Abstract
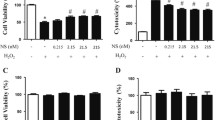
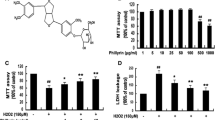
A number of reports indicate the potential for redox signalling via extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK) during neuronal injury. We have previously found that sustained ERK activation contributes to toxicity elicited by 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) in the B65 neuronal cell line. To determine whether reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a role in mediating ERK activation and 6-OHDA toxicity, we examined the effects of catalase, superoxide dismutase (SOD1), and metalloporphyrin antioxidants (‘SOD mimetics’) on 6-OHDA-treated cells. We found that catalase and metalloporphyrin antioxidants not only conferred protection against 6-OHDA but also inhibited development of sustained ERK phosphorylation in both differentiated and undifferentiated B65 cells. However, exogenously added SOD1 and heat-inactivated catalase had no effect on either toxicity or sustained ERK phosphorylation. This correlation between antioxidant protection and inhibition of 6-OHDA-induced sustained ERK phosphorylation suggests that redox regulation of ERK signalling cascades may contribute to neuronal toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERK:
-
Extracelluar signal-regulated protein kinase
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase
- MnTBAP:
-
Mn-tetrakis-(4-benzoic acid) porphyrin
- MTS:
-
metabolism of the tetrazolium salt [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulphophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner saltxxx]
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-hydroxydopamine
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
References
Aebi H 1984 Catalasein vitro;Methods Enzymol. 105 121–126
Antunes F and Cadenas E 2000 Estimation of H2O2 gradients across bio membrane s;FEBS Lett. 475 121–126
Asanuma M, Hirata H and Cadet J L 1998 Attenuation of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic nigrostriatal lesions in superoxide dismutase transgenic mice;Neuroscience 85 907–917
Cavanaugh J E, Ham J, Hetman M, Poser S, Yan C and Xia Z 2001 Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and ERK5 by neurotrophins, neuronal activity, and cAMP in neurons;J. Neurosci. 21 434–443
Chu C T, Caruso J L, Cummings T J, Ervin J, Rosenberg C and Hulette C M 2000 Ubiquitin immunochemistry as a diagnostic aid for community pathologists evaluating patients who have dementia;Modern Pathol. 13 420–426
Chu C T, Everiss K D, Batra S, Wikstrand C J, Kung H-J and Bigner D D 1997 Receptor dimerization is not a factor in the signalling activity of a transforming variant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII);Biochem. J. 324 855–861
Cohen G and Heikkila R E 1974 The generation of hydrogen peroxide, superoxide radical, and hydroxyl radical by 6-hydroxydopamine, dialuric acid, and related cytotoxic agents;J. Biol. Chem. 249 2447–2452
Day B J, Fridovich I and Crapo J D 1997 Manganic porphyrins possess catalase activity and protect endothelial cells against hydrogen peroxide-mediated injury;Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 347 256–262
Fattman C L, Chu C T, Kulich S M, Enghild J J and Oury T D 2001 Altered expression of extracellular superoxide dismutase in mouse lung after bleomycin treatment;Free Radical Biol. Med. 31 1198–1207
Glinka Y Y and Youdim M B 1995 Inhibition of mitochondrial complexes I and IV by 6-hydroxydopamine;Eur. J. Pharmacol. 292 329–332
Hashimoto K, Guroff G and Katagiri Y 2000 Delayed and sustained activation of p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase induced by proteasome inhibitors through p21(ras) in PC12 cells;J. Neurochem. 74 92–98
Hastings T G, Lewis D A and Zigmond M J 1996 Role of oxidation in the neurotoxic effects of intrastriatal dopamine injections;Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93 1956–1961
Kulich S M and Chu C T 2001 Sustained extracellular signalregulated kinase activation by 6-hydroxydopamine: Implications for Parkinson’s disease;J. Neurochem. 77 1058–1066
Li Q Y, Pedersen C, Day B J and Patel M 2001 Dependence of excitotoxic neurodegeneration on mitochondrial aconitase inactivation;J. Neurochem. 78 746–755
Luo Y, Umegaki H, Xiantao W, Abe R and Roth G S 1998 Dopamine induces apoptosis through an oxidation-involved SAPK/JNK activation pathway;J. Biol. Chem. 273 3756–3764
Nishida M, Maruyama Y, Tanaka R, Kontani K, Nagao T and Kurose H 2000 G alpha(i) and G alpha(o) are target proteins of reactive oxygen species;Nature (London) 408 492–495
Oh-hashi K, Maruyama W, Yi H, Takahashi T, Naoi M and Isobe K 1999 Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediates peroxynitrite-induced apoptosis in human dopaminergic neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells;Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 263 504–509
Patel M and Day B J 1999 Metalloporphyrin class of therapeutic catalytic antioxidants;Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 20 359–364
Runden E, Seglen P O, Haug F M, Ottersen O P, Wieloch T, Shamloo M and Laake J H 1998 Regional selective neuronal degeneration after protein phosphatase inhibition in hippocampal slice cultures: evidence for a MAP kinase-dependent mechanism;J. Neurosci. 18 7296–7305
Schubert D, Heinemann S, Carlisle W, Tarikas H, Kimes B, Patrick J and Steinback J H 1974 Clonal cell lines from the rat central nervous system;Nature (London) 249 224–227
Stanciu M, Wang Y, Kentor R, Burke N, Watkins S, Kress G, Reynolds I, Klann E, Angiolieri M, Johnson J and DeFranco D B 2000 Persistent activation of ERK contributes to glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in a neuronal cell line and primary cortical neuron cultures;J. Biol. Chem. 275 12200–12206
Suzuki Y J, Forman H J and Sevanian A 1997 Oxidants as stimulators of signal transduction;Free Radical Biol. Med. 11 269–285
Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Saneto R P, Proctor P H and Perez-Polo J R 1982 Participation of active oxygen species in 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity to a human neuroblastoma cell line;Biochem. Pharmacol. 31 181–188
Torres M and Forman H J 1999 Activation of several MAP kinases upon stimulation of rat alveolar macrophages: role of the NADPH oxidase;Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 366 231–239
Ungerstedt U 1968 6-Hydroxy-dopamine induced degeneration of central monoamine neurons;Eur. J. Pharmacol. 5 107–110
Wang X and Studzinski G P 2001 Phosphorylation of raf-1 by kinase suppressor of ras is inhibited by “MEK-specific” inhibitors PD 098059 and U0126 in differentiating HL60 cells;Exp. Cell Res. 268 294–300
Zhu J-H, Kulich S M, Oury T D and Chu C T 2002 Cytoplasmic aggregates of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase in Lewy body diseases;Am. J. Pathol. 161 2087–2098
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulich, S.M., Chu, C.T. Role of reactive oxygen species in extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase phosphorylation and 6-hydroxydopamine cytotoxicity. J. Biosci. 28, 83–89 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02970136
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02970136