Abstract
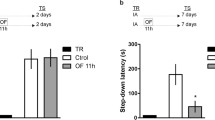
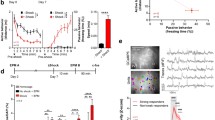
In addition to their well-known role in neural development, the neurotrophins BDNF and NGF help mediate the plasticity that occurs in the brain to promote learning. Exposure to learning procedures often leads to increases in neurotrophins, while exposure to stress often results in decreases. It is unclear how the neurotrophins would respond to an aversive learning task. Therefore, BDNF and NGF content in the dorsal striatum, hippocampus, and basal forebrain was measured following discrete trial lever-press escape/avoidance conditioning. Conditioning significantly increased levels of both neurotrophins in hippocampus and basal forebrain, relative to home cage controls (HCC). Contrary to expectations, the dorsal striatum did not show any significant changes. However, significant correlations were observed between dorsal striatal neurotrophins and aspects of avoidance performance. This may indicate that the dorsal striatum is involved in the performance aspects of the task. Results are discussed in terms of the role of neurotrophins in the acquisition of new information, and the neural structures involved in different types of memory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albeck, D.S., Mesches, M.H., Juthberg, S., Browning, M., Bickford, P.C., Rose, G.M., & Granholm, A.C. (2003). Exogenous NGF restores endogenous NGF distribution in the brain of the cognitively impaired aged rat.Brain Research, 967, 306–310.
Altar, C.A., Cai, N., Bliven, T., Juhasz, M., Conner, J.M., Acheson, A.L., Lindsay, R.M., & Wiegand, S. J. (1997). Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain.Nature, 389, 856–860.
Berger, D.F. & Starzec, J.J. (1988). Contrasting lever-press avoidance behaviors of spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats (Rattus norvegicus).Journal of Comparative Psychology, 102, 279–286.
Bizon, J.L., Lauterborn, J.C., & Gall, C.M. (1999). Subpopulations of striatal interneurons can be distinguished on the basis of neurotrophic factor expression.Journal of Comparative Neurology, 408, 283–298.
Brennan, F.X., Beck, K.D., & Servatius, R.J. (2003). Leverpress escape/avoidance conditioning in rats: safety signal length and avoidance performance.Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science, 38, 36–44.
Brennan, F.X. (2004). Genetic differences in leverpress escape/avoidance conditioning in seven mouse strains.Genes, Brain, and Behavior, 3, 110–114.
Ceccatelli, A., Erenfors, P., Villar, M.J., Persson, H., & Hokfelt, T. (1991). Expanded distribution of mRNA for NGF BDNF and NT-3 in the rat brain after colchicine treatment.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 88, 10352–10356.
Conner, J.M., Lauterborn, J.C., Yan, Q., Gall, C.M., & Varon, S. (1997). Distribution of BDNF protein and mRNA in the normal adult rat CNS: Evidence for anterograde axonal transport.Journal of Neuroscience, 17, 2295–2313.
Hall, J., Thomas, K.L., & Everitt, B.J. (2000). Rapid and selective induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during contextual learning.Nature Neuroscience, 3, 533–535.
Kelly, A., Conroy, S., & Lynch, M.A. (1998). Evidence that nerve growth factor plays a role in long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus.Neuropharmacology, 37, 561–570.
Kovalchuk, Y., Hanse, E., Kafitz, K.W., & Konnerth, A. (2002). Postsynaptic Induction of BDNF-Mediated Long-Term Potentiation.Science, 295, 1729–1734.
Kung, L., Sano, K., & Albeck, D.S. (2004). The effect of treadmill exercise on NGF levels in both female and male rats.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts, 30.
Kung, L., Sano, K., & Albeck, D.S. (2003). Chronic and acute physical exercise alters hippocampal BDNF levels in both female and male rats.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts, 29.
Meyer, D. Cho, D., & Wesemann, A. (1960). On problems of conditioned discriminated lever-press avoidance responses.Psychological Review, 67, 224–228.
Mufson, E.J., Kroin, J.S., Sendera, T.J., & Sobreviela, T. (1999). Distribution and retrograde transport of trophic factors in the CNS: functional implications for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Progress in Neurobiology, 57, 451–484.
Packard, M.G. & Knowlton, B.J. (2002). Learning and memory functions of the Basal Ganglia.Annual Review of Neuroscience, 25, 563–593.
Paxinos, G. & Watson, C. (1998).The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th edition. Academic Press, New York. USA.
Schinder, A.F. & Poo, M.M. (2000). The neurotrophin hypothesis for synaptic plasticity.Trends in Neurosciences, 23, 639–645.
von Richthofen, S., Lang, U.E., & Hellweg, R. (2003). Effects of different kinds of acute stress on nerve growth factor content in rat brain.Brain Research, 987, 207–213.
Wetmore, C., Ernfors, P., Persson, H., & Olson, L. (1990). Localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA to neurons in the brain by in situ hybridization.Experimental Neurology, 109, 141–152.
White N.M. & McDonald, R.J. (2002). Multiple parallel memory systems in the brain of the rat.Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 77, 125–184.
Woolf, N.J. Milov, A.M., Schweitzer, E.S., & Roghani, A. (2001). Elevation of nerve growth factor and antisense knockdown of TrkA receptor during contextual memory consolidation.Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 1047–1055.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albeck, D.S., Beck, K.D., Kung, LH. et al. Leverpress escape/avoidance training increases neurotrophin levels in rat brain. Integr. psych. behav. 40, 28–34 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02734186
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02734186