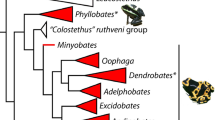
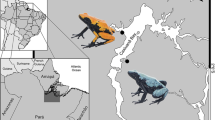
Abstract
Herein we review what is known about the chemical ecology of poison frogs with a focus on dendrobatid poison frogs. While five anuran families are known to have an alkaloid-derived chemical defense, the dendrobatids have been studied in greatest detail and provides chemical ecologists with a complex model system for understanding how chemical defenses operate in real time and may have evolved through evolutionary time. We describe the diversity of alkaloid defenses known from frogs, alkaloid sequestration, biosynthesis and modification, and we review what is known concerning arthropod sources for alkaloids. There is variation in nearly every attribute of the system and we try to describe some of the challenges associated with unraveling the complexities of this model system.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriamaharavo NR, Garraffo HM, Saporito RA, Daly JW, Razafindrakoto CR, Andriantsiferana M, Spande TF (2010) Roughing it: a mantellid poison frog shows greater alkaloid diversity in some disturbed habitats. J Nat Prod 73:322–330
Baldo D, Basso N (2004) A new species of Melanophryniscus (Anura: Bufonidae), with comments on the species of the genus reported for Misiones, Northeastern Argentina. J Herp 38:393–403
Berenbaum MR (1995) The chemistry of defense: theory and practice. P Natl Acad Sci USA 92:2–8
Berenbaum MR, Zangerl AR (1998) Chemical phenotype matching between a plant and its insect herbivore. P Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13743–13748
Bonansea MI, Vaira M (2007) Geographic variation of the diet of Melanophryniscus rubriventris (Anura, Bufonidae) in northwestern Argentina. J Herp 41:231–236
Boppre M (1990) Lepidoptera and pyrrolizidine alkaloids: exemplification of complexity in chemical ecology. J Chem Ecol 16:165–185
Bowers MD, Williams EH (1995) Variable chemical defense in the checkerspot butterfly Euphydryas gillettii (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Ecol Entom 20:208–212
Braekman JC, Daloze D, Pasteels JM (1998) Alkaloids in animals. In: Roberts WM (ed) Alkaloids: biochemistry, ecology, and medicinal applications. Plenum Press, New York, pp 349–378
Brodie ED, Tumbarello MS (1978) Antipredator functions of Dendrobates auratus (Amphibia, Anura, Dendrobatidae) skin secretion in regard to a snake predator (Thamnophis). J Herp 12:264–265
Caldwell JP (1996) The evolution of myrmecophagy and its correlates in poison frogs (Family: Dendrobatidae). J Zool 240:75–101
Clark VC, Raxworthy CJ, Rakotomalala V, Sierwald P, Fisher BL (2005) Convergent evolution of chemical defense in poison frogs and arthropod prey between Madagascar and the Neotropics. P Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11617–11622
Clark VC, Rakotomalala V, Ramilijaona O, Abrell L, Fisher BL (2006) Individual variation in alkaloid content of poison frogs of Madagascar (Mantella; Mantellidae). J Chem Ecol 32:2219–2233
Daloze D, Braekman JC, Pasteels JM (1995) Ladybird defence alkaloids: structural, chemotaxonomic and biosynthetic aspects. Chemoecology 5(6):173–183
Daly JW (2004) Marine toxins and non marine toxins: convergence or symbiotic organism? J Nat Prod 67:1211–1215
Daly JW, Myers CW (1967) Toxicity of Panamanian poison frogs (Dendrobates): some biological and chemical aspects. Science 156:970–973
Daly JW, Myers CW, Warnick JE, Albuquerque EX (1980) Levels of batrachotoxin and lack of sensitivity to its action in poison-dart frogs (Phyllobates). Science 208:1383–1385
Daly JW, Myers CW, Whittaker N (1987) Further classification of skin alkaloids from neotropical poison frogs (Dendrobatidae), with a general survey of toxic noxious substances in the amphibia. Toxicon 25:1023–1095
Daly JW, Garraffo HM, Pannell LK, Spande TF (1990) Alkaloids from Australian frogs (Myobatrachidae): Pseudophrynamines and pumiliotoxins. J Nat Prod 53:407–421
Daly JW, Gusovsky F, Myers CW, Yotsu-Yamashita M, Yasumoto T (1994) First occurrence of tetrodotoxin in a dendrobatid frog (Colostethus inguinalis), with further reports for the bufonid genus Atelopus. Toxicon 32:279–285
Daly JW, Andriamaharavo NR, Andriantsiferana M, Myers CW (1996) Madagascan poison frogs (Mantella) and their skin alkaloids. Am Mus Nov 3177:1–34
Daly JW, Garraffo HM, Spande TF (1999) Alkaloids from amphibian skins. In: Pelletier SW (ed) Alkaloids: chemical and biological perspectives, vol 13. Pergamon New York, pp 1–161
Daly JW, Kaneko T, Wilham J, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Espinosa A, Donnelly MA (2002) Bioactive alkaloids of frog skins: combinatorial bioprospecting reveals that pumiliotoxins have an arthropod source. P Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13996–14001
Daly JW, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Clark VC, Ma JY, Ziffer H, Cover JF Jr (2003) Evidence for an enantioselective pumiliotoxin 7-hydroxylase in dendrobatid poison frogs of the genus Dendrobates. P Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11092–11097
Daly JW, Noimai N, Kongkathip B, Kongkathip N, Wilham JM, Garraffo HM, Kaneko T, Spande TF, Nimit Y, Nabhitabhata J, Chan-Ard J (2004) Biologically active substances from amphibians: preliminary studies on anurans from twenty-one genera of Thailand. Toxicon 44:805–815
Daly JW, Spande TF, Garraffo HM (2005) Alkaloids from amphibian skin: a tabulation of over eight-hundred compounds. J Nat Prod 68:1556–1575
Daly JW, Wilham JM, Spande TF, Garraffo HM, Gil RR, Silva GL, Vaira M (2007) Alkaloids in bufonid toads (Melanophryniscus): temporal and geographic determinants for two Argentinian species. J Chem Ecol 31:871–887
Daly JW, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Yeh HJC, Peltzer PM, Cacivio PM, Baldo JD, Faivovich J (2008a) Indolizidine 239Q and quinolizidine 275I: major alkaloids in two Argentinian bufonid toads (Melanophryniscus). Toxicon 52:858–870
Daly JW, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Giddings LA, Saporito RA, Vieites DR, Vences M (2008b) Individual and geographic variation of skin alkaloids in three species of Madagascan poison frogs (Mantella). J Chem Ecol 32:252–279
Daly JW, Ware N, Saporito RA, Spande HM, Garraffo HM (2009) N-Methyldecahydroquinolines: an unexpected class of alkaloids from Amazonian poison frogs (Dendrobatidae). J Nat Prod 72:1110–1114
Darst CR, Cummings ME (2006) Predator learning favours mimicry of a less-toxic model in poison frogs. Nature 440:208–211
Darst CR, Menendez-Guerrero PA, Coloma LA, Cannatella DC (2005) Evolution of dietary specialization and chemical defense in poison frogs (Dendrobatidae): a comparative analysis. Am Nat 165:56–69
Darst CR, Cummings ME, Cannatella DC (2006) A mechanism for diversity in warning signals: conspicuousness versus toxicity in poison frogs. P Natl Acad Sci USA 103:5852–5857
Delfino G, Brizzi R, Kracke-Berndorff R, Alvarez B (1998) Serous gland dimorphism in the skin of Melanophryniscus stelzneri (Anura: Bufonidae). J Morph 237:19–32
Dobler S (2001) Evolutionary aspects of defense by recycled plant compounds in herbivorous insects. Basic Appl Ecol 2:15–26
Donnelly MA (1991) Feeding patterns of the strawberry poison frog, Dendrobates pumilio (Anura: Dendrobatidae). Copeia 3:723–730
Dumbacher JP, Wako A, Derrickson SR, Samuelson A, Spande TF, Daly JW (2004) Melyrid beetles (Choresine): a putative source for the batrachotoxin alkaloids found in poison-dart frogs and toxic passerine birds. P Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15857–15860
Dumbacher JP, Menon GK, Daly JW (2009) Skin as toxin storage organ in the endemic New Guinea genus Pitohui. Auk 126:520–530
Fahey SJ, Garson MJ (2002) Geographic variation of natural products of tropical nudibranch Asteronotus cespitosus. J Chem Ecol 28:1773–1785
Fritz G, Rand SA, Depamphilis CW (1981) The aposematically colored frog, Dendrobates pumilio, is distasteful to the large, predatory ant, Paraponera clavata. Biotropica 13:158–159
Frost DR (2011) Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 5.5 (31 January, 2011). Electronic Database accessible at http://research.amnh.org/vz/herpetology/amphibia/. American Museum of Natural History, New York, USA
Glaw F, Vences M (2007) A field guide to the amphibians and reptiles of Madagascar Third edition. Vences and Glaw Verlag, Cologne
Grant T (2007) A new, toxic species of Colostethus (Anura: Dendrobatidae: Colostethinae) from the Cordillera Central of Colombia. Zootaxa 1555:39–51
Grant T, Frost DR, Caldwell JP, Gagliardo R, Haddad CFB, Kok PJR, Means BD, Noonan BP, Schargel WE, Wheeler W (2006) Phylogenetic systematics of dart-poison frogs and their relatives (Amphibia, Athesphatanura, Dendrobatidae). Bull Am Mus Nat Hist 299:1–262
Hutchinson DA, Savitzky AH, Mori A, Burghardt GM, Meinwald J, Schroeder FC (2011) Chemical investigations of defensive steroid sequestration by the Asian snake Rhabdophis tigrinus Chemoecol, published online 01 May 2011
Jones TH, Voegtle HL, Miras HM, Weatherford RG, Spande TF, Garraffo HM, Daly JW, Davidson DW, Snelling RR (2007) Venom chemistry of the ant Myrmicaria melanogaster from Brunei. J Nat Prod 70:160–168
Kubanek J, Williams DE, Dilip De Silva E, Allen T, Andersen RJ (1995) Cytotoxic alkaloids from the flatworm Prostheceraeus villatus and its tunicate prey Clavelina lepadiformis. Tetrahedron Lett 36:6189–6192
Lindigkeit R, Biller A, Buch M, Schiebel HM, Boppre M, Hartmann T (1997) The two faces of pyrrolizidine alkaloids: the role of the tertiary amine and its N-oxide in chemical defense of insects with acquired plant alkaloids. Europ J Biocchem 245:626–636
Maan and Cummings (2011) Poison frog colors are honest signals of toxicity, particularly for bird predators. Am Nat (in press)
Macfoy C, Danosus D, Sandit R, Jones TH, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Daly JW (2005) Alkaloids of anuran skin: antimicrobial function? Zeitschrift fuer Naturforschung 60c:932–937
Mebs D (2001) Toxicity in animals: trends in evolution? Toxicon 39:87–96
Mebs D, Pogoda W, Maneyro R, Kwet A (2005) Studies on the poisonous skin secretion of individual red bellied toads, Melanophryniscus montevidensis (Anura, Bufonidae), from Uruguay. Toxicon 46:641–650
Moranz R, Brower LP (1998) Geographic and temporal variation of cardienolide-based chemical defenses of queen butterfly (Danaus gilippus) in northern Florida. J Chem Ecol 24:905–932
Mortari MR, Schwartz ENF, Schwartz CA, Pires OR, Santos MM Jr, Bloch C Jr, Sebben A (2004) Main alkaloids from the Brazilian dendrobatidae frog Epipedobates flavopictus: Pumiliotoxin 251D, histrionicotoxin and decahydroquinolines. Toxicon 43:303–310
Myers CW, Daly JW, Malkin B (1978) A dangerously toxic new frog (Phyllobates) used by Embera Indians of western Colombia, with discussion of blowgun fabrication and dart poisoning. Am Mus Novitates 161:307–366
Myers CW, Daly JW, Garraffo HM, Wisnieski A, Cover JF Jr (1995) Discovery of the Costa Rican poison frog Dendrobates granuliferus in sympatry with Dendrobates pumilio, and comments on taxanomic use of skin alkaloids. Am Mus Novit 3144:1–21
Neuwirth M, Daly JW, Myers CW, Tice LW (1979) Morphology of the granular secretory glands in skin of poison-dart frogs (Dendrobatidae). Tissue Cell 11:755–771
Nishida R (2002) Sequestration of defensive substances from plants by Lepidoptera. Ann Rev Ent 47:57–92
Opitz SEW, Müller C (2009) Plant chemistry and insect sequestration. Chemoecol 19:117–154
Osborne WS (1989) Distribution, relative abundance and conservation status of Corroboree frogs, Pseudophryne corroboree Moore (Anura: Myobatrachidae). Aust Wildl Res 16:537–547
Rodríguez A, Poth D, Schulz S, Vences M (2011) Discovery of skin alkaloids in a miniaturized eleutherodactylid frog from Cuba. Biol Lett 7:414–418
Santos JC, Cannatella DC (2011) Phenotypic integration emerges from aposematism and scale in poison frogs. P Natl Acad Sci USA 108:6175–6180
Santos JC, Coloma LA, Cannatella DC (2003) Multiple, recurring origins of aposematism and diet specialization in poison frogs. P Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12792–12797
Santos RR, Grant T (2011) Diel patterns of migration in a poisonous toad from Brazil and the evolution of chemical defenses in diurnal amphibians. Evol Ecol 25:249–258
Saporito RA, Donnelly MA, Hoffman RL, Garraffo HM, Daly JW (2003) A siphonotid millipede (Rhinotus) as the source of spiropyrrolizidine oximes of dendrobatid frogs. J Chem Ecol 29:2781–2786
Saporito RA, Garraffo HM, Donnelly MA, Edwards AL, Longino JT, Daly JW (2004) Formicine ants: an arthropod source for the pumiliotoxin alkaloids of dendrobatid poison frogs. P Natl Acad Sci USA 101:8045–8050
Saporito RA, Donnelly MA, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Daly JW (2006) Geographic and seasonal variation in alkaloid-based chemical defenses of Dendrobates pumilio from Bocas del Toro, Panama. J Chem Ecol 32:795–814
Saporito RA, Zuercher R, Roberts M, Gerrow KG, Donnelly MA (2007a) Experimental evidence for aposematism in the poison frog Oophaga pumilio. Copeia 4:1006–1011
Saporito RA, Donnelly MA, Norton RA, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Daly JW (2007b) Oribatid mites as a major dietary source for alkaloids in poison frogs. P Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8885–8890
Saporito RA, Donnelly MA, Jain P, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Daly JW (2007c) Spatial and temporal patterns of alkaloid variation in the poison frog Oophaga pumilio in Costa Rica and Panama over 30 years. Toxicon 50:757–778
Saporito RA, Spande TF, Garraffo HM, Donnelly MA (2009a) Arthropod alkaloids in poison frogs: a review of the “dietary hypothesis”. Heterocycles 79:277–297
Saporito RA, Donnelly MA, Madden AA, Garraffo HM, Spande TF (2009b) Sex-related differences in alkaloid defenses of the dendrobatid frog Oophaga pumilio from Cayo Nancy, Bocas del Toro, Panama. J Nat Prod 73:317–321
Saporito RA, Isola M, Maccachero VC, Condon K, Donnelly MA (2010) Ontogenetic scaling of poison glands in a dendrobatid frog. J Zool 282:238–245
Saporito RA, Norton RA, Andriamaharavo NR, Garraffo HM, Spande TF (2011) Alkaloids in the mite Scheloribates laevigatus: further alkaloids common to oribatid mites and poison frogs. J Chem Ecol 37:213–218
Simon MP, Toft CA (1991) Diet specialization in small vertebrates: mite-eating in frogs. Oikos 61:263–278
Smith BP, Tyler MJ, Kaneko T, Garraffo HM, Spande TF, Daly JW (2002) Evidence for biosynthesis of pseudophrynamine alkaloids by an Australian myobatrachid frog (Pseudophryne) and for sequestration of dietary pumiliotoxins. J Nat Prod 65:439–447
Summers K, Clough ME (2001) The evolution of coloration and toxicity in the poison-dart frog family (Dendrobatidae). P Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6227–6232
Szelistowski WA (1985) Unpalatability of the poison arrow frog Dendrobates pumilio to the ctenid spider Cupiennius coccineus. Biotropica 17:345–346
Takada W, Sakata T, Shimano S, Enami Y, Mori N, Nishida R, Kuwahara Y (2005) Scheloribatid mites as the source of pumiliotoxins in dendrobatid frogs. J Chem Ecol 31:2403–2415
Termonia AJ, Pasteels M, Windsoer DM, Milinkovitch MC (2001) Dual chemical sequestration: a key mechanism in transitions among ecological specialization. P Roy Soc Lond 269:1–6
Tokuyama T, Daly JW (1983) Steroidal alkaloids (batrachotoxins and 4-beta-hydroxybatrachotoxins), indole alkaloids (calycanthine and chimonanthine) and a piperidinyldipyridine alkaloid (noranabasamine) in skin extracts from the Colombian poison-dart frog Phyllobates terribilis (Dendrobatidae). Tetrahedron 39:41–47
Valderrama-Vernaza M, Ramírez-Pinilla MP, Serrano-Cardoza VH (2009) Diet of the Andean frog Ranitomeya virolinensis (Athesphatanura: Dendrobatidae). J Herp 43:114–123
Vences M, Glaw F, Bohme W (1998) Evolutionary correlates of microphagy in alkaloid-containing frogs (Amphibia: Anura). Zool Anz 236:217–230
Vences M, Kosuch J, Boistel R, Haddad CFB, La Marca E, Lötters S, Veith M (2003) Convergent evolution of aposematic coloration in Neotropical poison frogs: a molecular phylogenetic perspective. Organ Div Evol 3:215–226
Wang I (2011) Inversely related aposemtic traits: reduced conspicuous evolves with increased toxicity in a polymorphic poison-dart frog. Evol 65:1637–1649
Weldon PJ, Kramer M, Gordon S, Spande TF, Daly JW (2006) A common pumiliotoxin from poison frogs exhibits enantioselective toxicity against mosquitoes. P Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17818–17821
Williams BL, Hanifin CT, Brodie ED Jr, Brodie ED III (2011) Predators usurp prey defenses: toxicokinetics of tetrodotoxin in common garter snakes after consumption of rough-skinned newts. Chemoecol (in review)
Acknowledgments
This paper is dedicated to the memory of our friend and colleague John W. Daly, whose pioneering research founded and continues to inspire the study of poison frog chemical ecology. We would also like to acknowledge his life-long colleague, C.W. Myers (Curator Emeritus, Department of Herpetology, American Museum of Natural History), who collaborated extensively with John over the past 40 years on the study of poison frogs. We thank Tappey H. Jones (Virginia Military Institute), who collaborated with John in the identification and synthesis of ant alkaloids. We also thank Richard L. Hoffman (Virginia Museum of Natural History), John T. Longino (Evergreen State College), and Roy A. Norton (State University of New York, Syracuse) for their assistance in identifying many of the alkaloid-containing arthropods. We are grateful to Alan H. Savitzky and Jenise M. Snyder for providing valuable comments that improved the quality of this manuscript. We would like to thank the Environmental Protection Agency, Florida International University, National Geographic Society, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Organization for Tropical Studies, and Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute for their generous funding. A National Science Foundation Postdoctoral Research Fellowship partially supported R.A.S. This work is derived from a presentation in the symposium “Sequestered Defensive Compounds in Tetrapod Vertebrates: A Symposium in Memory of John W. Daly,” held at the Sixth World Congress of Herpetology in Manaus, Brazil, on 21 August 2008 and supported by NSF IOS-0813842.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sequestered chemical defenses in vertebrates, dedicated to J.W. DALY.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saporito, R.A., Donnelly, M.A., Spande, T.F. et al. A review of chemical ecology in poison frogs. Chemoecology 22, 159–168 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-011-0088-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-011-0088-0