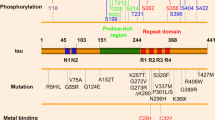
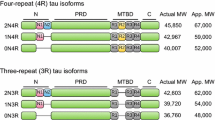
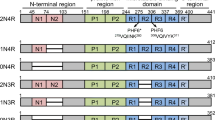
Abstract
Pathological accumulation of the microtubule-associated protein tau, in the form of neurofibrillary tangles, is a major hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, the most prevalent neurodegenerative condition worldwide. In addition to Alzheimer’s disease, a number of neurodegenerative diseases, called tauopathies, are characterized by the accumulation of aggregated tau in a variety of brain regions. While tau normally plays an important role in stabilizing the microtubule network of the cytoskeleton, its dissociation from microtubules and eventual aggregation into pathological deposits is an area of intense focus for therapeutic development. Here we discuss the known cellular factors that affect tau aggregation, from post-translational modifications to molecular chaperones.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Quinlan M, Tung YC, Zaidi MS, Wisniewski HM (1986) Microtubule-associated protein tau. A component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem 261(13):6084–6089
Goedert M (2005) Tau gene mutations and their effects. Mov Disord Off J Mov Disord Soc 20(Suppl 12):S45–S52. doi:10.1002/mds.20539
Powers JM, Byrne NP, Ito M, Takao M, Yankopoulou D, Spillantini MG, Ghetti B (2003) A novel leukoencephalopathy associated with tau deposits primarily in white matter glia. Acta Neuropathol 106(2):181–187. doi:10.1007/s00401-003-0719-9
Spillantini MG, Goedert M, Crowther RA, Murrell JR, Farlow MR, Ghetti B (1997) Familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia: a disease with abundant neuronal and glial tau filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(8):4113–4118
Bird TD, Nochlin D, Poorkaj P, Cherrier M, Kaye J, Payami H, Peskind E, Lampe TH, Nemens E, Boyer PJ, Schellenberg GD (1999) A clinical pathological comparison of three families with frontotemporal dementia and identical mutations in the tau gene (P301L). Brain J Neurol 122(Pt 4):741–756
Dickson DW, Ahmed Z, Algom AA, Tsuboi Y, Josephs KA (2010) Neuropathology of variants of progressive supranuclear palsy. Curr Opin Neurol 23(4):394–400. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e32833be924
Dickson DW, Kouri N, Murray ME, Josephs KA (2011) Neuropathology of frontotemporal lobar degeneration-tau (FTLD-tau). J Molecul Neurosci MN 45(3):384–389. doi:10.1007/s12031-011-9589-0
Togo T, Dickson DW (2002) Tau accumulation in astrocytes in progressive supranuclear palsy is a degenerative rather than a reactive process. Acta Neuropathol 104(4):398–402. doi:10.1007/s00401-002-0569-x
Iwasaki Y, Yoshida M, Hattori M, Goto A, Aiba I, Hashizume Y, Sobue G (2004) Distribution of tuft-shaped astrocytes in the cerebral cortex in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 108(5):399–405. doi:10.1007/s00401-004-0904-5
Munoz DG, Ferrer I (2008) Neuropathology of hereditary forms of frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism. Handbook Clin Neurol 89:393–414. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(07)01237-7
Takeda T, Sato T, Ito T, Sumi Y, Kobayashi T, Kitagawa M, Hirokawa K, Uchihara T (2013) Four-repeat tau-selective deposition in subthalamic nucleus and motor cortex in Alzheimer disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(5):641–643. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.06.030
Neve RL, Harris P, Kosik KS, Kurnit DM, Donlon TA (1986) Identification of cDNA clones for the human microtubule-associated protein tau and chromosomal localization of the genes for tau and microtubule-associated protein 2. Brain Res 387(3):271–280
Majounie E, Cross W, Newsway V, Dillman A, Vandrovcova J, Morris CM, Nalls MA, Ferrucci L, Owen MJ, O’Donovan MC, Cookson, Singleton AB, de Silva R, Morris HR (2013) Variation in tau isoform expression in different brain regions and disease states. Neurobiol Aging 34(7):1922e1912–1922e1927. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.01.017
Andreadis A, Brown WM, Kosik KS (1992) Structure and novel exons of the human tau gene. Biochemistry 31(43):10626–10633
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Cairns NJ, Crowther RA (1992) Tau proteins of Alzheimer paired helical filaments: abnormal phosphorylation of all six brain isoforms. Neuron 8(1):159–168
Barghorn S, Mandelkow E (2002) Toward a unified scheme for the aggregation of tau into Alzheimer paired helical filaments. Biochemistry 41(50):14885–14896
Yoshida H, Crowther RA, Goedert M (2002) Functional effects of tau gene mutations deltaN296 and N296H. J Neurochem 80(3):548–551
Chang E, Kim S, Yin H, Nagaraja HN, Kuret J (2008) Pathogenic missense MAPT mutations differentially modulate tau aggregation propensity at nucleation and extension steps. J Neurochem 107(4):1113–1123. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05692.x
Poorkaj P, Muma NA, Zhukareva V, Cochran EJ, Shannon KM, Hurtig H, Koller WC, Bird TD, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Schellenberg GD (2002) An R5L tau mutation in a subject with a progressive supranuclear palsy phenotype. Ann Neurol 52(4):511–516. doi:10.1002/ana.10340
Alonso Adel C, Mederlyova A, Novak M, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2004) Promotion of hyperphosphorylation by frontotemporal dementia tau mutations. J Biol Chem 279(33):34873–34881. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405131200
Han D, Qureshi HY, Lu Y, Paudel HK (2009) Familial FTDP-17 missense mutations inhibit microtubule assembly-promoting activity of tau by increasing phosphorylation at Ser202 in vitro. J Biol Chem 284(20):13422–13433. doi:10.1074/jbc.M901095200
Conrad C, Andreadis A, Trojanowski JQ, Dickson DW, Kang D, Chen X, Wiederholt W, Hansen L, Masliah E, Thal LJ, Katzman R, Xia Y, Saitoh T (1997) Genetic evidence for the involvement of tau in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 41(2):277–281. doi:10.1002/ana.410410222
Bikkavilli RK, Avasarala S, Van Scoyk M, Karuppusamy Rathinam MK, Tauler J, Borowicz S, Winn RA (2014) In vitro methylation assay to study protein arginine methylation. J Visualized Exp JoVE (92). doi:10.3791/51997
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Petersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaff E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebrand M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski J, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd PR, Hayward N, Kwok JB, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann D, Lynch T, Heutink P (1998) Association of missense and 5’-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393(6686):702–705. doi:10.1038/31508
Rizzu P, Van Swieten JC, Joosse M, Hasegawa M, Stevens M, Tibben A, Niermeijer MF, Hillebrand M, Ravid R, Oostra BA, Goedert M, van Duijn CM, Heutink P (1999) High prevalence of mutations in the microtubule-associated protein tau in a population study of frontotemporal dementia in the Netherlands. Am J Hum Genet 64(2):414–421. doi:10.1086/302256
van Swieten JC, Stevens M, Rosso SM, Rizzu P, Joosse M, de Koning I, Kamphorst W, Ravid R, Spillantini MG, Niermeijer, Heutink P (1999) Phenotypic variation in hereditary frontotemporal dementia with tau mutations. Ann Neurol 46(4):617–626
Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Bruce J, Richter-Landsberg C, Zhang B, Hong M, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2000) Distinct FTDP-17 missense mutations in tau produce tau aggregates and other pathological phenotypes in transfected CHO cells. Mol Biol Cell 11(12):4093–4104
Miyasaka T, Morishima-Kawashima M, Ravid R, Heutink P, van Swieten JC, Nagashima K, Ihara Y (2001) Molecular analysis of mutant and wild-type tau deposited in the brain affected by the FTDP-17 R406W mutation. Am J Pathol 158(2):373–379. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63979-X
Saito Y, Geyer A, Sasaki R, Kuzuhara S, Nanba E, Miyasaka T, Suzuki K, Murayama S (2002) Early-onset, rapidly progressive familial tauopathy with R406W mutation. Neurology 58(5):811–813
Rosso SM, van Herpen E, Pijnenburg YA, Schoonenboom NS, Scheltens P, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (2003) Total tau and phosphorylated tau 181 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with frontotemporal dementia due to P301L and G272V tau mutations. Arch Neurol 60(9):1209–1213. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.9.1209
Rademakers R, Dermaut B, Peeters K, Cruts M, Heutink P, Goate A, Van Broeckhoven C (2003) Tau (MAPT) mutation Arg406Trp presenting clinically with Alzheimer disease does not share a common founder in Western Europe. Hum Mutat 22(5):409–411. doi:10.1002/humu.10269
Ostojic J, Elfgren C, Passant U, Nilsson K, Gustafson L, Lannfelt L, Froelich Fabre S (2004) The tau R406W mutation causes progressive presenile dementia with bitemporal atrophy. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17(4):298–301. doi:10.1159/000077158
Passant U, Ostojic J, Froelich Fabre S, Gustafson L, Lannfelt L, Larsson EM, Nilsson K, Rosen I, Elfgren C (2004) Familial presenile dementia with bitemporal atrophy. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17(4):287–292. doi:10.1159/000077156
Lindquist SG, Holm IE, Schwartz M, Law I, Stokholm J, Batbayli M, Waldemar G, Nielsen JE (2008) Alzheimer disease-like clinical phenotype in a family with FTDP-17 caused by a MAPT R406 W mutation. Euro J Neurol Off J Euro Fed Neurol Soc 15(4):377–385. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2008.02069.x
Ikeuchi T, Kaneko H, Miyashita A, Nozaki H, Kasuga K, Tsukie T, Tsuchiya M, Imamura T, Ishizu H, Aoki K, Ishikawa A, Onodera O, Kuwano R, Nishizawa M (2008) Mutational analysis in early-onset familial dementia in the Japanese population. The role of PSEN1 and MAPT R406W mutations. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 26(1):43–49. doi:10.1159/000141483
Lindquist SG, Schwartz M, Batbayli M, Waldemar G, Nielsen JE (2009) Genetic testing in familial AD and FTD: mutation and phenotype spectrum in a Danish cohort. Clin Genet 76(2):205–209. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2009.01191.x
Dumanchin C, Camuzat A, Campion D, Verpillat P, Hannequin D, Dubois B, Saugier-Veber P, Martin C, Penet C, Charbonnier F, Agid Y, Frebourg T, Brice A (1998) Segregation of a missense mutation in the microtubule-associated protein tau gene with familial frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism. Hum Mol Genet 7(11):1825–1829
Clark LN, Poorkaj P, Wszolek Z, Geschwind DH, Nasreddine ZS, Miller B, Li D, Payami H, Awert F, Markopoulou K, Andreadis A, D’Souza I, Lee VM, Reed L, Trojanowski JQ, Zhukareva V, Bird T, Schellenberg G, Wilhelmsen KC (1998) Pathogenic implications of mutations in the tau gene in pallido-ponto-nigral degeneration and related neurodegenerative disorders linked to chromosome 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(22):13103–13107
Spillantini MG, Goedert M (1998) Tau protein pathology in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 21(10):428–433
Mirra SS, Murrell JR, Gearing M, Spillantini MG, Goedert M, Crowther RA, Levey AI, Jones R, Green J, Shoffner JM, Wainer BH, Schmidt ML, Trojanowski JQ, Ghetti B (1999) Tau pathology in a family with dementia and a P301L mutation in tau. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58(4):335–345
Nasreddine ZS, Loginov M, Clark LN, Lamarche J, Miller BL, Lamontagne A, Zhukareva V, Lee VM, Wilhelmsen KC, Geschwind DH (1999) From genotype to phenotype: a clinical pathological, and biochemical investigation of frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism (FTDP-17) caused by the P301L tau mutation. Ann Neurol 45(6):704–715
Houlden H, Baker M, Adamson J, Grover A, Waring S, Dickson D, Lynch T, Boeve B, Petersen RC, Pickering-Brown S, Owen F, Neary D, Craufurd D, Snowden J, Mann D, Hutton M (1999) Frequency of tau mutations in three series of non-Alzheimer’s degenerative dementia. Ann Neurol 46(2):243–248
Kodama K, Okada S, Iseki E, Kowalska A, Tabira T, Hosoi N, Yamanouchi N, Noda S, Komatsu N, Nakazato M, Kumakiri C, Yazaki M, Sato T (2000) Familial frontotemporal dementia with a P301L tau mutation in Japan. J Neurol Sci 176(1):57–64
Tanaka R, Kobayashi T, Motoi Y, Anno M, Mizuno Y, Mori H (2000) A case of frontotemporal dementia with tau P301L mutation in the Far East. J Neurol 247(9):705–707
Rizzu P, Joosse M, Ravid R, Hoogeveen A, Kamphorst W, van Swieten JC, Willemsen R, Heutink P (2000) Mutation-dependent aggregation of tau protein and its selective depletion from the soluble fraction in brain of P301L FTDP-17 patients. Hum Mol Genet 9(20):3075–3082
von Bergen M, Barghorn S, Li L, Marx A, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2001) Mutations of tau protein in frontotemporal dementia promote aggregation of paired helical filaments by enhancing local beta-structure. J Biol Chem 276(51):48165–48174. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105196200
Poorkaj P, Grossman M, Steinbart E, Payami H, Sadovnick A, Nochlin D, Tabira T, Trojanowski JQ, Borson S, Galasko D, Reich S, Quinn B, Schellenberg G, Bird TD (2001) Frequency of tau gene mutations in familial and sporadic cases of non-Alzheimer dementia. Arch Neurol 58(3):383–387
Kowalska A, Asada T, Arima K, Kumakiri C, Kozubski W, Takahashi K, Tabira T (2001) Genetic analysis in patients with familial and sporadic frontotemporal dementia: two tau mutations in only familial cases and no association with apolipoprotein epsilon4. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 12(6):387–392 (51285)
Kobayashi T, Mori H, Okuma Y, Dickson DW, Cookson N, Tsuboi Y, Motoi Y, Tanaka R, Miyashita N, Anno M, Narabayashi H, Mizuno Y (2002) Contrasting genotypes of the tau gene in two phenotypically distinct patients with P301L mutation of frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17. J Neurol 249(6):669–675. doi:10.1007/s00415-002-0687-3
Walker RH, Friedman J, Wiener J, Hobler R, Gwinn-Hardy K, Adam A, DeWolfe J, Gibbs R, Baker M, Farrer M, Hutton M, Hardy J (2002) A family with a tau P301L mutation presenting with parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Related Disorders 9(2):121–123
Binetti G, Nicosia F, Benussi L, Ghidoni R, Feudatari E, Barbiero L, Signorini S, Villa A, Mattioli F, Zanetti O, Alberici A (2003) Prevalence of TAU mutations in an Italian clinical series of familial frontotemporal patients. Neurosci Lett 338(1):85–87
Sobrido MJ, Miller BL, Havlioglu N, Zhukareva V, Jiang Z, Nasreddine ZS, Lee VM, Chow TW, Wilhelmsen KC, Cummings JL, Wu JY, Geschwind DH (2003) Novel tau polymorphisms, tau haplotypes, and splicing in familial and sporadic frontotemporal dementia. Arch Neurol 60(5):698–702. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.5.698
Stanford PM, Brooks WS, Teber ET, Hallupp M, McLean C, Halliday GM, Martins RN, Kwok JB, Schofield PR (2004) Frequency of tau mutations in familial and sporadic frontotemporal dementia and other tauopathies. J Neurol 251(9):1098–1104. doi:10.1007/s00415-004-0489-x
Benussi L, Ghidoni R, Paterlini A, Nicosia F, Alberici AC, Signorini S, Barbiero L, Binetti G (2005) Interaction between tau and alpha-synuclein proteins is impaired in the presence of P301L tau mutation. Exp Cell Res 308(1):78–84. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.04.021
Llado A, Sanchez-Valle R, Rey MJ, Ezquerra M, Tolosa E, Ferrer I, Molinuevo JL, Catalan collaborative Study Group for F (2008) Clinicopathological and genetic correlates of frontotemporal lobar degeneration and corticobasal degeneration. J Neurol 255(4):488–494. doi:10.1007/s00415-008-0565-8
Lopez de Munain A, Alzualde A, Gorostidi A, Otaegui D, Ruiz-Martinez J, Indakoetxea B, Ferrer I, Perez-Tur J, Saenz A, Bergareche A, Barandiaran M, Poza JJ, Zabalza R, Ruiz I, Urtasun M, Fernandez-Manchola I, Olasagasti B, Espinal JB, Olaskoaga J, Ruibal M, Moreno F, Carrera N, Marti Masso JF (2008) Mutations in progranulin gene: clinical, pathological, and ribonucleic acid expression findings. Biol Psychiatry 63(10):946–952. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.08.015
Bugiani O, Murrell JR, Giaccone G, Hasegawa M, Ghigo G, Tabaton M, Morbin M, Primavera A, Carella F, Solaro C, Grisoli M, Savoiardo M, Spillantini MG, Tagliavini F, Goedert M, Ghetti B (1999) Frontotemporal dementia and corticobasal degeneration in a family with a P301S mutation in tau. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58(6):667–677
Sperfeld AD, Collatz MB, Baier H, Palmbach M, Storch A, Schwarz J, Tatsch K, Reske S, Joosse M, Heutink P, Ludolph AC (1999) FTDP-17: an early-onset phenotype with parkinsonism and epileptic seizures caused by a novel mutation. Ann Neurol 46(5):708–715
Yasuda M, Yokoyama K, Nakayasu T, Nishimura Y, Matsui M, Yokoyama T, Miyoshi K, Tanaka C (2000) A Japanese patient with frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism by a tau P301S mutation. Neurology 55(8):1224–1227
Morris HR, Schrag A, Nath U, Burn D, Quinn NP, Daniel S, Wood NW, Lees AJ (2001) Effect of ApoE and tau on age of onset of progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy. Neurosci Lett 312(2):118–120
Lossos A, Reches A, Gal A, Newman JP, Soffer D, Gomori JM, Boher M, Ekstein D, Biran I, Meiner Z, Abramsky O, Rosenmann H (2003) Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism with the P301S tau gene mutation in a Jewish family. J Neurol 250(6):733–740. doi:10.1007/s00415-003-1074-4
Huey ED, Grafman J, Wassermann EM, Pietrini P, Tierney MC, Ghetti B, Spina S, Baker M, Hutton M, Elder JW, Berger SL, Heflin KA, Hardy J, Momeni P (2006) Characteristics of frontotemporal dementia patients with a Progranulin mutation. Ann Neurol 60(3):374–380. doi:10.1002/ana.20969
Han D, Paudel HK (2009) FTDP-17 missense mutations site-specifically inhibit as well as promote dephosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau by protein phosphatases of HEK-293 cell extract. Neurochem Int 54(1):14–27. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2008.09.014
Heutink P, Stevens M, Rizzu P, Bakker E, Kros JM, Tibben A, Niermeijer MF, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, van Swieten JC (1997) Hereditary frontotemporal dementia is linked to chromosome 17q21-q22: a genetic and clinicopathological study of three Dutch families. Ann Neurol 41(2):150–159. doi:10.1002/ana.410410205
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Kamphorst W, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (1998) Tau pathology in two Dutch families with mutations in the microtubule-binding region of tau. Am J Pathol 153(5):1359–1363. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65721-5
Bronner IF, ter Meulen BC, Azmani A, Severijnen LA, Willemsen R, Kamphorst W, Ravid R, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (2005) Hereditary Pick’s disease with the G272V tau mutation shows predominant three-repeat tau pathology. Brain : a journal of neurology 128(Pt 11):2645–2653. doi:10.1093/brain/awh591
Neumann M, Diekmann S, Bertsch U, Vanmassenhove B, Bogerts B, Kretzschmar HA (2005) Novel G335V mutation in the tau gene associated with early onset familial frontotemporal dementia. Neurogenetics 6(2):91–95. doi:10.1007/s10048-005-0210-y
Arima K, Kowalska A, Hasegawa M, Mukoyama M, Watanabe R, Kawai M, Takahashi K, Iwatsubo T, Tabira T, Sunohara N (2000) Two brothers with frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism with an N279K mutation of the tau gene. Neurology 54(9):1787–1795
Rossi G, Gasparoli E, Pasquali C, Di Fede G, Testa D, Albanese A, Bracco F, Tagliavini F (2004) Progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease in a family with a new mutation in the tau gene. Ann Neurol 55(3):448. doi:10.1002/ana.20006
Ros R, Thobois S, Streichenberger N, Kopp N, Sanchez MP, Perez M, Hoenicka J, Avila J, Honnorat J, de Yebenes JG (2005) A new mutation of the tau gene, G303V, in early-onset familial progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 62(9):1444–1450. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.9.1444
Neumann M, Mittelbronn M, Simon P, Vanmassenhove B, de Silva R, Lees A, Klapp J, Meyermann R, Kretzschmar HA (2005) A new family with frontotemporal dementia with intronic 10+3 splice site mutation in the tau gene: neuropathology and molecular effects. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 31(4):362–373. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2005.00629.x
Iseki E, Matsumura T, Marui W, Hino H, Odawara T, Sugiyama N, Suzuki K, Sawada H, Arai T, Kosaka K (2001) Familial frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism with a novel N296H mutation in exon 10 of the tau gene and a widespread tau accumulation in the glial cells. Acta Neuropathol 102(3):285–292
Grover A, England E, Baker M, Sahara N, Adamson J, Granger B, Houlden H, Passant U, Yen SH, DeTure M, Hutton M (2003) A novel tau mutation in exon 9 (1260 V) causes a four-repeat tauopathy. Exp Neurol 184(1):131–140
Hogg M, Grujic ZM, Baker M, Demirci S, Guillozet AL, Sweet AP, Herzog LL, Weintraub S, Mesulam MM, LaPointe NE, Gamblin TC, Berry RW, Binder LI, de Silva R, Lees A, Espinoza M, Davies P, Grover A, Sahara N, Ishizawa T, Dickson D, Yen SH, Hutton M, Bigio EH (2003) The L266 V tau mutation is associated with frontotemporal dementia and Pick-like 3R and 4R tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol 106(4):323–336. doi:10.1007/s00401-003-0734-x
Kobayashi T, Ota S, Tanaka K, Ito Y, Hasegawa M, Umeda Y, Motoi Y, Takanashi M, Yasuhara M, Anno M, Mizuno Y, Mori H (2003) A novel L266 V mutation of the tau gene causes frontotemporal dementia with a unique tau pathology. Ann Neurol 53(1):133–137. doi:10.1002/ana.10447
Hayashi S, Toyoshima Y, Hasegawa M, Umeda Y, Wakabayashi K, Tokiguchi S, Iwatsubo T, Takahashi H (2002) Late-onset frontotemporal dementia with a novel exon 1 (Arg5His) tau gene mutation. Ann Neurol 51(4):525–530
Hutton M (2000) “Missing” tau mutation identified. Ann Neurol 47(4):417–418
Yasuda M, Takamatsu J, D’Souza I, Crowther RA, Kawamata T, Hasegawa M, Hasegawa H, Spillantini MG, Tanimukai S, Poorkaj P, Varani L, Varani G, Iwatsubo T, Goedert M, Schellenberg DG, Tanaka C (2000) A novel mutation at position +12 in the intron following exon 10 of the tau gene in familial frontotemporal dementia (FTD-Kumamoto). Ann Neurol 47(4):422–429
Pickering-Brown SM, Richardson AM, Snowden JS, McDonagh AM, Burns A, Braude W, Baker M, Liu WK, Yen SH, Hardy J, Hutton M, Davies Y, Allsop D, Craufurd D, Neary D, Mann DM (2002) Inherited frontotemporal dementia in nine British families associated with intronic mutations in the tau gene. Brain J Neurol 125(Pt 4):732–751
Barghorn S, Biernat J, Mandelkow E (2005) Purification of recombinant tau protein and preparation of Alzheimer-paired helical filaments in vitro. Methods Mol Biol 299:35–51
Barghorn S, Zheng-Fischhofer Q, Ackmann M, Biernat J, von Bergen M, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2000) Structure, microtubule interactions, and paired helical filament aggregation by tau mutants of frontotemporal dementias. Biochemistry 39(38):11714–11721
von Bergen M, Barghorn S, Jeganathan S, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2006) Spectroscopic approaches to the conformation of tau protein in solution and in paired helical filaments. Neuro Degener Dis 3(4–5):197–206. doi:10.1159/000095257
von Bergen M, Friedhoff P, Biernat J, Heberle J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2000) Assembly of tau protein into Alzheimer paired helical filaments depends on a local sequence motif ((306)VQIVYK(311)) forming beta structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(10):5129–5134
von Bergen M, Li L, Mandelkow E (2005) Intrinsic fluorescent detection of tau conformation and aggregation. Methods Mol Biol 299:175–184
Biernat J, Gustke N, Drewes G, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (1993) Phosphorylation of Ser262 strongly reduces binding of tau to microtubules: distinction between PHF-like immunoreactivity and microtubule binding. Neuron 11(1):153–163
Schweers O, Schonbrunn-Hanebeck E, Marx A, Mandelkow E (1994) Structural studies of tau protein and Alzheimer paired helical filaments show no evidence for beta-structure. J Biol Chem 269(39):24290–24297
Mylonas E, Hascher A, Bernado P, Blackledge M, Mandelkow E, Svergun DI (2008) Domain conformation of tau protein studied by solution small-angle X-ray scattering. Biochemistry 47(39):10345–10353. doi:10.1021/bi800900d
Jeganathan S, von Bergen M, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (2008) The natively unfolded character of tau and its aggregation to Alzheimer-like paired helical filaments. Biochemistry 47(40):10526–10539. doi:10.1021/bi800783d
Uversky VN (2002) Natively unfolded proteins: a point where biology waits for physics. Protein Sci Publ Protein Soc 11(4):739–756. doi:10.1110/ps.4210102
Jicha GA, Bowser R, Kazam IG, Davies P (1997) Alz-50 and MC-1, a new monoclonal antibody raised to paired helical filaments, recognize conformational epitopes on recombinant tau. J Neurosci Res 48(2):128–132
Carmel G, Mager EM, Binder LI, Kuret J (1996) The structural basis of monoclonal antibody Alz50’s selectivity for Alzheimer’s disease pathology. J Biol Chem 271(51):32789–32795
Jeganathan S, von Bergen M, Brutlach H, Steinhoff HJ, Mandelkow E (2006) Global hairpin folding of tau in solution. Biochemistry 45(7):2283–2293. doi:10.1021/bi0521543
Mukrasch MD, Bibow S, Korukottu J, Jeganathan S, Biernat J, Griesinger C, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2009) Structural polymorphism of 441-residue tau at single residue resolution. PLoS Biol 7(2):e34. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000034
Elbaum-Garfinkle S, Rhoades E (2012) Identification of an aggregation-prone structure of tau. J Am Chem Soc 134(40):16607–16613. doi:10.1021/ja305206m
Weingarten MD, Lockwood AH, Hwo SY, Kirschner MW (1975) A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72(5):1858–1862
Goode BL, Denis PE, Panda D, Radeke MJ, Miller HP, Wilson L, Feinstein SC (1997) Functional interactions between the proline-rich and repeat regions of tau enhance microtubule binding and assembly. Mol Biol Cell 8(2):353–365
Breuzard G, Hubert P, Nouar R, De Bessa T, Devred F, Barbier P, Sturgis JN, Peyrot V (2013) Molecular mechanisms of Tau binding to microtubules and its role in microtubule dynamics in live cells. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 13):2810–2819. doi:10.1242/jcs.120832
Bunker JM, Wilson L, Jordan MA, Feinstein SC (2004) Modulation of microtubule dynamics by tau in living cells: implications for development and neurodegeneration. Mol Biol Cell 15(6):2720–2728. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-01-0062
Choi MC, Raviv U, Miller HP, Gaylord MR, Kiris E, Ventimiglia D, Needleman DJ, Kim MW, Wilson L, Feinstein SC, Safinya CR (2009) Human microtubule-associated-protein tau regulates the number of protofilaments in microtubules: a synchrotron x-ray scattering study. Biophys J 97(2):519–527. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2009.04.047
Panda D, Samuel JC, Massie M, Feinstein SC, Wilson L (2003) Differential regulation of microtubule dynamics by three- and four-repeat tau: implications for the onset of neurodegenerative disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(16):9548–9553. doi:10.1073/pnas.1633508100
Fischer D, Mukrasch MD, von Bergen M, Klos-Witkowska A, Biernat J, Griesinger C, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2007) Structural and microtubule binding properties of tau mutants of frontotemporal dementias. Biochemistry 46(10):2574–2582. doi:10.1021/bi061318s
van Herpen E, Rosso SM, Serverijnen LA, Yoshida H, Breedveld G, van de Graaf R, Kamphorst W, Ravid R, Willemsen R, Dooijes D, Majoor-Krakauer D, Kros JM, Crowther RA, Goedert M, Heutink P, van Swieten JC (2003) Variable phenotypic expression and extensive tau pathology in two families with the novel tau mutation L315R. Ann Neurol 54(5):573–581. doi:10.1002/ana.10721
Hasegawa M, Smith MJ, Goedert M (1998) Tau proteins with FTDP-17 mutations have a reduced ability to promote microtubule assembly. FEBS Lett 437(3):207–210
Hasegawa M, Smith MJ, Iijima M, Tabira T, Goedert M (1999) FTDP-17 mutations N279 K and S305 N in tau produce increased splicing of exon 10. FEBS Lett 443(2):93–96
Iyer A, Lapointe NE, Zielke K, Berdynski M, Guzman E, Barczak A, Chodakowska-Zebrowska M, Barcikowska M, Feinstein S, Zekanowski C (2013) A novel MAPT mutation, G55R, in a frontotemporal dementia patient leads to altered Tau function. PLoS ONE 8(9):e76409. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076409
Pooler AM, Usardi A, Evans CJ, Philpott KL, Noble W, Hanger DP (2012) Dynamic association of tau with neuronal membranes is regulated by phosphorylation. Neurobiol Aging 33(2):431e427–431e438. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.01.005
Brandt R, Leger J, Lee G (1995) Interaction of tau with the neural plasma membrane mediated by tau’s amino-terminal projection domain. J Cell Biol 131(5):1327–1340
Dixit R, Ross JL, Goldman YE, Holzbaur EL (2008) Differential regulation of dynein and kinesin motor proteins by tau. Science 319(5866):1086–1089. doi:10.1126/science.1152993
Yu D, LaPointe NE, Guzman E, Pessino V, Wilson L, Feinstein SC, Valentine MT (2014) Tau proteins harboring neurodegeneration-linked mutations impair kinesin translocation in vitro. J Alzheimer’s Dis JAD 39(2):301–314. doi:10.3233/JAD-131274
Gilley J, Seereeram A, Ando K, Mosely S, Andrews S, Kerschensteiner M, Misgeld T, Brion JP, Anderton B, Hanger DP, Coleman MP (2012) Age-dependent axonal transport and locomotor changes and tau hypophosphorylation in a “P301L” tau knockin mouse. Neurobiol Aging 33(3):621e615–621e621. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.02.014
Zhang B, Higuchi M, Yoshiyama Y, Ishihara T, Forman MS, Martinez D, Joyce S, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2004) Retarded axonal transport of R406 W mutant tau in transgenic mice with a neurodegenerative tauopathy. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 24(19):4657–4667. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0797-04.2004
Loomis PA, Howard TH, Castleberry RP, Binder LI (1990) Identification of nuclear tau isoforms in human neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87(21):8422–8426
Sultan A, Nesslany F, Violet M, Begard S, Loyens A, Talahari S, Mansuroglu Z, Marzin D, Sergeant N, Humez S, Colin M, Bonnefoy E, Buee L, Galas MC (2011) Nuclear tau, a key player in neuronal DNA protection. J Biol Chem 286(6):4566–4575. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.199976
Sjoberg MK, Shestakova E, Mansuroglu Z, Maccioni RB, Bonnefoy E (2006) Tau protein binds to pericentromeric DNA: a putative role for nuclear tau in nucleolar organization. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 10):2025–2034. doi:10.1242/jcs.02907
Sugino E, Nishiura C, Minoura K, In Y, Sumida M, Taniguchi T, Tomoo K, Ishida T (2009) Three-/four-repeat-dependent aggregation profile of tau microtubule-binding domain clarified by dynamic light scattering analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385(2):236–240. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.047
von Bergen M, Barghorn S, Muller SA, Pickhardt M, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Davies P, Aebi U, Mandelkow E (2006) The core of tau-paired helical filaments studied by scanning transmission electron microscopy and limited proteolysis. Biochemistry 45(20):6446–6457. doi:10.1021/bi052530j
Necula M, Kuret J (2004) A static laser light scattering assay for surfactant-induced tau fibrillization. Anal Biochem 333(2):205–215. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2004.05.044
Necula M, Kuret J (2004) Electron microscopy as a quantitative method for investigating tau fibrillization. Anal Biochem 329(2):238–246. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2004.02.023
Lippens G, Sillen A, Smet C, Wieruszeski JM, Leroy A, Buee L, Landrieu I (2006) Studying the natively unfolded neuronal Tau protein by solution NMR spectroscopy. Protein Pept Lett 13(3):235–246
Akoury E, Pickhardt M, Gajda M, Biernat J, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2013) Mechanistic basis of phenothiazine-driven inhibition of Tau aggregation. Angew Chem 52(12):3511–3515. doi:10.1002/anie.201208290
Daebel V, Chinnathambi S, Biernat J, Schwalbe M, Habenstein B, Loquet A, Akoury E, Tepper K, Muller H, Baldus M, Griesinger C, Zweckstetter M, Mandelkow E, Vijayan V, Lange A (2012) beta-Sheet core of tau paired helical filaments revealed by solid-state NMR. J Am Chem Soc 134(34):13982–13989. doi:10.1021/ja305470p
Ramachandran G, Udgaonkar JB (2013) Mechanistic studies unravel the complexity inherent in tau aggregation leading to Alzheimer’s disease and the tauopathies. Biochemistry 52(24):4107–4126. doi:10.1021/bi400209z
Perez M, Valpuesta JM, Medina M, Montejo de Garcini E, Avila J (1996) Polymerization of tau into filaments in the presence of heparin: the minimal sequence required for tau-tau interaction. J Neurochem 67(3):1183–1190
Goedert M, Jakes R, Spillantini MG, Hasegawa M, Smith MJ, Crowther RA (1996) Assembly of microtubule-associated protein tau into Alzheimer-like filaments induced by sulphated glycosaminoglycans. Nature 383(6600):550–553. doi:10.1038/383550a0
Kampers T, Friedhoff P, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (1996) RNA stimulates aggregation of microtubule-associated protein tau into Alzheimer-like paired helical filaments. FEBS Lett 399(3):344–349
Kampers T, Pangalos M, Geerts H, Wiech H, Mandelkow E (1999) Assembly of paired helical filaments from mouse tau: implications for the neurofibrillary pathology in transgenic mouse models for Alzheimer’s disease. FEBS Lett 451(1):39–44
Gamblin TC, King ME, Dawson H, Vitek MP, Kuret J, Berry RW, Binder LI (2000) In vitro polymerization of tau protein monitored by laser light scattering: method and application to the study of FTDP-17 mutants. Biochemistry 39(20):6136–6144
King ME, Ahuja V, Binder LI, Kuret J (1999) Ligand-dependent tau filament formation: implications for Alzheimer’s disease progression. Biochemistry 38(45):14851–14859
Alonso A, Zaidi T, Novak M, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2001) Hyperphosphorylation induces self-assembly of tau into tangles of paired helical filaments/straight filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(12):6923–6928. doi:10.1073/pnas.121119298
Wang JZ, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2007) Kinases and phosphatases and tau sites involved in Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration. Euro J Neurosci 25(1):59–68. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05226.x
Nath A, Sammalkorpi M, DeWitt DC, Trexler AJ, Elbaum-Garfinkle S, O’Hern CS, Rhoades E (2012) The conformational ensembles of alpha-synuclein and tau: combining single-molecule FRET and simulations. Biophys J 103(9):1940–1949. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2012.09.032
Eliezer D, Barre P, Kobaslija M, Chan D, Li X, Heend L (2005) Residual structure in the repeat domain of tau: echoes of microtubule binding and paired helical filament formation. Biochemistry 44(3):1026–1036. doi:10.1021/bi048953n
Yu X, Luo Y, Dinkel P, Zheng J, Wei G, Margittai M, Nussinov R, Ma B (2012) Cross-seeding and conformational selection between three- and four-repeat human Tau proteins. J Biol Chem 287(18):14950–14959. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.340794
Luo Y, Ma B, Nussinov R, Wei G (2014) Structural insight into tau protein’s paradox of intrinsically disordered behavior, self-acetylation activity, and aggregation. J Phys Chem Lett 5(17):3026–3031. doi:10.1021/jz501457f
Perez M, Arrasate M, Montejo De Garcini E, Munoz V, Avila J (2001) In vitro assembly of tau protein: mapping the regions involved in filament formation. Biochemistry 40(20):5983–5991
Abraha A, Ghoshal N, Gamblin TC, Cryns V, Berry RW, Kuret J, Binder LI (2000) C-terminal inhibition of tau assembly in vitro and in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 21):3737–3745
Sergeant N, Bretteville A, Hamdane M, Caillet-Boudin ML, Grognet P, Bombois S, Blum D, Delacourte A, Pasquier F, Vanmechelen E, Schraen-Maschke S, Buee L (2008) Biochemistry of Tau in Alzheimer’s disease and related neurological disorders. Expert Rev Proteomic 5(2):207–224. doi:10.1586/14789450.5.2.207
Bramblett GT, Goedert M, Jakes R, Merrick SE, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1993) Abnormal tau phosphorylation at Ser396 in Alzheimer’s disease recapitulates development and contributes to reduced microtubule binding. Neuron 10(6):1089–1099
Yoshida H, Ihara Y (1993) Tau in paired helical filaments is functionally distinct from fetal tau: assembly incompetence of paired helical filament-tau. J Neurochem 61(3):1183–1186
Poppek D, Keck S, Ermak G, Jung T, Stolzing A, Ullrich O, Davies KJ, Grune T (2006) Phosphorylation inhibits turnover of the tau protein by the proteasome: influence of RCAN1 and oxidative stress. Biochem J 400(3):511–520. doi:10.1042/BJ20060463
Watanabe A, Hasegawa M, Suzuki M, Takio K, Morishima-Kawashima M, Titani K, Arai T, Kosik KS, Ihara Y (1993) In vivo phosphorylation sites in fetal and adult rat tau. J Biol Chem 268(34):25712–25717
Liu MC, Kobeissy F, Zheng W, Zhang Z, Hayes RL, Wang KK (2011) Dual vulnerability of tau to calpains and caspase-3 proteolysis under neurotoxic and neurodegenerative conditions. ASN Neuro 3(1):e00051. doi:10.1042/AN20100012
Takahashi RH, Capetillo-Zarate E, Lin MT, Milner TA, Gouras GK (2010) Co-occurrence of Alzheimer’s disease ss-amyloid and tau pathologies at synapses. Neurobiol Aging 31(7):1145–1152. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.07.021
Hanger DP, Hughes K, Woodgett JR, Brion JP, Anderton BH (1992) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 induces Alzheimer’s disease-like phosphorylation of tau: generation of paired helical filament epitopes and neuronal localisation of the kinase. Neurosci Lett 147(1):58–62
Vega IE, Cui L, Propst JA, Hutton ML, Lee G, Yen SH (2005) Increase in tau tyrosine phosphorylation correlates with the formation of tau aggregates. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 138(2):135–144. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.04.015
Dolan PJ, Johnson GV (2010) The role of tau kinases in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel 13(5):595–603
Lee VM, Brunden KR, Hutton M, Trojanowski JQ (2011) Developing therapeutic approaches to tau, selected kinases, and related neuronal protein targets. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med 1(1):a006437. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a006437
Martin L, Latypova X, Wilson CM, Magnaudeix A, Perrin ML, Yardin C, Terro F (2013) Tau protein kinases: involvement in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 12(1):289–309. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2012.06.003
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Quinlan M, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI (1986) Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83(13):4913–4917
Augustinack JC, Schneider A, Mandelkow EM, Hyman BT (2002) Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 103(1):26–35
Crowther RA, Olesen OF, Smith MJ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1994) Assembly of Alzheimer-like filaments from full-length tau protein. FEBS Lett 337(2):135–138
Montejo de Garcini E, Serrano L, Avila J (1986) Self assembly of microtubule associated protein tau into filaments resembling those found in Alzheimer disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 141(2):790–796
Wille H, Drewes G, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (1992) Alzheimer-like paired helical filaments and antiparallel dimers formed from microtubule-associated protein tau in vitro. J Cell Biol 118(3):573–584
Dolai S, Shi W, Corbo C, Sun C, Averick S, Obeysekera D, Farid M, Alonso A, Banerjee P, Raja K (2011) “Clicked” sugar-curcumin conjugate: modulator of amyloid-beta and tau peptide aggregation at ultralow concentrations. ACS Chem Neurosci 2(12):694–699. doi:10.1021/cn200088r
Haase C, Stieler JT, Arendt T, Holzer M (2004) Pseudophosphorylation of tau protein alters its ability for self-aggregation. J Neurochem 88(6):1509–1520
Paudel HK (1997) The regulatory Ser262 of microtubule-associated protein tau is phosphorylated by phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem 272(3):1777–1785
Preuss U, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (1997) The ‘jaws’ model of tau-microtubule interaction examined in CHO cells. J Cell Sci 110(Pt 6):789–800
Gartner U, Janke C, Holzer M, Vanmechelen E, Arendt T (1998) Postmortem changes in the phosphorylation state of tau-protein in the rat brain. Neurobiol Aging 19(6):535–543
Luna-Munoz J, Chavez-Macias L, Garcia-Sierra F, Mena R (2007) Earliest stages of tau conformational changes are related to the appearance of a sequence of specific phospho-dependent tau epitopes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis JAD 12(4):365–375
Li T, Paudel HK (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta phosphorylates Alzheimer’s disease-specific Ser396 of microtubule-associated protein tau by a sequential mechanism. Biochemistry 45(10):3125–3133. doi:10.1021/bi051634r
Porzig R, Singer D, Hoffmann R (2007) Epitope mapping of mAbs AT8 and Tau5 directed against hyperphosphorylated regions of the human tau protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358(2):644–649. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.187
Otvos L Jr, Feiner L, Lang E, Szendrei GI, Goedert M, Lee VM (1994) Monoclonal antibody PHF-1 recognizes tau protein phosphorylated at serine residues 396 and 404. J Neurosci Res 39(6):669–673. doi:10.1002/jnr.490390607
Rankin CA, Sun Q, Gamblin TC (2005) Pseudo-phosphorylation of tau at Ser202 and Thr205 affects tau filament formation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 138(1):84–93. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.04.012
Rankin CA, Sun Q, Gamblin TC (2007) Tau phosphorylation by GSK-3beta promotes tangle-like filament morphology. Molecul Neurodegen 2:12. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-2-12
Connell JW, Gibb GM, Betts JC, Blackstock WP, Gallo J, Lovestone S, Hutton M, Anderton BH (2001) Effects of FTDP-17 mutations on the in vitro phosphorylation of tau by glycogen synthase kinase 3beta identified by mass spectrometry demonstrate certain mutations exert long-range conformational changes. FEBS Lett 493(1):40–44
Min SW, Cho SH, Zhou Y, Schroeder S, Haroutunian V, Seeley WW, Huang EJ, Shen Y, Masliah E, Mukherjee C, Meyers D, Cole PA, Ott M, Gan L (2010) Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy. Neuron 67(6):953–966. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.044
Cohen TJ, Guo JL, Hurtado DE, Kwong LK, Mills IP, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2011) The acetylation of tau inhibits its function and promotes pathological tau aggregation. Nature Commun 2:252. doi:10.1038/ncomms1255
Cook C, Carlomagno Y, Gendron TF, Dunmore J, Scheffel K, Stetler C, Davis M, Dickson D, Jarpe M, DeTure M, Petrucelli L (2014) Acetylation of the KXGS motifs in tau is a critical determinant in modulation of tau aggregation and clearance. Hum Mol Genet 23(1):104–116. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddt402
Ding H, Dolan PJ, Johnson GV (2008) Histone deacetylase 6 interacts with the microtubule-associated protein tau. J Neurochem 106(5):2119–2130. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05564.x
Cook C, Gendron TF, Scheffel K, Carlomagno Y, Dunmore J, DeTure M, Petrucelli L (2012) Loss of HDAC6, a novel CHIP substrate, alleviates abnormal tau accumulation. Hum Mol Genet 21(13):2936–2945. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds125
Xiong Y, Zhao K, Wu J, Xu Z, Jin S, Zhang YQ (2013) HDAC6 mutations rescue human tau-induced microtubule defects in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(12):4604–4609. doi:10.1073/pnas.1207586110
Julien C, Tremblay C, Phivilay A, Berthiaume L, Emond V, Julien P, Calon F (2010) High-fat diet aggravates amyloid-beta and tau pathologies in the 3xTg-AD mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 31(9):1516–1531. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.08.022
Cohen TJ, Friedmann D, Hwang AW, Marmorstein R, Lee VM (2013) The microtubule-associated tau protein has intrinsic acetyltransferase activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20(6):756–762. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2555
Kamah A, Huvent I, Cantrelle FX, Qi H, Lippens G, Landrieu I, Smet-Nocca C (2014) Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of the acetylation pattern of the neuronal Tau protein. Biochemistry 53(18):3020–3032. doi:10.1021/bi500006v
Rissman RA, Poon WW, Blurton-Jones M, Oddo S, Torp R, Vitek MP, LaFerla FM, Rohn TT, Cotman CW (2004) Caspase-cleavage of tau is an early event in Alzheimer disease tangle pathology. J Clin Investig 114(1):121–130. doi:10.1172/JCI20640
Basurto-Islas G, Luna-Munoz J, Guillozet-Bongaarts AL, Binder LI, Mena R, Garcia-Sierra F (2008) Accumulation of aspartic acid421- and glutamic acid391-cleaved tau in neurofibrillary tangles correlates with progression in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67(5):470–483. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e31817275c7
Ugolini G, Cattaneo A, Novak M (1997) Co-localization of truncated tau and DNA fragmentation in Alzheimer’s disease neurones. NeuroReport 8(17):3709–3712
Cotman CW, Poon WW, Rissman RA, Blurton-Jones M (2005) The role of caspase cleavage of tau in Alzheimer disease neuropathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64(2):104–112
Gamblin TC, Chen F, Zambrano A, Abraha A, Lagalwar S, Guillozet AL, Lu M, Fu Y, Garcia-Sierra F, LaPointe N, Miller R, Berry RW, Binder LI, Cryns VL (2003) Caspase cleavage of tau: linking amyloid and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(17):10032–10037. doi:10.1073/pnas.1630428100
Park SY, Ferreira A (2005) The generation of a 17 kDa neurotoxic fragment: an alternative mechanism by which tau mediates beta-amyloid-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 25(22):5365–5375. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1125-05.2005
Kenessey A, Nacharaju P, Ko LW, Yen SH (1997) Degradation of tau by lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D: implication for Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration. J Neurochem 69(5):2026–2038
Arai T, Guo JP, McGeer PL (2005) Proteolysis of non-phosphorylated and phosphorylated tau by thrombin. J Biol Chem 280(7):5145–5153. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409234200
Yang LS, Gordon-Krajcer W, Ksiezak-Reding H (1997) Tau released from paired helical filaments with formic acid or guanidine is susceptible to calpain-mediated proteolysis. J Neurochem 69(4):1548–1558
Ferreira A, Bigio EH (2011) Calpain-mediated tau cleavage: a mechanism leading to neurodegeneration shared by multiple tauopathies. Mol Med 17(7–8):676–685. doi:10.2119/molmed.2010.00220
Garg S, Timm T, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E, Wang Y (2011) Cleavage of Tau by calpain in Alzheimer’s disease: the quest for the toxic 17 kD fragment. Neurobiol Aging 32(1):1–14. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.09.008
Zhang Z, Song M, Liu X, Kang SS, Kwon IS, Duong DM, Seyfried NT, Hu WT, Liu Z, Wang JZ, Cheng L, Sun YE, Yu SP, Levey AI, Ye K (2014) Cleavage of tau by asparagine endopeptidase mediates the neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 20(11):1254–1262. doi:10.1038/nm.3700
Takahashi M, Tsujioka Y, Yamada T, Tsuboi Y, Okada H, Yamamoto T, Liposits Z (1999) Glycosylation of microtubule-associated protein tau in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Acta Neuropathol 97(6):635–641
Wang JZ, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1996) Glycosylation of microtubule-associated protein tau: an abnormal posttranslational modification in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 2(8):871–875
Kuhla B, Haase C, Flach K, Luth HJ, Arendt T, Munch G (2007) Effect of pseudophosphorylation and cross-linking by lipid peroxidation and advanced glycation end product precursors on tau aggregation and filament formation. J Biol Chem 282(10):6984–6991. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609521200
Nacharaju P, Ko L, Yen SH (1997) Characterization of in vitro glycation sites of tau. J Neurochem 69(4):1709–1719
Bulbarelli A, Lonati E, Cazzaniga E, Gregori M, Masserini M (2009) Pin1 affects Tau phosphorylation in response to Abeta oligomers. Molecul Cell Neurosci 42(1):75–80. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2009.06.001
Horiguchi T, Uryu K, Giasson BI, Ischiropoulos H, LightFoot R, Bellmann C, Richter-Landsberg C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2003) Nitration of tau protein is linked to neurodegeneration in tauopathies. Am J Pathol 163(3):1021–1031. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63462-1
Singer SM, Zainelli GM, Norlund MA, Lee JM, Muma NA (2002) Transglutaminase bonds in neurofibrillary tangles and paired helical filament tau early in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 40(1):17–30
Dorval V, Fraser PE (2006) Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of natively unfolded proteins tau and alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 281(15):9919–9924. doi:10.1074/jbc.M510127200
Schweers O, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Mandelkow E (1995) Oxidation of cysteine-322 in the repeat domain of microtubule-associated protein tau controls the in vitro assembly of paired helical filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(18):8463–8467
Arnaud LT, Myeku N, Figueiredo-Pereira ME (2009) Proteasome-caspase-cathepsin sequence leading to tau pathology induced by prostaglandin J2 in neuronal cells. J Neurochem 110(1):328–342. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06142.x
David DC, Layfield R, Serpell L, Narain Y, Goedert M, Spillantini MG (2002) Proteasomal degradation of tau protein. J Neurochem 83(1):176–185
Yu CH, Si T, Wu WH, Hu J, Du JT, Zhao YF, Li YM (2008) O-GlcNAcylation modulates the self-aggregation ability of the fourth microtubule-binding repeat of tau. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 375(1):59–62. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.07.101
Liu F, Shi J, Tanimukai H, Gu J, Gu J, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Gong CX (2009) Reduced O-GlcNAcylation links lower brain glucose metabolism and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain J Neurol 132(Pt 7):1820–1832. doi:10.1093/brain/awp099
Necula M, Kuret J (2004) Pseudophosphorylation and glycation of tau protein enhance but do not trigger fibrillization in vitro. J Biol Chem 279(48):49694–49703. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405527200
Ledesma MD, Medina M, Avila J (1996) The in vitro formation of recombinant tau polymers: effect of phosphorylation and glycation. Molecul Chem Neuropathol/Spons Int Soc Neurochem World Fed Neurol Res Groups Neurochem Cerebrospinal Fluid 27(3):249–258
Reynolds MR, Berry RW, Binder LI (2005) Site-specific nitration differentially influences tau assembly in vitro. Biochemistry 44(42):13997–14009. doi:10.1021/bi051028w
Reynolds MR, Reyes JF, Fu Y, Bigio EH, Guillozet-Bongaarts AL, Berry RW, Binder LI (2006) Tau nitration occurs at tyrosine 29 in the fibrillar lesions of Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. J Neurosci Off J Soci Neurosci 26(42):10636–10645. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2143-06.2006
Reyes JF, Reynolds MR, Horowitz PM, Fu Y, Guillozet-Bongaarts AL, Berry R, Binder LI (2008) A possible link between astrocyte activation and tau nitration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 31(2):198–208. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2008.04.005
Takahashi K, Ishida M, Komano H, Takahashi H (2008) SUMO-1 immunoreactivity co-localizes with phospho-Tau in APP transgenic mice but not in mutant Tau transgenic mice. Neurosci Lett 441(1):90–93. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.06.012
Wang DS, Dickson DW, Malter JS (2008) Tissue transglutaminase, protein cross-linking and Alzheimer’s disease: review and views. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 1(1):5–18
Appelt DM, Kopen GC, Boyne LJ, Balin BJ (1996) Localization of transglutaminase in hippocampal neurons: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Histochem Cytochem Off J Histochem Soc 44(12):1421–1427
Wilhelmus MM, de Jager M, Rozemuller AJ, Breve J, Bol JG, Eckert RL, Drukarch B (2012) Transglutaminase 1 and its regulator tazarotene-induced gene 3 localize to neuronal tau inclusions in tauopathies. J Pathol 226(1):132–142. doi:10.1002/path.2984
Dou F, Netzer WJ, Tanemura K, Li F, Hartl FU, Takashima A, Gouras GK, Greengard P, Xu H (2003) Chaperones increase association of tau protein with microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(2):721–726
Chen B, Piel WH, Gui L, Bruford E, Monteiro A (2005) The HSP90 family of genes in the human genome: insights into their divergence and evolution. Genomics 86(6):627–637. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.08.012
Garnier C, Barbier P, Gilli R, Lopez C, Peyrot V, Briand C (1998) Heat-shock protein 90 (hsp90) binds in vitro to tubulin dimer and inhibits microtubule formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 250(2):414–419. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9319
Dickey CA, Eriksen J, Kamal A, Burrows F, Kasibhatla S, Eckman CB, Hutton M, Petrucelli L (2005) Development of a high throughput drug screening assay for the detection of changes in tau levels—proof of concept with HSP90 inhibitors. Curr Alzheimer Res 2(2):231–238
Dickey CA, Dunmore J, Lu B, Wang JW, Lee WC, Kamal A, Burrows F, Eckman C, Hutton M, Petrucelli L (2006) HSP induction mediates selective clearance of tau phosphorylated at proline-directed Ser/Thr sites but not KXGS (MARK) sites. Faseb J 20(6):753–755
Dickey CA, Kamal A, Lundgren K, Klosak N, Bailey RM, Dunmore J, Ash P, Shoraka S, Zlatkovic J, Eckman CB, Patterson C, Dickson DW, Nahman NS Jr, Hutton M, Burrows F, Petrucelli L (2007) The high-affinity HSP90-CHIP complex recognizes and selectively degrades phosphorylated tau client proteins. J Clin Investig 117(3):648–658
Luo W, Dou F, Rodina A, Chip S, Kim J, Zhao Q, Moulick K, Aguirre J, Wu N, Greengard P, Chiosis G (2007) Roles of heat-shock protein 90 in maintaining and facilitating the neurodegenerative phenotype in tauopathies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(22):9511–9516. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701055104
Tortosa E, Santa-Maria I, Moreno F, Lim F, Perez M, Avila J (2009) Binding of Hsp90 to tau promotes a conformational change and aggregation of tau protein. J Alzheimer’s Dis JAD 17(2):319–325. doi:10.3233/JAD-2009-1049
Karagoz GE, Duarte AM, Akoury E, Ippel H, Biernat J, Moran Luengo T, Radli M, Didenko T, Nordhues BA, Veprintsev DB, Dickey CA, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M, Boelens R, Madl T, Rudiger SG (2014) Hsp90-Tau complex reveals molecular basis for specificity in chaperone action. Cell 156(5):963–974. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.037
Jinwal UK, Koren J 3rd, Borysov SI, Schmid AB, Abisambra JF, Blair LJ, Johnson AG, Jones JR, Shults CL, O’Leary JC 3rd, Jin Y, Buchner J, Cox MB, Dickey CA (2010) The Hsp90 cochaperone, FKBP51, increases Tau stability and polymerizes microtubules. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 30(2):591–599. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4815-09.2010
Blair LJ, Nordhues BA, Hill SE, Scaglione KM, O’Leary JC 3rd, Fontaine SN, Breydo L, Zhang B, Li P, Wang L, Cotman C, Paulson HL, Muschol M, Uversky VN, Klengel T, Binder EB, Kayed R, Golde TE, Berchtold N, Dickey CA (2013) Accelerated neurodegeneration through chaperone-mediated oligomerization of tau. J Clin Investig 123(10):4158–4169. doi:10.1172/JCI69003
Chambraud B, Sardin E, Giustiniani J, Dounane O, Schumacher M, Goedert M, Baulieu EE (2010) A role for FKBP52 in Tau protein function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(6):2658–2663. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914957107
Jinwal UK, Trotter JH, Abisambra JF, Koren J 3rd, Lawson LY, Vestal GD, O’Leary JC 3rd, Johnson AG, Jin Y, Jones JR, Li Q, Weeber EJ, Dickey CA (2011) The Hsp90 kinase co-chaperone Cdc37 regulates tau stability and phosphorylation dynamics. J Biol Chem 286(19):16976–16983. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.182493
Gong CX, Liu F, Wu G, Rossie S, Wegiel J, Li L, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2004) Dephosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau by protein phosphatase 5. J Neurochem 88(2):298–310
Liu F, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Rossie S, Gong CX (2005) Dephosphorylation of tau by protein phosphatase 5: impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 280(3):1790–1796. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410775200
Young JC, Agashe VR, Siegers K, Hartl FU (2004) Pathways of chaperone-mediated protein folding in the cytosol. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(10):781–791. doi:10.1038/nrm1492
Shimura H, Schwartz D, Gygi SP, Kosik KS (2004) CHIP-Hsc70 complex ubiquitinates phosphorylated tau and enhances cell survival. J Biol Chem 279(6):4869–4876
Jinwal UK, Akoury E, Abisambra JF, O’Leary JC 3rd, Thompson AD, Blair LJ, Jin Y, Bacon J, Nordhues BA, Cockman M, Zhang J, Li P, Zhang B, Borysov S, Uversky VN, Biernat J, Mandelkow E, Gestwicki JE, Zweckstetter M, Dickey CA (2013) Imbalance of Hsp70 family variants fosters tau accumulation. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 27(4):1450–1459. doi:10.1096/fj.12-220889
Sarkar M, Kuret J, Lee G (2008) Two motifs within the tau microtubule-binding domain mediate its association with the hsc70 molecular chaperone. J Neurosci Res 86(12):2763–2773. doi:10.1002/jnr.21721
Jinwal UK, O’Leary JC 3rd, Borysov SI, Jones JR, Li Q, Koren J 3rd, Abisambra JF, Vestal GD, Lawson LY, Johnson AG, Blair LJ, Jin Y, Miyata Y, Gestwicki JE, Dickey CA (2010) Hsc70 rapidly engages tau after microtubule destabilization. J Biol Chem 285(22):16798–16805. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.113753
Petrucelli L, Dickson D, Kehoe K, Taylor J, Snyder H, Grover A, De Lucia M, McGowan E, Lewis J, Prihar G, Kim J, Dillmann WH, Browne SE, Hall A, Voellmy R, Tsuboi Y, Dawson TM, Wolozin B, Hardy J, Hutton M (2004) CHIP and Hsp70 regulate tau ubiquitination, degradation and aggregation. Hum Mol Genet 13(7):703–714. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh083
Elliott E, Laufer O, Ginzburg I (2009) BAG-1M is up-regulated in hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease patients and associates with tau and APP proteins. J Neurochem 109(4):1168–1178. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06047.x
Elliott E, Tsvetkov P, Ginzburg I (2007) BAG-1 associates with Hsc70.Tau complex and regulates the proteasomal degradation of tau protein. J Biol Chem 282(51):37276–37284. doi:10.1074/jbc.M706379200
Carrettiero DC, Hernandez I, Neveu P, Papagiannakopoulos T, Kosik KS (2009) The cochaperone BAG2 sweeps paired helical filament- insoluble tau from the microtubule. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29(7):2151–2161. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4660-08.2009
Patterson KR, Ward SM, Combs B, Voss K, Kanaan NM, Morfini G, Brady ST, Gamblin TC, Binder LI (2011) Heat shock protein 70 prevents both tau aggregation and the inhibitory effects of preexisting tau aggregates on fast axonal transport. Biochemistry 50(47):10300–10310. doi:10.1021/bi2009147
Voss K, Combs B, Patterson KR, Binder LI, Gamblin TC (2012) Hsp70 alters tau function and aggregation in an isoform specific manner. Biochemistry 51(4):888–898. doi:10.1021/bi2018078
Patterson KR, Remmers C, Fu Y, Brooker S, Kanaan NM, Vana L, Ward S, Reyes JF, Philibert K, Glucksman MJ, Binder LI (2011) Characterization of prefibrillar Tau oligomers in vitro and in Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 286(26):23063–23076. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.237974
Miyata Y, Li X, Lee HF, Jinwal UK, Srinivasan SR, Seguin SP, Young ZT, Brodsky JL, Dickey CA, Sun D, Gestwicki JE (2013) Synthesis and initial evaluation of YM-08, a blood-brain barrier permeable derivative of the heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) inhibitor MKT-077, which reduces tau levels. ACS Chem Neurosci 4(6):930–939. doi:10.1021/cn300210g
Abisambra J, Jinwal UK, Miyata Y, Rogers J, Blair L, Li X, Seguin SP, Wang L, Jin Y, Bacon J, Brady S, Cockman M, Guidi C, Zhang J, Koren J, Young ZT, Atkins CA, Zhang B, Lawson LY, Weeber EJ, Brodsky JL, Gestwicki JE, Dickey CA (2013) Allosteric heat shock protein 70 inhibitors rapidly rescue synaptic plasticity deficits by reducing aberrant tau. Biol Psychiatry 74(5):367–374. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.02.027
Wilhelmus MM, Otte-Holler I, Wesseling P, de Waal RM, Boelens WC, Verbeek MM (2006) Specific association of small heat shock proteins with the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32(2):119–130. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00689.x
Shimura H, Miura-Shimura Y, Kosik KS (2004) Binding of tau to heat shock protein 27 leads to decreased concentration of hyperphosphorylated tau and enhanced cell survival. J Biol Chem 279(17):17957–17962. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400351200
Abisambra JF, Blair LJ, Hill SE, Jones JR, Kraft C, Rogers J, Koren J 3rd, Jinwal UK, Lawson L, Johnson AG, Wilcock D, O’Leary JC, Jansen-West K, Muschol M, Golde TE, Weeber EJ, Banko J, Dickey CA (2010) Phosphorylation dynamics regulate Hsp27-mediated rescue of neuronal plasticity deficits in tau transgenic mice. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 30(46):15374–15382. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3155-10.2010
Wang S, Toth ME, Bereczki E, Santha M, Guan ZZ, Winblad B, Pei JJ (2011) Interplay between glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and tau in the cerebellum of Hsp27 transgenic mouse. J Neurosci Res 89(8):1267–1275. doi:10.1002/jnr.22660
Renkawek K, Bosman GJ, de Jong WW (1994) Expression of small heat-shock protein hsp 27 in reactive gliosis in Alzheimer disease and other types of dementia. Acta Neuropathol 87(5):511–519
Renkawek K, Voorter CE, Bosman GJ, van Workum FP, de Jong WW (1994) Expression of alpha B-crystallin in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 87(2):155–160
Bjorkdahl C, Sjogren MJ, Zhou X, Concha H, Avila J, Winblad B, Pei JJ (2008) Small heat shock proteins Hsp27 or alphaB-crystallin and the protein components of neurofibrillary tangles: tau and neurofilaments. J Neurosci Res 86(6):1343–1352. doi:10.1002/jnr.21589
Dabir DV, Trojanowski JQ, Richter-Landsberg C, Lee VM, Forman MS (2004) Expression of the small heat-shock protein alphaB-crystallin in tauopathies with glial pathology. Am J Pathol 164(1):155–166
Lopez-Gonzalez I, Carmona M, Arregui L, Kovacs GG, Ferrer I (2014) alphaB-crystallin and HSP27 in glial cells in tauopathies. Neuropathol Off J Japn Soc Neuropathol. doi:10.1111/neup.12134
Aaltonen T, Adelman J, Akimoto T, Alvarez Gonzalez B, Amerio S, Amidei D, Anastassov A, Annovi A, Antos J, Apollinari G, Apresyan A, Arisawa T, Artikov A, Ashmanskas W, Attal A, Aurisano A, Azfar F, Badgett W, Barbaro-Galtieri A, Barnes VE, Barnett BA, Barria P, Bartos P, Bartsch V, Bauer G, Beauchemin PH, Bedeschi F, Beecher D, Behari S, Bellettini G, Bellinger J, Benjamin D, Beretvas A, Beringer J, Bhatti A, Binkley M, Bisello D, Bizjak I, Blair RE, Blocker C, Blumenfeld B, Bocci A, Bodek A, Boisvert V, Bolla G, Bortoletto D, Boudreau J, Boveia A, Brau B, Bridgeman A, Brigliadori L, Bromberg C, Brubaker E, Budagov J, Budd HS, Budd S, Burke S, Burkett K, Busetto G, Bussey P, Buzatu A, Byrum KL, Cabrera S, Calancha C, Campanelli M, Campbell M, Canelli F, Canepa A, Carls B, Carlsmith D, Carosi R, Carrillo S, Carron S, Casal B, Casarsa M, Castro A, Catastini P, Cauz D, Cavaliere V, Cavalli-Sforza M, Cerri A, Cerrito L, Chang SH, Chen YC, Chertok M, Chiarelli G, Chlachidze G, Chlebana F, Cho K, Chokheli D, Chou JP, Choudalakis G, Chuang SH, Chung K, Chung WH, Chung YS, Chwalek T, Ciobanu CI, Ciocci MA, Clark A, Clark D, Compostella G, Convery ME, Conway J, Cordelli M, Cortiana G, Cox CA, Cox DJ, Crescioli F, Cuenca Almenar C, Cuevas J, Culbertson R, Cully JC, Dagenhart D, Datta M, Davies T, de Barbaro P, De Cecco S, Deisher A, De Lorenzo G, Dell’Orso M, Deluca C, Demortier L, Deng J, Deninno M, Derwent PF, Di Canto A, di Giovanni GP, Dionisi C, Di Ruzza B, Dittmann JR, D’Onofrio M, Donati S, Dong P, Donini J, Dorigo T, Dube S, Efron J, Elagin A, Erbacher R, Errede D, Errede S, Eusebi R, Fang HC, Farrington S, Fedorko WT, Feild RG, Feindt M, Fernandez JP, Ferrazza C, Field R, Flanagan G, Forrest R, Frank MJ, Franklin M, Freeman JC, Furic I, Gallinaro M, Galyardt J, Garberson F, Garcia JE, Garfinkel AF, Garosi P, Genser K, Gerberich H, Gerdes D, Gessler A, Giagu S, Giakoumopoulou V, Giannetti P, Gibson K, Gimmell JL, Ginsburg CM, Giokaris N, Giordani M, Giromini P, Giunta M, Giurgiu G, Glagolev V, Glenzinski D, Gold M, Goldschmidt N, Golossanov A, Gomez G, Gomez-Ceballos G, Goncharov M, Gonzalez O, Gorelov I, Goshaw AT, Goulianos K, Gresele A, Grinstein S, Grosso-Pilcher C, Group RC, Grundler U, Guimaraes da Costa J, Gunay-Unalan Z, Haber C, Hahn K, Hahn SR, Halkiadakis E, Han BY, Han JY, Happacher F, Hara K, Hare D, Hare M, Harper S, Harr RF, Harris RM, Hartz M, Hatakeyama K, Hays C, Heck M, Heijboer A, Heinrich J, Henderson C, Herndon M, Heuser J, Hewamanage S, Hidas D, Hill CS, Hirschbuehl D, Hocker A, Hou S, Houlden M, Hsu SC, Huffman BT, Hughes RE, Husemann U, Hussein M, Huston J, Incandela J, Introzzi G, Iori M, Ivanov A, James E, Jang D, Jayatilaka B, Jeon EJ, Jha MK, Jindariani S, Johnson W, Jones M, Joo KK, Jun SY, Jung JE, Junk TR, Kamon T, Kar D, Karchin PE, Kato Y, Kephart R, Ketchum W, Keung J, Khotilovich V, Kilminster B, Kim DH, Kim HS, Kim HW, Kim JE, Kim MJ, Kim SB, Kim SH, Kim YK, Kimura N, Kirsch L, Klimenko S, Knuteson B, Ko BR, Kondo K, Kong DJ, Konigsberg J, Korytov A, Kotwal AV, Kreps M, Kroll J, Krop D, Krumnack N, Kruse M, Krutelyov V, Kubo T, Kuhr T, Kulkarni NP, Kurata M, Kwang S, Laasanen AT, Lami S, Lammel S, Lancaster M, Lander RL, Lannon K, Lath A, Latino G, Lazzizzera I, LeCompte T, Lee E, Lee HS, Lee SW, Leone S, Lewis JD, Lin CS, Linacre J, Lindgren M, Lipeles E, Lister A, Litvintsev DO, Liu C, Liu T, Lockyer NS, Loginov A, Loreti M, Lovas L, Lucchesi D, Luci C, Lueck J, Lujan P, Lukens P, Lungu G, Lyons L, Lys J, Lysak R, MacQueen D, Madrak R, Maeshima K, Makhoul K, Maki T, Maksimovic P, Malde S, Malik S, Manca G, Manousakis-Katsikakis A, Margaroli F, Marino C, Marino CP, Martin A, Martin V, Martinez M, Martinez-Ballarin R, Maruyama T, Mastrandrea P, Masubuchi T, Mathis M, Mattson ME, Mazzanti P, McFarland KS, McIntyre P, McNulty R, Mehta A, Mehtala P, Menzione A, Merkel P, Mesropian C, Miao T, Miladinovic N, Miller R, Mills C, Milnik M, Mitra A, Mitselmakher G, Miyake H, Moggi N, Mondragon MN, Moon CS, Moore R, Morello MJ, Morlock J, Movilla Fernandez P, Mulmenstadt J, Mukherjee A, Muller T, Mumford R, Murat P, Mussini M, Nachtman J, Nagai Y, Nagano A, Naganoma J, Nakamura K, Nakano I, Napier A, Necula V, Nett J, Neu C, Neubauer MS, Neubauer S, Nielsen J, Nodulman L, Norman M, Norniella O, Nurse E, Oakes L, Oh SH, Oh YD, Oksuzian I, Okusawa T, Orava R, Osterberg K, Pagan Griso S, Pagliarone C, Palencia E, Papadimitriou V, Papaikonomou A, Paramonov AA, Parks B, Pashapour S, Patrick J, Pauletta G, Paulini M, Paus C, Peiffer T, Pellett DE, Penzo A, Phillips TJ, Piacentino G, Pianori E, Pinera L, Pitts K, Plager C, Pondrom L, Poukhov O, Pounder N, Prakoshyn F, Pronko A, Proudfoot J, Ptohos F, Pueschel E, Punzi G, Pursley J, Rademacker J, Rahaman A, Ramakrishnan V, Ranjan N, Redondo I, Renton P, Renz M, Rescigno M, Richter S, Rimondi F, Ristori L, Robson A, Rodrigo T, Rodriguez T, Rogers E, Rolli S, Roser R, Rossi M, Rossin R, Roy P, Ruiz A, Russ J, Rusu V, Rutherford B, Saarikko H, Safonov A, Sakumoto WK, Salto O, Santi L, Sarkar S, Sartori L, Sato K, Savoy-Navarro A, Schlabach P, Schmidt A, Schmidt EE, Schmidt MA, Schmidt MP, Schmitt M, Schwarz T, Scodellaro L, Scribano A, Scuri F, Sedov A, Seidel S, Seiya Y, Semenov A, Sexton-Kennedy L, Sforza F, Sfyrla A, Shalhout SZ, Shears T, Shepard PF, Shimojima M, Shiraishi S, Shochet M, Shon Y, Shreyber I, Sinervo P, Sisakyan A, Slaughter AJ, Slaunwhite J, Sliwa K, Smith JR, Snider FD, Snihur R, Soha A, Somalwar S, Sorin V, Spreitzer T, Squillacioti P, Stanitzki M, St Denis R, Stelzer B, Stelzer-Chilton O, Stentz D, Strologas J, Strycker GL, Suh JS, Sukhanov A, Suslov I, Suzuki T, Taffard A, Takashima R, Takeuchi Y, Tanaka R, Tecchio M, Teng PK, Terashi K, Thom J, Thompson AS, Thompson GA, Thomson E, Tipton P, Ttito-Guzman P, Tkaczyk S, Toback D, Tokar S, Tollefson K, Tomura T, Tonelli D, Torre S, Torretta D, Totaro P, Tourneur S, Trovato M, Tsai SY, Tu Y, Turini N, Ukegawa F, Vallecorsa S, van Remortel N, Varganov A, Vataga E, Vazquez F, Velev G, Vellidis C, Vidal M, Vidal R, Vila I, Vilar R, Vine T, Vogel M, Volobouev I, Volpi G, Wagner P, Wagner RG, Wagner RL, Wagner W, Wagner-Kuhr J, Wakisaka T, Wallny R, Wang SM, Warburton A, Waters D, Weinberger M, Weinelt J, Wester WC, 3rd, Whitehouse B, Whiteson D, Wicklund AB, Wicklund E, Wilbur S, Williams G, Williams HH, Wilson P, Winer BL, Wittich P, Wolbers S, Wolfe C, Wright T, Wu X, Wurthwein F, Xie S, Yagil A, Yamamoto K, Yamaoka J, Yang UK, Yang YC, Yao WM, Yeh GP, Yi K, Yoh J, Yorita K, Yoshida T, Yu GB, Yu I, Yu SS, Yun JC, Zanello L, Zanetti A, Zhang X, Zheng Y, Zucchelli S, Collaboration CDF (2009) Search for Higgs bosons predicted in two-Higgs-doublet models via decays to tau lepton pairs in 1.96 TeV pp collisions. Phys Rev Lett 103(20):201801
Dammer EB, Lee AK, Duong DM, Gearing M, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Seyfried NT (2014) Quantitative phosphoproteomics of alzheimer’s disease reveals crosstalk between kinases and small heat shock proteins. Proteomics. doi:10.1002/pmic.201400189
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NS073899 to C.A.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fontaine, S.N., Sabbagh, J.J., Baker, J. et al. Cellular factors modulating the mechanism of tau protein aggregation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 1863–1879 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1839-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1839-9