Abstract
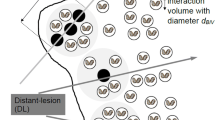
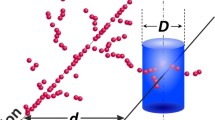
There is a growing interest in the study of interactions of ionizing radiation with condensed matter at the nanometer level. The motivation for this research is the hypothesis that the number of ionizations occurring within short segments of DNA-size subvolumes is a major factor determining the biological effectiveness of ionizing radiation. A novel dosimetry technique, called nanodosimetry, measures the spatial distribution of individual ionizations in an irradiated low-pressure gas model of DNA. The measurement of nanodosimetric event size spectra may enable improved characterization of radiation quality, with applications in proton and charged-particle therapy, radiation protection, and space research. We describe an ion-counting nanodosimeter developed for measuring radiation-induced ionization clusters in small, wall-less low-pressure gas volumes, simulating short DNA segments. It measures individual radiation-induced ions, deposited in 1 Torr propane within a tissue-equivalent cylindrical volume of 2–4 nm diameter and up to 100 nm length. We present first ionization cluster size distributions obtained with 13.6 MeV protons, 4.25 MeV alpha particles and 24.8 MeV carbon nuclei in propane; they correspond to a wide LET range of 4–500 keV/μm. We are currently developing plasmid-based assays to characterize the local clustering of DNA damage with biological methods. First results demonstrate that there is increasing complexity of DNA damage with increasing LET. Systematic comparison of biological and nanodosimetric data will help us to validate biophysical models predicting radiation quality based on nanodosimetric spectra. Possible applications for charged particle radiation therapy planning are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rossi, H.H.,Specification of radiation quality, Radiat Res. 10: 522–531, 1959.
Kellerer, A.M., and Chmelevsky, D.,Concepts of microdosimetry. II. Probability distributions of the microscopic variables, Radiat Environ Biophys. 12: 205–216, 1975.
Prise, K.M., Pinto, M., Newman, H.C., and Michael, B.D.,A review of studies of ionizing radiation-induced double-strand break clustering, Radiat Res. 156: 572–576, 2001.
Ward, J.F.,The complexity of DNA damage—relevance to biological consequences, Int J Radiat Biol. 66: 427–432, 1994.
Shchemelinin, S., Breskin, A., Chechik, R., Pansky, A., and Colautti, P.,Microdosimetry — An interdisciplinary approach, The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 375–378, 1997.
Shchemelinin, S., Breskin, A., Chechik, R., Pansky, A., Colautti, P., Conte, V., De Nardo, L., and Tornielli, G.,Ionization measurements in small gas samples by single ion counting, Nucl Instr Meth A. 368: 859–861, 1996.
Shchemelinin, S., Breskin, A., Chechik, R., Colautti, P., and Schulte, R.W.,First ionization cluster measurements on the DNA scale in a wall-less sensitive volume, Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 82: 43–50, 1999.
Chmelewski, D., Parmentier, N., and Le Grand, J.,Proceedings of the Fourth Symposium on Microdosimetry, EUR 5122 d-e-f, CEC, Luxemburg, 869, 1973.
Breskin, A., Chechik, R., Colautti, P., Conte, V., Pansky, A., Shchemelinin, S., Talpo, G., and Tornielli, G.,A single-electron counter for nanodosimetry. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 61: 199–204, 1995.
Schulte, R., Bashkirov, V., Shchemelinin, S., Garty, G., Chechik, R., and Breskin, A.,Modeling of radiation action based on nanodosimetric event spectra, Phys Med. XVII: 177–180, 2001.
Garty, G., Shchemelinin, S., Breskin, A., Chechik, R., Assaf, G., Orion, I., Bashkirov, V., Schulte, R., and Grosswendt, B.,The performance of a novel ion-counting nanodosimeter, Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 492: 212–235, 2002.
Nikjoo, H., O…Neill, P., Terrissol, M., and Goodhead, D.T.,Quantitative modelling of DNA damage using Monte Carlo track structure, Radiat Environ Biophys. 38: 31–38, 1999.
Nikjoo, H., O…Neill, P., Wilson, W.E., and Goodhead, D.T.,Computational approach for determining the spectrum of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation, Radiat Res. 156: 577–583, 2001.
Sutherland, B.M., Bennett, P.V., Sidorkina, O., and Laval, J.,Clustered damages and total lesions induced in DNA by ionizing radiation: oxidized bases and strand breaks, Biochemistry. 39: 8026–8031, 2000.
Milligan, J.R., Aguilera, J.A., Paglinawan, R.A., Ward, J.F., and Limoli, C.L.,DNA strand break yields after post-high LET irradiation incubation with endonuclease-III and evidence for hydroxyl radical clustering, Int J Radiat Biol. 77: 155–164, 2001.
Shao, C., Saito, M., and Yu, Z.,Formation of single- and double-strand breaks of pBR322 plasmid irradiated in the presence of scavengers, Radiat Environ Biophys. 38: 105–109, 1999.
Milligan, J.R., Aguilera, J.A., Nguyen, T.T., Paglinawan, R.A., and Ward, J.F.,DNA strand-break yields after postirradiation incubation with base excision repair endonucleases implicate hydroxyl radical pairs in doublestrand break formation, Int J Radiat Biol. 76: 1475–1483, 2000.
Nikjoo H, O…Neill P, Wilson WE, and Goodhead DT.,Computational approach for determining the spectrum of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation, Radiat Res. 156: 577–583, 2001.
Loeffler, J.S., Smith, A.R., and Suit, H.D.,The potential role of proton beams in radiation oncology, Semin Oncol. 24: 686–695, 1997.
Orecchia, R., Zurlo, A., Loasses, A., Krengli, M., Tosi, G., Zurrida, S., Zucali, P., and Veronesi, U.,Particle beam therapy (hadron therapy): basis for interest and clinical experience, Eur J Cancer. 34: 459–468, 1998.
Kraft, G.,Radiotherapy with heavy ions: radiobiology, clinical indications and experience at GSI, Darmstadt, Tumori. 84: 200–204, 1998.
Gerweck, L.E., and Kozin, S.V.,Relative biological effectiveness of proton beams in clinical therapy, Radiother Oncol. 50: 135–142, 1999.
Robertson, J.B., Eaddy, J..M., Archambeau,, J.O., Coutrakon, G.B., Miller, D.W., Moyers, M..F., Siebers, J.V., Slater, J.M., and Dicello, J.F.,Relative biological effectiveness and microdosimetry of a mixed energy field of protons up to 200 MeV, Adv Space Res. 14: 271–275, 1994.
Jones, B., and Dale, R.G.,Estimation of optimum dose per fraction for high LET radiations: implications for proton radiotherapy, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 48: 1549–1557, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulte, R., Bashkirov, V., Garty, G. et al. Ion-counting nanodosimetry: current status and future applications. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 26, 149–155 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179174
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179174