Abstract
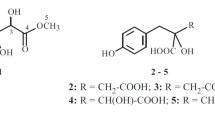
Activity-guided fractionation of the EtOAc-soluble extract of the stems of Couepia ulei, using a bioassay based on the induction of quinone reductase (QR) in cultured Hepa 1c1c7 mouse hepatoma cells led to the isolation of two active compounds, a new natural product,erythro-2,3-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-ethoxypropan-1-ol (1), and a known compound, evofolin-B (2), along with five inactive compounds all of known structure, viz., betulinic acid, oleanolic acid, pomolic acid, (±)-syringaresinol, and ursolic acid. These isolates were identified by analysis of physical and spectral data. Compounds1 and2 exhibited QR inducing activity, with observed CD (concentration required to double induction) values of 16.7 and 16.4 μM, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhakuni, R. S., Shukla, Y. N., and Thakur, R. S., New triterpenoid and aliphatic esters fromCornus capitata.Fitoterapia, 59, 45–46 (1988).
Cheng, D. and Cao, X., Pomolic acid derivatives from the root ofSanguisorba officinalis.Phytochemistry, 31, 1317–1320 (1992).
Gerhauser, C., You., M., Liu, J., Moriarty, R. M., Hawthorne, M., Mehta, R. G., Moon, R. C., and Pezzuto, J. M., Cancer chemopreventive potential of sulforamate, a novel analogue of suforaphane that induces phase 2 drug-metabolizing enzymes.Cancer Res., 57, 272–278 (1997).
Hwang, B. Y., Chai, H.-B., Kardono, L. B. S., Riswan, S., Farnsworth, N. R., Cordell, G. A., Pezzuto, J. M., and Kinghorn, A. D., Cytotoxic triterpenes from the twigs ofCeltis philippinensis.Phytochemistry, 62, 197–201 (2003).
Jang, D. S., Park, E. J., Hawthorne, M. E., Vigo, J. S., Graham, J. G., Cabieses, F., Santarsiero, B. D., Mesecar, A. D., Fong, H. H. S., Mehta, R. G., Pezzuto, J. M., and Kinghorn, A. D., Constituents ofMusa x paradisiaca cultivar with the potential to induce the phase II enzyme, quinone reductase.J. Agric. Food Chem., 50, 6330–6334 (2002).
Jang, D. S., Park, E. J., Kang, Y.-H., Su, B.-N., Hawthorne, M. E., Vigo, J. S., Graham, J. G., Cabieses, F., Fong, H. H. S., Mehta, R. G., Pezzuto, J. M., and Kinghorn, A. D., Compounds obtained fromSida acuta with the potential to induce quinone reductase and to inhibit 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthraceneinduced preneoplastic lesions in a mouse mammary organ culture model.Arch. Pharm. Res., 26, 585–590 (2003).
Kakuno, T., Yoshikawa, K., and Arihara, S., Triterpenoid saponins fromIlex crenata fruit.Phytochemistry, 31, 3553–3557 (1992).
Kinghorn, A. D., Su, B.-N., Lee, D., Gu, J.-Q., and Pezzuto, J. M., Cancer chemopreventive agents discovered by activity-guided fractionation: an update.Curr. Org. Chem., 7, 213–226 (2003).
Lee, T.-H., Kuo, Y.-C., Wang, G.-J., Kuo, Y.-H., Chang, C.-l., Lu, C.-K., and Lee, C.-K., Five new phenolics from the roots ofFicus beecheyana.J. Nat. Prod., 65, 1497–1500 (2002).
Mahato, B. S. and Kundu, P. A.,13C-NMR spectra of pentacyclic triterpenoids- A compilation and some salient features.Phytochemistry, 37, 1517–1575 (1994).
Maxuitenko, Y. Y., MacMillan, D. L., Kensler, T. W., and Roebuck, B. D., Evaluations of the post-initiation effects of oltipraz on aflatoxin B1-induced preneoplastic foci in a rat model of hepatic tumorigenesis.Carcinogenesis, 14, 2423–2425 (1993).
Nawwar, M. A. M., Buddrus, J., and Bauer, H., Dimeric phenolic constituents from the roots ofTamarix nilotica.Phytochemistry, 21, 1755–1758 (1982).
Pezzuto, J. M., Song, L. L., Lee, S. K., Shamon, L. A., Mata-Greenwood, E., Jang, M., Jeong, H.-J., Pisha, E., Mehta, R. G., and Kinghorn, A. D., Bioassay methods useful for activityguided isolation of natural product cancer chemopreventive agents. In Hostettmann, K., Gupta, M. P., and Marston, A. (Eds.).Chemistry, Biological and Pharmacological Properties of Medicinal Plants from the Americas. Harwood Academic Publishers, Amsterdam, pp. 81–110 (1999).
Sanduja, R., Alam, M., and Euler, K. L., Constituents ofCouepia paraensis.J. Nat. Prod., 46, 149 (1983).
Sanduja, R., Euler, K. L., Alam, M., Korp, J. D., and Bernal, I., Isolation and crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2,8-dimethyl-6,7-dimethoxybenzopyran-4-one fromCouepia paraensis.Phytochemistry, 21, 1457–1453 (1982).
Spitzer, V., Marx, R., Maia, J. G. S., and Pfeilsticker, K., Occurrence of conjugated fatty acids in the seed oil of Couepia longipendula (Chrysobalanaceae).J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 68, 440–442 (1991).
Su, B.-N., Cuendet, M., Farnsworth, N. R., Fong, H. H. S., Pezzuto, J. M., and Kinghorn, A. D., Activity-guided fractionation of the seeds ofZiziphus jujuba using a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory assay.Planta Med., 68, 1125–1128 (2002).
Talalay, P., De Long, M. J., and Prochaska, H. J., Molecular mechanisms in protection against carcinogenesis. In Cory, J. G., and Szentivanyi, A. (Eds.).Cancer Biology and Therapeutics. Plenum Press, New York, NY, pp. 197–216 (1981).
Takeoka, G., Dao, L., Teranish, R., Wong, R., Flessa, S., Harden, L., and Edwards, R., Identification of three triterpenoids in almond hulls.J. Agric. Food Chem., 48, 3437–3439 (2000).
Wattenberg, L. W., An overview of chemoprevention: current status and future prospects.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 216, 133–141 (1997).
Wu, T.-S., Teh, J.-H., and Wu, P.-L., The heartwood constituents ofTetradium glabrifolium.Phytochemistry, 40, 121–124 (1995).
Yoshikawa, K., Mimura, N., and Arihara, S., Isolation and absolute structures of enantiomeric 1,2-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-propanediol 1-O-glucosides from the bark ofHovenia trichocarpa.J. Nat. Prod., 61, 1137–1139 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, D.S., Park, E.J., Kang, YH. et al. Phenolic compounds obtained from stems ofcouepia ulei with the potential to induce quinone reductase. Arch Pharm Res 27, 169–172 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980101
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980101