Abstract
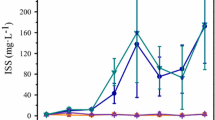
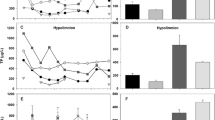
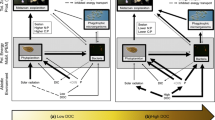
One debate about lake restoration is whether there is overemphasis of a “Phosphorus (P)-only” paradigm, while overlooking the limiting effect of nitrogen (N). In particular, the roles of internal nutrient cycling which could act as drivers of algal blooms are not yet well assessed. However, it is hardly possible to identify the complex mechanisms of nutrient limitation patterns in lakes only by in-situ experiments or monitored data. Numerical modeling can serve as a complementary approach by providing quantitative internal variations with high spatial and temporal resolutions. A three-dimensional model-based N:P stoichiometric approach was developed to explore the storage pools and fluxes that affect the limiting nutrient in hyper-eutrophic Lake Dianchi, the most eutrophic large lake in China with seasonal N limitation. The results highlighted the role of benthic P fluxes, which fluctuated considerably within a year and could supply enough P for algae, contributing over 50% of P input and leading to relative N deficiency during algal bloom. Further insights into N cycling indicated that N deficiency could be attributed to low N fixation and extremely high N losses from denitrification (~ 50% of total loss). Considering the continuous sediment P release and N losses that promote N deficiency, controlling both N and P loadings will benefit lake restoration.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell JM, Ozkundakci D, Hamilton DP (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of phytoplankton growth in New Zealand lakes: implications for eutrophication control. Ecosystems 13(7):966–977
Bergstrom AK (2010) The use of TN:TP and DIN:TP ratios as indicators for phytoplankton nutrient limitation in oligotrophic lakes affected by N deposition. Aquat Sci 72(3):277–281
Bernhardt ES (2013) Cleaner lakes are dirtier lakes. Science 342(6155):205–206
Boyd IL (2012) The art of ecological modeling. Science 337(6092):306–307
Bruesewitz DA, Tank JL, Hamilton SK (2012) Incorporating spatial variation of nitrification and denitrification rates into whole-lake nitrogen dynamics. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 117:G00N07. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JG002006
Carpenter SR (2008) Phosphorus control is critical to mitigating eutrophication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(32):11039–11040
Cha Y, Alameddine I, Qian SS, Stow CA (2016) A cross-scale view of N and P limitation using a Bayesian hierarchical model. Limnol Oceanogr 61(6):2276–2285
Chen X, Li H, Hou J, Cao X, Song C, Zhou Y (2016) Sediment-water interaction in phosphorus cycling as affected by trophic states in a Chinese shallow lake (Lake Donghu). Hydrobiologia 776(1):19–33
Chen M, Ding S, Chen X, Sun Q, Fan X, Lin J, Ren M, Yang L, Zhang C (2018) Mechanisms driving phosphorus release during algal blooms based on hourly changes in iron and phosphorus concentrations in sediments. Water Res 133:153–164
Conley DJ, Paerl HW, Howarth RW, Boesch DF, Seitzinger SP, Havens KE, Lancelot C, Likens GE (2009) Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323(5917):1014–1015
Davidson EA, Howarth RW (2007) Environmental science—nutrients in synergy. Nature 449(7165):1000–1001
Ding S, Chen M, Gong M, Fan X, Qin B, Xu H, Gao S, Jin Z, Tsang DCW, Zhang C (2018) Internal phosphorus loading from sediments causes seasonal nitrogen limitation for harmful algal blooms. Sci Total Environ 625:872–884
Dittrich M, Chesnyuk A, Gudimo A, McCulloch J, Quazi S, Young J, Winter J, Stainsby E, Arhonditsis G (2013) Phosphorus retention in a mesotrophic lake under transient loading conditions: Insights from a sediment phosphorus binding form study. Water Res 47(3):1433–1447
Dolman AM, Mischke U, Wiedner C (2016) Lake-type-specific seasonal patterns of nutrient limitation in German lakes, with target nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations for good ecological status. Freshw Biol 61(4):444–456
Finlay JC, Small GE, Sterner RW (2013) Human influences on nitrogen removal in lakes. Science 342(6155):247–250
Gao W, Howarth RW, Hong B, Swaney DP, Guo HC (2014) Estimating net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs (NANI) in the Lake Dianchi basin of China. Biogeosciences 11(16):4577–4586
Grantz EM, Haggard BE, Scott JT (2014) Stoichiometric imbalance in rates of nitrogen and phosphorus retention, storage, and recycling can perpetuate nitrogen deficiency in highly-productive reservoirs. Limnol Oceanogr 59(6):2203–2216
Guildford SJ, Hecky RE (2000) Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: Is there a common relationship? Limnol Oceanogr 45(6):1213–1223
Hamrick JM (1992) A three-dimensional environmental fluid dynamics computer code: Theoretical and computational aspects. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary, Williamsburg
Hasegawa T, Okino T (2004) Seasonal variation of denitrification rate in Lake Suwa sediment. Limnology 5(1):33–39
Havens KE, Kukushima T, Xie P, Iwakuma T, James RT, Takamura N, Hanazato T, Yamamoto T (2001) Nutrient dynamics and the eutrophication of shallow lakes Kasumigaura (Japan), Donghu (PR China), and Okeechobee (USA). Environ Pollut 111(2):263–272
Havens KE, James RT, East TL, Smith VH (2003) N : P ratios, light limitation, and cyanobacterial dominance in a subtropical lake impacted by non-point source nutrient pollution. Environ Pollut 122(3):379–390
Holmroos H, Hietanen S, Niemisto J, Horppila J (2012) Sediment resuspension and denitrification affect the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio of shallow lake waters. Fundam Appl Limnol 180(3):193–205
Iachetti CM, Eugenia Llames M (2015) Light limitation helps stabilize the phytoplankton assemblage steady-state in a temperate and highly turbid, hypertrophic shallow lake (Laguna ChascomA(0)s, Argentina). Hydrobiologia 752(1):33–46
Kim DK, Zhang WT, Rao YR, Watson S, Mugalingam S, Labencki T, Dittrich M, Morley A, Arhonditsis GB (2013) Improving the representation of internal nutrient recycling with phosphorus mass balance models: a case study in the Bay of Quinte, Ontario, Canada. Ecol Model 256:53–68
Kohler J, Hilt S, Adrian R, Nicklisch A, Kozerski HP, Walz N (2005) Long-term response of a shallow, moderately flushed lake to reduced external phosphorus and nitrogen loading. Freshw Biol 50(10):1639–1650
Kolzau S, Wiedner C, Ruecker J, Koehler J, Koehler A, Dolman AM (2014) Seasonal patterns of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation in four german lakes and the predictability of limitation status from ambient nutrient concentrations. PLoS ONE 9(4):e96065
Kong XZ, Dong L, He W, Wang QM, Mooij WM, Xu FL (2015) Estimation of the long-term nutrient budget and thresholds of regime shift for a large shallow lake in China. Ecol Ind 52:231–244
Kowalczewska-Madura K, Goldyn R, Dera M (2015) Spatial and seasonal changes of phosphorus internal loading in two lakes with different trophy. Ecol Eng 74:187–195
Li H, Song C-L, Cao X-Y, Zhou Y-Y (2016) The phosphorus release pathways and their mechanisms driven by organic carbon and nitrogen in sediments of eutrophic shallow lakes. Sci Total Environ 572:280–288
Liu Y, Chen W, Li D, Shen Y, Liu Y, Song L (2006) Analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins in Aphanizomenon DC-1 from Lake Dianchi. China Environ Toxicol 21(3):289–295
Liu Y, Wang Y, Sheng H, Dong F, Zou R, Zhao L, Guo H, Zhu X, He B (2014) Quantitative evaluation of lake eutrophication responses under alternative water diversion scenarios: a water quality modeling based statistical analysis approach. Sci Total Environ 468–469(Supplement C):219–227
Liu J, Luo X, Zhang N, Wu Y (2016) Phosphorus released from sediment of Dianchi Lake and its effect on growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(16):16321–16328
Malecki LM, White JR, Reddy KR (2004) Nitrogen and phosphorus flux rates from sediment in the Lower St. Johns River estuary. J Environ Qual 33(4):1545–1555
Moss B, Jeppesen E, Sondergaard M, Lauridsen TL, Liu ZW (2013) Nitrogen, macrophytes, shallow lakes and nutrient limitation: resolution of a current controversy? Hydrobiologia 710(1):3–21
Müller S, Mitrovic SM (2015) Phytoplankton co-limitation by nitrogen and phosphorus in a shallow reservoir: progressing from the phosphorus limitation paradigm. Hydrobiologia 744(1):255–269
Nishri A, Hamilton DP (2010) A mass balance evaluation of the ecological significance of historical nitrogen fluxes in Lake Kinneret. Hydrobiologia 655(1):109–119
Nowlin WH, Evarts JL, Vanni MJ (2005) Release rates and potential fates of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediments in a eutrophic reservoir. Freshw Biol 50(2):301–322
Orihel DM, Schindler DW, Ballard NC, Graham MD, O'Connell DW, Wilson LR, Vinebrooke RD (2015) The “nutrient pump:” Iron-poor sediments fuel low nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratios and cyanobacterial blooms in polymictic lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 60(3):856–871
Paerl HW, Xu H, McCarthy MJ, Zhu G, Qin B, Li Y, Gardner WS (2011) Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res 45(5):1973–1983
Paerl HW, Gardner WS, McCarthy MJ, Peierls BL, Wilhelm SW (2014) Algal blooms: noteworthy nitrogen. Science 346(6206):175
Paerl HW, Scott JT, McCarthy MJ, Newell SE, Gardner WS, Havens KE, Hoffman DK, Wilhelm SW, Wurtsbaugh WA (2016) It takes two to tango: when and where dual nutrient (N & P) reductions are needed to protect lakes and downstream ecosystems. Environ Sci Technol 50(20):10805–10813
Park K, Kuo AY, Shen J, Hamrick JM (1995) A three-dimensional hydrodynamic-eutrophication model (HEM-3D): description of water quality and sediment process submodels. In: Special report in applied marine science and ocean engineering; no. 327. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary. https://doi.org/10.21220/V5ZH9N
Pina-Ochoa E, Alvarez-Cobelas M (2006) Denitrification in aquatic environments: a cross-system analysis. Biogeochemistry 81(1):111–130
Redfield AC (1958) The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am Sci 46(3):A221–230A
Saunders DL, Kalff J (2001) Denitrification rates in the sediments of Lake Memphremagog. Canada-USA Water Res 35(8):1897–1904
Scheffer M (1998) Ecology of shallow lakes. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht
Schindler DW (1974) Eutrophication and recovery in experimental lakes: implications for lake management. Science 184(4139):897–899
Schindler DW (2012) The dilemma of controlling cultural eutrophication of lakes. Proceed R Soc B-Biol Sci 279(1746):4322–4333
Schindler DW, Hecky RE (2009) Eutrophication: more nitrogen data needed. Science 324(5928):721–722
Schindler DW, Hecky R, Findlay D, Stainton M, Parker B, Paterson M, Beaty K, Lyng M, Kasian S (2008) Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(32):11254–11258
Schindler DW, Carpenter SR, Chapra SC, Hecky RE, Orihel DM (2016) Reducing phosphorus to curb lake eutrophication is a success. Environ Sci Technol 50(17):8923–8929
Scott JT, McCarthy MJ (2010) Nitrogen fixation may not balance the nitrogen pool in lakes over timescales relevant to eutrophication management. Limnol Oceanogr 55(3):1265–1270
Seitzinger S (2008) Out of reach. Nature 452:162–163
Small GE, Cotner JB, Finlay JC, Stark RA, Sterner RW (2014) Nitrogen transformations at the sediment-water interface across redox gradients in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Hydrobiologia 731(1):95–108
Smith VH, Schindler DW (2009) Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends Ecol Evol 24(4):201–207
Smith VH, Wood SA, McBride CG, Atalah J, Hamilton DP, Abell J (2016) Phosphorus and nitrogen loading restraints are essential for successful eutrophication control of Lake Rotorua. N Z Inland Waters 6(2):273–283
Sondergaard M, Jensen PJ, Jeppesen E (2001) Retention and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow, eutrophic lakes. Sci World J 1:427–442
Sondergaard M, Bjerring R, Jeppesen E (2013) Persistent internal phosphorus loading during summer in shallow eutrophic lakes. Hydrobiologia 710(1):95–107
Sondergaard M, Lauridsen TL, Johansson LS, Jeppesen E (2017) Nitrogen or phosphorus limitation in lakes and its impact on phytoplankton biomass and submerged macrophyte cover. Hydrobiologia 795(1):35–48
Spears BM, Carvalho L, Perkins R, Kirika A, Paterson DM (2012) Long-term variation and regulation of internal phosphorus loading in Loch Leven. Hydrobiologia 681(1):23–33
Vanni MJ, Renwick WH, Bowling AM, Horgan MJ, Christian AD (2011) Nutrient stoichiometry of linked catchment-lake systems along a gradient of land use. Freshw Biol 56(5):791–811
Verburg P, Horrox J, Chaney E, Rutherford JC, Quinn JM, Wilcock RJ, Howard-Williams CW (2013) Nutrient ratios, differential retention, and the effect on nutrient limitation in a deep oligotrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 718(1):119–130
Wang HJ, Wang HZ (2009) Mitigation of lake eutrophication: loosen nitrogen control and focus on phosphorus abatement. Prog Nat Sci 19(10):1445–1451
Wang H, Appan A, Gulliver JS (2003a) Modeling of phosphorus dynamics in aquatic sediments: I—model development. Water Res 37(16):3928–3938
Wang H, Appan A, Gulliver JS (2003b) Modeling of phosphorus dynamics in aquatic sediments: II—examination of model performance. Water Res 37(16):3939–3953
Wang Z, Zou R, Zhu X, He B, Yuan G, Zhao L, Liu Y (2014) Predicting lake water quality responses to load reduction: a three-dimensional modeling approach for total maximum daily load. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(2):423–436
Wu Z, Liu Y, Liang Z, Wu S, Guo H (2017) Internal cycling, not external loading, decides the nutrient limitation in eutrophic lake: a dynamic model with temporal Bayesian hierarchical inference. Water Res 116:231–240
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin B, Zhu G, Gao G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu. China Limnol Oceanogr 55(1):420–432
Yang L, Lei K, Yan W, Li Y (2013) Internal loads of nutrients in lake Chaohu of China: implications for lake eutrophication. Int J Environ Res 7(4):1021–1028
Yao XL, Zhang L, Zhang YL, Xu HX, Jiang XY (2016) Denitrification occurring on suspended sediment in a large, shallow, subtropical lake (Poyang Lake, China). Environ Pollut 219:501–511
Yi X, Zou R, Guo HC (2016) Global sensitivity analysis of a three-dimensional nutrients-algae dynamic model for a large shallow lake. Ecol Model 327:74–84
Yu Q, Chen Y, Liu Z, De Giesen NV, Zhu D (2015) The influence of a eutrophic lake to the river downstream: spatiotemporal algal composition changes and the driving factors. Water 7(5):2184–2201
Zhang X, Zou R, Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhao L, Zhu X, Guo H (2016) Is water age a reliable indicator for evaluating water quality effectiveness of water diversion projects in eutrophic lakes? J Hydrol 542:281–291
Zou R, Carter S, Shoemaker L, Parker A, Henry T (2006) Integrated hydrodynamic and water quality modeling system to support nutrient total maximum daily load development for wissahickon creek. Pa J Environ Eng 132(4):555–566
Zou R, Wu Z, Zhao L, Elser JJ, Yu YH, Chen YH, Liu Y (2020) Seasonal algal blooms support sediment release of phosphorus via positive feedback in a eutrophic lake: insights from a nutrient flux tracking modeling. Ecol Model 416:108881
Acknowledgement
The paper was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (51721006) and the Open Research Foundation of Key Laboratory of the Pearl River Estuarine Dynamics and Associated Process Regulation, Ministry of Water Resources (Grant No.[2017]KJ11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zou, R., Jiang, Q. et al. What maintains seasonal nitrogen limitation in hyper-eutrophic Lake Dianchi? Insights from stoichiometric three-dimensional numerical modeling. Aquat Sci 82, 70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-020-00744-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-020-00744-w