Abstract
Objectives
We compared rates of smoking among those aged 45 years and older in Australia, the United States of America and South Korea, and examined cross-national gender differences in key socioeconomic differentials in smoking.
Methods
We conducted weighted analyses on cross-sectional data from nationally representative surveys conducted in 2006.
Results
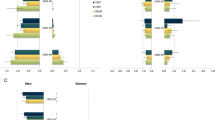
Current smoking was more prevalent for males than females in all countries; the gender difference was largest in Korea. Being unpartnered increased the likelihood of smoking in all countries, while greater wealth reduced it. In Korea, these effects interacted with gender; both indicators showed larger differentials among women than men. Lower educational attainment increased the likelihood of smoking for all groups except Korean women, among whom high school educated women were less likely to smoke than the tertiary educated.
Conclusions
Our findings support a cultural interpretation of gender differences in smoking: in countries with low gender empowerment, gender differences in smoking are greater. With increasing divorce and female tertiary education rates in nations like Korea, we highlight the need for health promotion messages targeted towards older and more educated women.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks J, Marmot M, Oldfield Z, Smith JP (2006) Disease and disadvantage in the United States and in England. JAMA 295:2037–2045. doi:10.1001/jama.295.17.2037
Bjartveit K, Tverdal A (2003) Health consequences of smoking 1–4 cigarettes per day. Tob Control 14:315–320. doi:10.1136/tc.2005.011932
Cho HJ, Khang YH, Jun HJ, Kawachi I (2008) Marital status and smoking in Korea: the influence of gender and age. Soc Sci Med 66:609–619. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.10.005
Dube SR, Asman K, Malarcher A, Carabollo R (2009) Cigarette smoking among adults and trends in smoking cessation—United States, 2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 58(44):1227–1232
Health and Retirement Study (2008a) Sample sizes and response rates. http://hrsonline.isr.umich.edu/sitedocs/sampleresponse.pdf. Accessed 17 June 2009
Health and Retirement Study (2008b) Wave 8/2006 public use dataset. Produced and distributed by the University of Michigan with funding from the National Institute on Aging (Grant Number NIA U01AG09740). University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Hitchman SC, Fong GT (2011) Gender empowerment and female-to-male smoking prevalence ratios. Bull World Health Organ 89:195–202. doi:10.2471/BLT.10.079905
Khang YH, Cho HJ (2006) Socioeconomic inequality in cigarette smoking: trends by gender, age, and socioeconomic position in South Korea, 1989–2003. Prev Med 42:415–422. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2006.02.010
Khang Y-H, Yun S-C, Cho H-J, Jung-Choi K (2009) The impact of governmental antismoking policy on socioeconomic disparities in cigarette smoking in South Korea. Nicotine Tob Res 11(3):262–269. doi:10.1093/ntr/ntn036
Kim SS, Son H, Nam KA (2005) Personal factors influencing Korean American men’s smoking behavior: addiction, health, and age. Arch Psychiatr Nurs 19(1):35–41. doi:10.1016/j.apnu.2004.11.005
Korea Labor Institute (2007) User guide for 2007 KLoSA. http://www.kli.re.kr:8080/klosa/en/about/introduce.jsp. Accessed 4 June 2009
Lee HY (2004) Divorce in Korea. Int Med J 11:194–199
Lopez AD, Collishaw NE, Piha T (1994) A descriptive model of the cigarette epidemic in developed countries. Tob Control 3:242–247. doi:10.1136/tc.3.3.242
Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research (2008) HILDA survey annual report 2007. The University of Melbourne, Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, Melbourne
Meyler D, Stimpson JP, Peek MK (2007) Health concordance within couples: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med 64(11):2297–2310. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.02.007
National Health and Medical Research Council (2009) Australian guidelines to reduce health risks from drinking alcohol. NHMRC Publications, Canberra
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (2008) Rethinking drinking: alcohol and your health. National Institutes of Health, US Department of Health and Human Services, Bethesda
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (2008a) Growing unequal? Income distribution and poverty in OECD countries. OECD, Paris
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (2008b) PPPs and exchange rates. http://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?datasetcode=SNA_TABLE4. Accessed 4 June 2009
Pampel FC (2006) Global patterns and determinants of sex differences in smoking. Int J Comp Sociol 47(6):466–487. doi:10.1177/0020715206070267
Park EJ, Koh HK, Kwon JW, Suh MK, Kim H, Cho SI (2009) Secular trends in adult male smoking from 1992 to 2006 in South Korea: age-specific changes with evolving tobacco-control policies. Public Health 123(10):657–664
Prescott E, Scharling H, Osler M, Schnohr P (2002) Importance of light smoking and inhalation habits on risk of myocardial infarction and all cause mortality. J Epidemiol Community Health 56:702–706. doi:10.1136/jech.56.9.702
Schaap MM, Kunst AE, Leinsalu M, Regidor E, Espelt A, Ekholm O et al (2009) Female ever-smoking, education, emancipation and economic development in 19 European countries. Soc Sci Med 68:1271–1278. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.01.007
Schone BS, Weinick RM (1998) Health-related behaviors and the benefits of marriage for elderly persons. Gerontologist 38:618–627
Scollo MM, Winstanley MH (eds) (2008) Tobacco in Australia: facts and issues, 3rd edn. Cancer Council Victoria, Melbourne
Sulander T, Helakorpi S, Rahkonen O, Nissinen A, Uutela A (2004) Smoking and alcohol consumption among the elderly: trends and associations, 1985–2001. Prev Med 39(2):413–418. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2004.02.049
United Nations Development Programme (2009) Human development report 2009; overcoming barriers: human mobility and development. Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke
United Nations Population Division (2010) Population ageing and development 2009. http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/ageing/ageing2009.htm. Accessed 24 Jan 2012
United Nations Population Division (2011) World population prospects: the 2010 revision (vol. II: demographic profiles). United Nations, New York
United Nations Statistics Division (2007) Women’s share of tertiary enrolment. http://data.un.org/Explorer.aspx?d=GenderStat. Accessed 18 Dec 2009
US Department of Health and Human Services (2004) The health consequences of smoking: a report of the surgeon general, Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health. http://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/sgr/2004/complete_report/index.htm. Accessed 25 Jan 2010
Van Loon AJM, Tijhuis M, Picavet HSJ, Surtees PG, Ormel J (2003) Survey non-response in the Netherlands: effects on prevalence estimates and associations. Ann Epidemiol 13(2):105–110. doi:10.1016/S1047-2797(02)00257-0
Wewers ME, Dhatt RK, Moeschberger ML, Guthrie RM, Kuun P, Chen MS (1995) Misclassification of smoking status among Southeast Asian adult immigrants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:1917–1921
Wooden M, Freidin S, Watson N (2002) The household, income and labour dynamics in Australia (HILDA) survey: wave 1. Aust Econ Rev 35(3):339–348
World Bank (2011) Gross domestic product 2010. http://siteresources.worldbank.org/DATASTATISTICS/Resources/GDP.pdf. Accessed 24 Jan 2012
World Health Organization (2011a) WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2011: tobacco control country profiles. http://www.who.int/tobacco/surveillance/policy/country_profile/en/index.html. Accessed 24 Jan 2012
World Health Organization (2011b) WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2011: warning about the dangers of tobacco. World Health Organization, Geneva
Acknowledgments
This paper uses unit record data of the Household, Income and Labour Dynamics in Australia (HILDA) Survey. The HILDA Project was initiated and is funded by the Australian Government Department of Families, Housing, Community Services and Indigenous Affairs (FaHCSIA) and is managed by the Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research (Melbourne Institute). The findings and views reported in this paper, however, are those of the author and should not be attributed to either FaHCSIA or the Melbourne Institute. Data from wave 8 of the Health and Retirement Study (HRS) are used with permission. HRS is sponsored by the National Institute of Aging (Grant Number NIA U01AG009740) and conducted by the University of Michigan. Data from the Korean Longitudinal Study of Ageing (KLoSA) are used with permission. KloSA is conducted by the Korean Labor Institute and funded by the Korean Ministry of Labor through the Employment Insurance Fund. This research was supported by a grant from the Australian Research Council Centre for Excellence in Population Ageing Research (CEPAR) and by National Health and Medical Research Council Research Fellowship No. 366756 to the last author.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
Each of the original studies included in this paper received appropriate institutional ethical approvals. Our study analyzed only de-identified data files, which did not require ethical approval. De-identified data were obtained and used with permission through registration with the appropriate organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
French, D.J., Jang, SN., Tait, R.J. et al. Cross-national gender differences in the socioeconomic factors associated with smoking in Australia, the United States of America and South Korea. Int J Public Health 58, 345–353 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-012-0430-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-012-0430-5