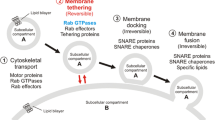
Abstract
Eukaryotic cells require selective sorting and transport of cargo between intracellular compartments. This is accomplished at least in part by vesicles that bud from a donor compartment, sequestering a subset of resident protein “cargos” destined for transport to an acceptor compartment. A key step in vesicle formation and targeting is the recruitment of specific proteins that form a coat on the outside of the vesicle in a process requiring the activation of regulatory GTPases of the ARF family. Like all such GTPases, ARFs cycle between inactive, GDP-bound, and membrane-associated active, GTP-bound, conformations. And like most regulatory GTPases the activating step is slow and thought to be rate limiting in cells, requiring the use of ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEFs). ARF GEFs are characterized by the presence of a conserved, catalytic Sec7 domain, though they also contain motifs or additional domains that confer specificity to localization and regulation of activity. These domains have been used to define and classify five different sub-families of ARF GEFs. One of these, the BIG/GBF1 family, includes three proteins that are each key regulators of the secretory pathway. GEF activity initiates the coating of nascent vesicles via the localized generation of activated ARFs and thus these GEFs are the upstream regulators that define the site and timing of vesicle production. Paradoxically, while we have detailed molecular knowledge of how GEFs activate ARFs, we know very little about how GEFs are recruited and/or activated at the right time and place to initiate transport. This review summarizes the current knowledge of GEF regulation and explores the still uncertain mechanisms that position GEFs at “budding ready” membrane sites to generate highly localized activated ARFs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aridor M, Hannan LA (2002) Traffic jams II: an update of diseases of intracellular transport. Traffic 3(11):781–790
Aridor M (2007) Visiting the ER: the endoplasmic reticulum as a target for therapeutics in traffic related diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59(8):759–781
Pan H, Yu J et al (2008) A novel small molecule regulator of guanine nucleotide exchange activity of the ADP-ribosylation factor and Golgi membrane trafficking. J Biol Chem 283(45):31087–31096
Saenz JB, Sun WJ et al (2009) Golgicide A reveals essential roles for GBF1 in Golgi assembly and function. Nat Chem Biol 5(3):157–165
Boal F, Guetzoyan L et al (2010) LG186: an inhibitor of GBF1 function that causes Golgi disassembly in human and canine cells. Traffic 11(12):1537–1551
Jackson CL, Casanova JE (2000) Turning on ARF: the Sec7 family of guanine-nucleotide-exchange factors. Trends Cell Biol 10(2):60–67
Moss J, Vaughan M (1977) Choleragen activation of solubilized adenylate cyclase: requirement for GTP and protein activator for demonstration of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74(10):4396–4400
Enomoto K, Gill DM (1980) Cholera toxin activation of adenylate cyclase. Roles of nucleoside triphosphates and a macromolecular factor in the ADP ribosylation of the GTP-dependent regulatory component. J Biol Chem 255(4):1252–1258
Kahn RA, Gilman AG (1984) Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem 259(10):6228–6234
Kahn RA, Gilman AG (1986) The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem 261(17):7906–7911
Tsai SC, Noda M et al (1988) Stimulation of choleragen enzymatic activities by GTP and two soluble proteins purified from bovine brain. J Biol Chem 263(4):1768–1772
Noda M, Tsai SC et al (1989) Activation of immobilized, biotinylated choleragen AI protein by a 19-kilodalton guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Biochemistry 28(19):7936–7940
Noda M, Tsai SC et al (1990) Mechanism of cholera toxin activation by a guanine nucleotide-dependent 19 kDa protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1034(2):195–199
Vaughan M, Moss J (1997) Activation of toxin ADP-ribosyltransferases by the family of ADP-ribosylation factors. Adv Exp Med Biol 419:315–320
Clark J, Moore L et al (1993) Selective amplification of additional members of the ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) family: cloning of additional human and Drosophila ARF-like genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(19):8952–8956
Kahn RA, Bruford E et al (2008) Consensus nomenclature for the human ArfGAP domain-containing proteins. J Cell Biol 182(6):1039–1044
Dong JH, Wen JF et al (2007) Homologs of eukaryotic Ras superfamily proteins in prokaryotes and their novel phylogenetic correlation with their eukaryotic analogs. Gene 396(1):116–124
Lee CM, Haun RS et al (1992) Characterization of the human gene encoding ADP-ribosylation factor 1, a guanine nucleotide-binding activator of cholera toxin. J Biol Chem 267(13):9028–9034
Lee FJ, Stevens LA et al (1994) Characterization of class II and class III ADP-ribosylation factor genes and proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem 269(34):21555–21560
Lee FJ, Stevens LA et al (1994) Characterization of a glucose-repressible ADP-ribosylation factor 3 (ARF3) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 269(33):20931–20937
Kahn RA, Kern FG et al (1991) Human ADP-ribosylation factors. A functionally conserved family of GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 266(4):2606–2614
Bui QT, Golinelli-Cohen MP et al (2009) Large Arf1 guanine nucleotide exchange factors: evolution, domain structure, and roles in membrane trafficking and human disease. Mol Genet Genomics 282(4):329–350
Pasqualato S, Renault L et al (2002) Arf, Arl, Arp and Sar proteins: a family of GTP-binding proteins with a structural device for ‘front-back’ communication. EMBO Rep 3(11):1035–1041
Renault L, Guibert B et al (2003) Structural snapshots of the mechanism and inhibition of a guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Nature 426(6966):525–530
Kahn RA, Goddard C et al (1988) Chemical and immunological characterization of the 21-kDa ADP-ribosylation factor of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem 263(17):8282–8287
Kahn RA, Randazzo P et al (1992) The amino terminus of ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) is a critical determinant of ARF activities and is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein transport. J Biol Chem 267(18):13039–13046
Achstetter T, Franzusoff A et al (1988) SEC7 encodes an unusual, high molecular weight protein required for membrane traffic from the yeast Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem 263(24):11711–11717
Beraud-Dufour S, Robineau S et al (1998) A glutamic finger in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor ARNO displaces Mg2+ and the beta-phosphate to destabilize GDP on ARF1. EMBO J 17(13):3651–3659
Cherfils J, Menetrey J et al (1998) Structure of the Sec7 domain of the Arf exchange factor ARNO. Nature 392(6671):101–105
Goldberg J (1998) Structural basis for activation of ARF GTPase: mechanisms of guanine nucleotide exchange and GTP-myristoyl switching. Cell 95(2):237–248
Mossessova E, Gulbis JM et al (1998) Structure of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Sec7 domain of human arno and analysis of the interaction with ARF GTPase. Cell 92(3):415–423
Peyroche A, Antonny B et al (1999) Brefeldin A acts to stabilize an abortive ARF-GDP-Sec7 domain protein complex: involvement of specific residues of the Sec7 domain. Mol Cell 3(3):275–285
Mossessova E, Corpina RA et al (2003) Crystal structure of ARF1*Sec7 complexed with Brefeldin A and its implications for the guanine nucleotide exchange mechanism. Mol Cell 12(6):1403–1411
Pasqualato S, Senic-Matuglia F et al (2004) The structural GDP/GTP cycle of Rab11 reveals a novel interface involved in the dynamics of recycling endosomes. J Biol Chem 279(12):11480–11488
Claude A, Zhao BP et al (1999) GBF1: a novel Golgi-associated BFA-resistant guanine nucleotide exchange factor that displays specificity for ADP-ribosylation factor 5. J Cell Biol 146(1):71–84
Togawa A, Morinaga N et al (1999) Purification and cloning of a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein for ADP-ribosylation factors. J Biol Chem 274(18):12308–12315
Jones HD, Moss J et al (2005) BIG1 and BIG2, brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange factors for ADP-ribosylation factors. Methods Enzymol 404:174–184
Manolea F, Claude A et al (2008) Distinct functions for Arf guanine nucleotide exchange factors at the Golgi complex: GBF1 and BIGs are required for assembly and maintenance of the Golgi stack and trans-Golgi network, respectively. Mol Biol Cell 19(2):523–535
Szul T, Grabski R et al (2007) Dissecting the role of the ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 in Golgi biogenesis and protein trafficking. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 22):3929–3940
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Li Y et al (2005) Isoform-selective effects of the depletion of ADP-ribosylation factors 1–5 on membrane traffic. Mol Biol Cell 16(10):4495–4508
Kawamoto K, Yoshida Y et al (2002) GBF1, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for ADP-ribosylation factors, is localized to the cis-Golgi and involved in membrane association of the COPI coat. Traffic 3(7):483–495
Zhao X, Lasell TK et al (2002) Localization of large ADP-ribosylation factor-guanine nucleotide exchange factors to different Golgi compartments: evidence for distinct functions in protein traffic. Mol Biol Cell 13(1):119–133
Claude A, Zhao BP et al (2003) Characterization of alternatively spliced and truncated forms of the Arf guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 defines regions important for activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303(1):160–169
Garcia-Mata R, Sztul E (2003) The membrane-tethering protein p115 interacts with GBF1, an ARF guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor. EMBO Rep 4(3):320–325
Niu TK, Pfeifer AC et al (2005) Dynamics of GBF1, a brefeldin A-sensitive Arf1 exchange factor at the Golgi. Mol Biol Cell 16(3):1213–1222
Yamaji R, Adamik R et al (2000) Identification and localization of two brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors in a macromolecular complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(6):2567–2572
Shinotsuka C, Yoshida Y et al (2002) Overexpression of an ADP-ribosylation factor-guanine nucleotide exchange factor, BIG2, uncouples brefeldin A-induced adaptor protein-1 coat dissociation and membrane tubulation. J Biol Chem 277(11):9468–9473
Shinotsuka C, Waguri S et al (2002) Dominant-negative mutant of BIG2, an ARF-guanine nucleotide exchange factor, specifically affects membrane trafficking from the trans-Golgi network through inhibiting membrane association of AP-1 and GGA coat proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 294(2):254–260
Charych EI, Yu W et al (2004) The brefeldin A-inhibited GDP/GTP exchange factor 2, a protein involved in vesicular trafficking, interacts with the beta subunits of the GABA receptors. J Neurochem 90(1):173–189
Shin HW, Morinaga N et al (2004) BIG2, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for ADP-ribosylation factors: its localization to recycling endosomes and implication in the endosome integrity. Mol Biol Cell 15(12):5283–5294
Shin HW, Shinotsuka C et al (2005) Expression of BIG2 and analysis of its function in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol 404:206–215
Mansour SJ, Skaug J et al (1999) p200 ARF-GEP1: a Golgi-localized guanine nucleotide exchange protein whose Sec7 domain is targeted by the drug brefeldin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(14):7968–7973
Christis C, Munro S (2012) The small G protein Arl1 directs the trans-Golgi-specific targeting of the Arf1 exchange factors BIG1 and BIG2. J Cell Biol 196(3):327–335
Lowery J, Szul T et al (2013) The Sec7 guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 regulates membrane recruitment of BIG1 and BIG2 to the trans-Golgi network (TGN). J Biol Chem 288(16):11532–11545
Monetta P, Slavin I et al (2007) Rab1b Interacts with GBF1, modulates both ARF1 dynamics and COPI association. Mol Biol Cell 18(7):2400–2410
Wessels E, Duijsings D et al (2007) Molecular determinants of the interaction between coxsackievirus protein 3A and guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1. J Virol 81(10):5238–5245
Grebe M, Gadea J et al (2000) A conserved domain of the arabidopsis GNOM protein mediates subunit interaction and cyclophilin 5 binding. Plant Cell 12(3):343–356
Ramaen O, Joubert A et al (2007) Interactions between conserved domains within homodimers in the BIG1, BIG2, and GBF1 Arf guanine nucleotide exchange factors. J Biol Chem 282(39):28834–28842
Park SK, Hartnell LM et al (2005) Mutations in a highly conserved region of the Arf1p activator GEA2 block anterograde Golgi transport but not COPI recruitment to membranes. Mol Biol Cell 16(8):3786–3799
Szul T, Garcia-Mata R et al (2005) Dissection of membrane dynamics of the ARF-guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1. Traffic 6(5):374–385
Anders N, Nielsen M et al (2008) Membrane association of the Arabidopsis ARF exchange factor GNOM involves interaction of conserved domains. Plant Cell 20(1):142–151
Dehring DA, Adler AS et al (2008) A C-terminal sequence in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Sec7 mediates Golgi association and interaction with the Rsp5 ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem 283(49):34188–34196
Richardson BC, McDonold CM et al (2012) The Sec7 Arf-GEF is recruited to the trans-Golgi network by positive feedback. Dev Cell 22(4):799–810
Armbruster K, Luschnig S (2012) The Drosophila Sec7 domain guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein Gartenzwerg localizes at the cis-Golgi and is essential for epithelial tube expansion. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 5):1318–1328
Bouvet S, Golinelli-Cohen MP et al (2013) Targeting of the Arf-GEF GBF1 to lipid droplets and Golgi membranes. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 20):4794–4805
Soni KG, Mardones GA et al (2009) Coatomer-dependent protein delivery to lipid droplets. J Cell Sci 122(Pt 11):1834–1841
Ellong EN, Soni KG et al (2011) Interaction between the triglyceride lipase ATGL and the Arf1 activator GBF1. PLoS One 6(7):e21889
Takashima K, Saitoh A et al (2011) GBF1-Arf-COPI-ArfGAP-mediated Golgi-to-ER transport involved in regulation of lipid homeostasis. Cell Struct Funct 36(2):223–235
Chantalat S, Courbeyrette R et al (2003) A novel Golgi membrane protein is a partner of the ARF exchange factors Gea1p and Gea2p. Mol Biol Cell 14(6):2357–2371
Eimer S, Gottschalk A et al (2007) Regulation of nicotinic receptor trafficking by the transmembrane Golgi protein UNC-50. EMBO J 26(20):4313–4323
Jian X, Cavenagh M et al (2010) Modifications to the C-terminus of Arf1 alter cell functions and protein interactions. Traffic 11(6):732–742
Manolea F, Chun J et al (2010) Arf3 is activated uniquely at the trans-Golgi network by brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Mol Biol Cell 21(11):1836–1849
Lefrancois S, McCormick PJ (2007) The Arf GEF GBF1 is required for GGA recruitment to Golgi membranes. Traffic 8(10):1440–1451
Wessels E, Duijsings D et al (2006) Effects of picornavirus 3A proteins on protein transport and GBF1-dependent COP-I recruitment. J Virol 80(23):11852–11860
Wessels E, Duijsings D et al (2006) A viral protein that blocks Arf1-mediated COP-I assembly by inhibiting the guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1. Dev Cell 11(2):191–201
Wessels E, Notebaart RA et al (2006) Structure-function analysis of the coxsackievirus protein 3A: identification of residues important for dimerization, viral rna replication, and transport inhibition. J Biol Chem 281(38):28232–28243
Cohen LA, Honda A et al (2007) Active Arf6 recruits ARNO/cytohesin GEFs to the PM by binding their PH domains. Mol Biol Cell 18(6):2244–2253
Hofmann I, Thompson A et al (2007) The Arl4 family of small G proteins can recruit the cytohesin Arf6 exchange factors to the plasma membrane. Curr Biol 17(8):711–716
Stalder D, Barelli H et al (2011) Kinetic studies of the Arf activator Arno on model membranes in the presence of Arf effectors suggest control by a positive feedback loop. J Biol Chem 286(5):3873–3883
Malaby AW, van den Berg B et al (2013) Structural basis for membrane recruitment and allosteric activation of cytohesin family Arf GTPase exchange factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(35):14213–14218
Stalder D, Antonny B (2013) Arf GTPase regulation through cascade mechanisms and positive feedback loops. FEBS Lett 587(13):2028–2035
Margarit SM, Sondermann H et al (2003) Structural evidence for feedback activation by Ras.GTP of the Ras-specific nucleotide exchange factor SOS. Cell 112(5):685–695
Chen Z, Medina F et al (2010) Activated RhoA binds to the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of PDZ-RhoGEF, a potential site for autoregulation. J Biol Chem 285(27):21070–21081
Medina F, Carter AM et al (2013) Activated RhoA is a positive feedback regulator of the Lbc family of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor proteins. J Biol Chem 288(16):11325–11333
Aizel K, Biou V et al (2013) Integrated conformational and lipid-sensing regulation of endosomal ArfGEF BRAG2. PLoS Biol 11(9):e1001652
Folly-Klan M, Alix E et al (2013) A novel membrane sensor controls the localization and ArfGEF activity of bacterial RalF. PLoS Pathog 9(11):e1003747
Chen KY, Tsai PC et al (2010) Syt1p promotes activation of Arl1p at the late Golgi to recruit Imh1p. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 20):3478–3489
Chen KY, Tsai PC et al (2012) Competition between the Golgin Imh1p and the GAP Gcs1p stabilizes activated Arl1p at the late-Golgi. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 19):4586–4596
Jones S, Jedd G et al (1999) Genetic interactions in yeast between Ypt GTPases and Arf guanine nucleotide exchangers. Genetics 152(4):1543–1556
Dumaresq-Doiron K, Savard MF et al (2010) The phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase PI4KIIIalpha is required for the recruitment of GBF1 to Golgi membranes. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 13):2273–2280
Mazaki Y, Nishimura Y et al (2012) GBF1 bears a novel phosphatidylinositol-phosphate binding module, BP3K, to link PI3Kgamma activity with Arf1 activation involved in GPCR-mediated neutrophil chemotaxis and superoxide production. Mol Biol Cell 23(13):2457–2467
Caster AH, Kahn RA (2013) Recruitment of the Mint3 adaptor is necessary for export of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) from the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem 288(40):28567–28580
Caster AH, Sztul E et al (2013) A role for cargo in Arf-dependent adaptor recruitment. J Biol Chem 288(21):14788–14804
Lin S, Zhou C et al (2013) BIG1, a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein modulates ATP-binding cassette transporter A-1 trafficking and function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(2):e31–e38
Li YC, Wang MJ et al (2012) Hyperdopaminergic modulation of inhibitory transmission is dependent on GSK-3beta signaling-mediated trafficking of GABAA receptors. J Neurochem 122(2):308–320
Szul T, Burgess J et al (2011) The Garz Sec7 domain guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Arf regulates salivary gland development in Drosophila. Cell Logist 1(2):69–76
Edeling M, Smith C et al (2006) Life of a clathrin coat: insights from clathrin and AP structures. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(1):32–44
Szul T, Sztul E (2011) COPII and COPI traffic at the ER-Golgi interface. Physiology (Bethesda) 26(5):348–364
Popoff V, Adolf F et al (2011) COPI budding within the Golgi stack. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3(11):a005231
Deng Y, Golinelli-Cohen MP et al (2009) A COPI coat subunit interacts directly with an early-Golgi localized Arf exchange factor. EMBO Rep 10(1):58–64
Richardson BC, Fromme JC (2012) Autoregulation of Sec7 Arf-GEF activity and localization by positive feedback. Small GTPases 3(4):240–243
DiNitto J, Delprato A et al (2007) Structural basis and mechanism of autoregulation in 3-phosphoinositide-dependent Grp1 family Arf GTPase exchange factors. Mol Cell 28(4):569–583
Amor J, Swails J et al (2005) The structure of RalF, an ADP-ribosylation factor guanine nucleotide exchange factor from Legionella pneumophila, reveals the presence of a cap over the active site. J Biol Chem 280(2):1392–1400
Chantalat S, Park SK et al (2004) The Arf activator Gea2p and the P-type ATPase Drs2p interact at the Golgi in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 5):711–722
Natarajan P, Liu K et al (2009) Regulation of a Golgi flippase by phosphoinositides and an ArfGEF. Nat Cell Biol 11(12):1421–1426
Daleke DL (2003) Regulation of transbilayer plasma membrane phospholipid asymmetry. J Lipid Res 44(2):233–242
Zhou X, Graham TR (2009) Reconstitution of phospholipid translocase activity with purified Drs2p, a type-IV P-type ATPase from budding yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(39):16586–16591
Costantino BF, Bricker DK et al (2008) A novel ecdysone receptor mediates steroid-regulated developmental events during the mid-third instar of Drosophila. PLoS Genet 4(6):e1000102
Li CC, Kuo JC et al (2011) Effects of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange (BIG) 1 and KANK1 proteins on cell polarity and directed migration during wound healing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(48):19228–19233
Kakinuma N, Zhu Y et al (2009) Kank proteins: structure, functions and diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 66(16):2651–2659
Saeki N, Tokuo H et al (2005) BIG1 is a binding partner of myosin IXb and regulates its Rho-GTPase activating protein activity. J Biol Chem 280(11):10128–10134
Le K, Li CC et al (2013) Arf guanine nucleotide-exchange factors BIG1 and BIG2 regulate nonmuscle myosin IIA activity by anchoring myosin phosphatase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(34):E3162–E3170
Sapperstein SK, Walter DM et al (1995) p115 is a general vesicular transport factor related to the yeast endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport factor Uso1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(2):522–526
Alvarez C, Fujita H et al (1999) ER to Golgi transport: requirement for p115 at a pre-Golgi VTC stage. J Cell Biol 147(6):1205–1222
Seemann J, Jokitalo EJ et al (2000) The role of the tethering proteins p115 and GM130 in transport through the Golgi apparatus in vivo. Mol Biol Cell 11(2):635–645
Sztul E, Lupashin V (2009) Role of vesicle tethering factors in the ER-Golgi membrane traffic. FEBS Lett 583(23):3770–3783
Ungar D, Oka T et al (2002) Characterization of a mammalian Golgi-localized protein complex, COG, that is required for normal Golgi morphology and function. J Cell Biol 157(3):405–415
Fotso P, Koryakina Y et al (2005) Cog1p plays a central role in the organization of the yeast conserved oligomeric Golgi complex. J Biol Chem 280(30):27613–27623
Zolov SN, Lupashin VV (2005) Cog3p depletion blocks vesicle-mediated Golgi retrograde trafficking in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol 168(5):747–759
Shestakova A, Suvorova E et al (2007) Interaction of the conserved oligomeric Golgi complex with t-SNARE Syntaxin5a/Sed5 enhances intra-Golgi SNARE complex stability. J Cell Biol 179(6):1179–1192
Smith RD, Willett R et al (2009) The COG complex, Rab6 and COPI define a novel Golgi retrograde trafficking pathway that is exploited by SubAB toxin. Traffic 10(10):1502–1517
Chen S, Cai H et al (2011) Trs65p, a subunit of the Ypt1p GEF TRAPPII, interacts with the Arf1p exchange factor Gea2p to facilitate COPI-mediated vesicle traffic. Mol Biol Cell 22(19):3634–3644
Cai Y, Chin HF et al (2008) The structural basis for activation of the Rab Ypt1p by the TRAPP membrane-tethering complexes. Cell 133(7):1202–1213
Yip CK, Berscheminski J et al (2010) Molecular architecture of the TRAPPII complex and implications for vesicle tethering. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17(11):1298–1304
Choi C, Davey M et al (2011) Organization and assembly of the TRAPPII complex. Traffic 12(6):715–725
Yamasaki A, Menon S et al (2009) mTrs130 is a component of a mammalian TRAPPII complex, a Rab1 GEF that binds to COPI-coated vesicles. Mol Biol Cell 20(19):4205–4215
Zhang CJ, Bowzard JB et al (2002) Genetic interactions link ARF1, YPT31/32 and TRS130. Yeast 19(12):1075–1086
Whyte J, Munro S (2001) The Sec34/35 Golgi transport complex is related to the exocyst, defining a family of complexes involved in multiple steps of membrane traffic. Dev Cell 1(4):527–537
Spelbrink R, Nothwehr S (1999) The yeast GRD20 gene is required for protein sorting in the trans-Golgi network/endosomal system and for polarization of the actin cytoskeleton. Mol Biol Cell 10(12):4263–4281
Oka T, Vasile E et al (2005) Genetic analysis of the subunit organization and function of the conserved oligomeric golgi (COG) complex: studies of COG5- and COG7-deficient mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 280(38):32736–32745
Sacher M, Barrowman J et al (2001) TRAPP I implicated in the specificity of tethering in ER-to-Golgi transport. Mol Cell 7(2):433–442
Cai H, Zhang Y et al (2005) Mutants in trs120 disrupt traffic from the early endosome to the late Golgi. J Cell Biol 171(5):823–833
Xu KF, Shen X et al (2005) Interaction of BIG2, a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein, with exocyst protein Exo70. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(8):2784–2789
Colanzi A, Corda D (2007) Mitosis controls the Golgi and the Golgi controls mitosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19(4):386–393
Wei JH, Seemann J (2009) Mitotic division of the mammalian Golgi apparatus. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20(7):810–816
Corda D, Barretta ML et al (2012) Golgi complex fragmentation in G2/M transition: an organelle-based cell-cycle checkpoint. IUBMB Life 64(8):661–670
Preisinger C, Barr FA (2005) Kinases regulating Golgi apparatus structure and function. Biochem Soc Symp 72:15–30
Levine TP, Rabouille C et al (1996) Binding of the vesicle docking protein p115 to Golgi membranes is inhibited under mitotic conditions. J Biol Chem 271(29):17304–17311
Nakamura N, Lowe M et al (1997) The vesicle docking protein p115 binds GM130, a cis-Golgi matrix protein, in a mitotically regulated manner. Cell 89(3):445–455
Sohda M, Misumi Y et al (1998) Phosphorylation of the vesicle docking protein p115 regulates its association with the Golgi membrane. J Biol Chem 273(9):5385–5388
Dell KR, Turck CW et al (2000) Mitotic phosphorylation of the dynein light intermediate chain is mediated by cdc2 kinase. Traffic 1(1):38–44
Dirac-Svejstrup AB, Shorter J et al (2000) Phosphorylation of the vesicle-tethering protein p115 by a casein kinase II-like enzyme is required for Golgi reassembly from isolated mitotic fragments. J Cell Biol 150(3):475–488
Jesch SA, Lewis TS et al (2001) Mitotic phosphorylation of Golgi reassembly stacking protein 55 by mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK2. Mol Biol Cell 12(6):1811–1817
Wang Y, Seemann J et al (2003) A direct role for GRASP65 as a mitotically regulated Golgi stacking factor. EMBO J 22(13):3279–3290
Mao L, Li N et al (2013) AMPK phosphorylates GBF1 for mitotic Golgi disassembly. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 6):1498–1505
Morohashi Y, Balklava Z et al (2010) Phosphorylation and membrane dissociation of the ARF exchange factor GBF1 in mitosis. Biochem J 427(3):401–412
Miyamoto T, Oshiro N et al (2008) AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylates Golgi-specific brefeldin A resistance factor 1 at Thr1337 to induce disassembly of Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem 283(7):4430–4438
Kuroda F, Moss J et al (2007) Regulation of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein 1 (BIG1) and BIG2 activity via PKA and protein phosphatase 1gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(9):3201–3206
Citterio C, Jones HD et al (2006) Effect of protein kinase A on accumulation of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein 1 (BIG1) in HepG2 cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(8):2683–2688
Lowery J, Szul T et al (2011) Novel C-terminal motif within Sec7 domain of guanine nucleotide exchange factors regulates ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) binding and activation. J Biol Chem 286(42):36898–36906
Feng Y, Walsh CA (2004) The many faces of filamin: a versatile molecular scaffold for cell motility and signalling. Nat Cell Biol 6(11):1034–1038
Kawauchi T, Hoshino M (2008) Molecular pathways regulating cytoskeletal organization and morphological changes in migrating neurons. Dev Neurosci 30(1–3):36–46
Zhang J, Neal J et al (2012) Brefeldin A-inhibited guanine exchange factor 2 regulates filamin A phosphorylation and neuronal migration. J Neurosci 32(36):12619–12629
Naydenov NG, Harris G et al (2012) Loss of a membrane trafficking protein alphaSNAP induces non-canonical autophagy in human epithelia. Cell Cycle 11(24):4613–4625
Plutner H, Cox AD et al (1991) Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol 115(1):31–43
Tisdale EJ, Bourne JR et al (1992) GTP-binding mutants of rab1 and rab2 are potent inhibitors of vesicular transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol 119(4):749–761
Nuoffer C, Davidson HW et al (1994) A GDP-bound of rab1 inhibits protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum and transport between Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol 125(2):225–237
Wilson BS, Nuoffer C et al (1994) A Rab1 mutant affecting guanine nucleotide exchange promotes disassembly of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol 125(3):557–571
Romero N, Dumur CI et al (2013) Rab1b overexpression modifies Golgi size and gene expression in HeLa cells and modulates the thyrotrophin response in thyroid cells in culture. Mol Biol Cell 24(5):617–632
Wang S, Meyer H et al (2012) GBF1 (Gartenzwerg)-dependent secretion is required for Drosophila tubulogenesis. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 2):461–472
Abrams EW, Andrew DJ (2005) CrebA regulates secretory activity in the Drosophila salivary gland and epidermis. Development 132(12):2743–2758
Fox RM, Hanlon CD et al (2010) The CrebA/Creb3-like transcription factors are major and direct regulators of secretory capacity. J Cell Biol 191(3):479–492
Grzmil P, Enkhbaatar Z et al (2010) Early embryonic lethality in gene trap mice with disruption of the Arfgef2 gene. Int J Dev Biol 54(8–9):1259–1266
Shen X, Meza-Carmen V et al (2008) Interaction of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein (BIG) 1 and kinesin motor protein KIF21A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(48):18788–18793
Peyroche A, Jackson CL (2001) Functional analysis of ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) guanine nucleotide exchange factors Gea1p and Gea2p in yeast. Methods Enzymol 329:290–300
Padilla PI, Uhart M et al (2008) Association of guanine nucleotide-exchange protein BIG1 in HepG2 cell nuclei with nucleolin, U3 snoRNA, and fibrillarin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(9):3357–3361
Xu Z, Gong Q et al (2009) A role of histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferase components in endosomal trafficking. J Cell Biol 186(3):343–353
Padilla PI, Pachecho-Rodriguez G et al (2004) Nuclear localization and molecular partners of BIG1, a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein for ADP-ribosylation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(9):2752–2757
Shen X, Hong MS et al (2007) BIG1, a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein, is required for correct glycosylation and function of integrin beta1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(4):1230–1235
Ishizaki R, Shin HW et al (2006) AMY-1 (associate of Myc-1) localization to the trans-Golgi network through interacting with BIG2, a guanine-nucleotide exchange factor for ADP-ribosylation factors. Genes Cells 11(8):949–959
Puxeddu E, Uhart M et al (2009) Interaction of phosphodiesterase 3A with brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins BIG1 and BIG2 and effect on ARF1 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(15):6158–6163
Padilla PI, Chang MJ et al (2003) Interaction of FK506-binding protein 13 with brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein 1 (BIG1): effects of FK506. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(5):2322–2327
Belov GA, Habbersett C et al (2007) Activation of cellular Arf GTPases by poliovirus protein 3CD correlates with virus replication. J Virol 81(17):9259–9267
Li H, Adamik R et al (2003) Protein kinase A-anchoring (AKAP) domains in brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein 2 (BIG2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(4):1627–1632
Islam A, Shen X et al (2007) The brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein, BIG2, regulates the constitutive release of TNFR1 exosome-like vesicles. J Biol Chem 282(13):9591–9599
Islam A, Jones H et al (2008) cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) signaling induces TNFR1 exosome-like vesicle release via anchoring of PKA regulatory subunit RIIbeta to BIG2. J Biol Chem 283(37):25364–25371
Wolf JR, Lasher RS et al (1996) The putative membrane anchor protein for yeast Sec7p recruitment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 224(1):126–133
Deitz SB, Rambourg A et al (2000) Sec7p directs the transitions required for yeast Golgi biogenesis. Traffic 1(2):172–183
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Martin Lowe for providing unpublished images and Dr. Julie Brill for information regarding FlyBase. We apologize to all whose work we didn’t cover due to our ignorance, inadvertent oversight or space constraints.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, J., Kahn, R.A. & Sztul, E. Regulating the large Sec7 ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factors: the when, where and how of activation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71, 3419–3438 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1602-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1602-7