1 inhibits mitochondrial biogenesis and cellular respiration in VHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma by repression of C-MYC activity. Cancer Cell 11:407–420
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P, Chiche J, Roux D, Pouyssegur J, Mazure NM (2009) Hypoxia-induced autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol 29:2570–2581
Hagen T (2012) Oxygen versus reactive oxygen in the regulation of HIF-1alpha: the balance tips. Biochem Res Int 2012:436981
O'Hagan KA, Cocchiglia S, Zhdanov AV, Tambuwala MM, Cummins EP, Monfared M, Agbor TA, Garvey JF, Papkovsky DB, Taylor CT et al (2009) PGC-1alpha is coupled to HIF-1alpha-dependent gene expression by increasing mitochondrial oxygen consumption in skeletal muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2188–2193
Zhu L, Wang Q, Zhang L, Fang Z, Zhao F, Lv Z, Gu Z, Zhang J, Wang J, Zen K et al (2010) Hypoxia induces PGC-1alpha expression and mitochondrial biogenesis in the myocardium of TOF patients. Cell Res 20:676–687
Laderoute KR, Amin K, Calaoagan JM, Knapp M, Le T, Orduna J, Foretz M, Viollet B (2006) 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is induced by low-oxygen and glucose deprivation conditions found in solid-tumor microenvironments. Mol Cell Biol 26:5336–5347
Arany Z, Foo SY, Ma Y, Ruas JL, Bommi-Reddy A, Girnun G, Cooper M, Laznik D, Chinsomboon J, Rangwala SM et al (2008) HIF-independent regulation of VEGF and angiogenesis by the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha. Nature 451:1008–1012
Louet JF, Hayhurst G, Gonzalez FJ, Girard J, Decaux JF (2002) The coactivator PGC-1 is involved in the regulation of the liver carnitine palmitoyltransferase I gene expression by cAMP in combination with HNF4 alpha and cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB). J Biol Chem 277:37991–38000
Sugden MC, Holness MJ (2006) Mechanisms underlying regulation of the expression and activities of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases. Arch Physiol Biochem 112:139–149
Morin P Jr, Storey KB (2005) Cloning and expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha from the hibernating ground squirrel, Spermophilus tridecemlineatus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1729:32–40
Maistrovski Y, Biggar KK, Storey KB (2012) HIF-1alpha regulation in mammalian hibernators: role of non-coding RNA in HIF-1alpha control during torpor in ground squirrels and bats. J Comp Physiol B 182:849–859
Jansky L, Hart JS (1968) Cardiac output and organ blood flow in warm- and cold-acclimated rats exposed to cold. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 46:653–659
Vucetic M, Otasevic V, Korac A, Stancic A, Jankovic A, Markelic M, Golic I, Velickovic K, Buzadzic B, Korac B (2011) Interscapular brown adipose tissue metabolic reprogramming during cold acclimation: interplay of HIF-1alpha and AMPKalpha. Biochim Biophys Acta 1810:1252–1261
Bartelt A, Bruns OT, Reimer R, Hohenberg H, Ittrich H, Peldschus K, Kaul MG, Tromsdorf UI, Weller H, Waurisch C et al (2011) Brown adipose tissue activity controls triglyceride clearance. NatMed 17:200–205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
J. Jun was funded by National Institutes of Health 1K08-HL109475. V. Polotsky was funded by National Institutes of Health R01-HL080105, R01-HL128970, R01-HL133100, and P50-ES018176 and American Sleep Foundation 133-BS-15. P. Scherer was funded by National Institutes of Health R01-DK55758, P01-DK088761, and R01-DK099110.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 206 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, J.C., Devera, R., Unnikrishnan, D. et al. Adipose HIF-1α causes obesity by suppressing brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. J Mol Med 95, 287–297 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1480-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1480-6