Abstract
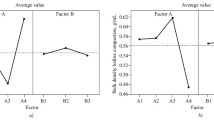
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of magnesium stearate on the physical stability of polydisperse powder mixtures. The effects of concentration of magnesium stearate and the time of lubrication of mixtures with magnesium stearate on the content uniformity of the active ingredient in the mixtures were evaluated in a model mixture of lactose and aspirin. These effects were compared in a random mixture of non-interacting components and a mixture based on particle interaction. A statistical model that adequately described the relationship between the factors examined and the response was generated. The model indicated the presence of an interaction between magnesium stearate concentration and lubrication time. At a given concentration of magnesium stearate, there was a significant reduction in the content uniformity of aspirin as the time of lubrication of the mixture with magnesium stearate was increased. This effect was larger in mixtures based on particle interaction than in random mixtures of non-interacting components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stewart PJ. Influence of magnesium stearate on the homogeneity of a prednisone-granule ordered mix. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1981;7(5):485–495.
Swaminathan V, Kildsig DO. Effect of particle morphology on the physical stability of pharmaceutical powder mixtures: effect of surface roughness of carrier on the stability of ordered mixtures. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000;26(4):356–373.
Hersey JA. Ordered mixing: a new concept in powder mixing practice. Powder Technol. 1975;11:41–44.
Montgomery DC. Design and Analysis of Experiments. 3rd ed. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 1991.
Swaminathan V, Kildsig DO. Polydisperse powder mixtures: effect of particle size and shape on mixture stability. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2002;28(1):41–48.
Staniforth JN, Rees JE. Electrostatic charge interactions in ordered powder mixes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1982;34(2):69–76.
Staniforth JN, Rees JE, Lai FK, Hersey JA. Interparticle forces in binary and ternary ordered powder mixes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1982;34(3):141–145.
Zografi G, Tam S. Wettability of pharmaceutical solids: estimates of solid surface polarity. J Pharm Sci. 1976;65:1145–1149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swaminathan, V., Kildsig, D.O. Effect of magnesium stearate on the content uniformity of active ingredient in pharmaceutical powder mixtures. AAPS PharmSciTech 3, 19 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1208/pt030319
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt030319