Abstract
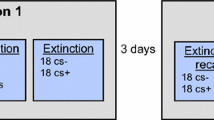
This study investigated whether low levels of the personality trait of constraint and early-onset alcoholism would be associated with deficits in aversive conditioning and smaller responses to novelty in a stimulus mismatch protocol. Personality traits (constraint and socialization) and skin conductance responses (SCRs) during conditioning and novelty paradigms were assessed in alcoholics (n=41) and non-alcoholics (n=32). The conditioning protocol involved measuring SCRs after conditioned stimuli (CS+: tones) paired with shock, CS− tones unpaired with shock, and CS+ probes unpaired with shock. The mismatch protocol involved measuring SCRs to auditory stimuli consisting of a series of 5 pure tones of the same pitch followed a shorter white noise stimulus (the novel stimulus). Contrary to the hypothesis, alcoholics did not differ from non-alcoholics in SCRs to CS+ probes or on the mismatch measure (SCR novel tone—SCR to 5th tone). Higher levels of constraint and self-reports of fear during conditioning were associated with smaller responses to both the CS+ probes and the CS− tones as well as the mismatch measure within non-alcoholics, but not within alcoholics. In alcoholics, low constraint was associated with greater habituation to CS+ probes, and poor differential conditioning on measures of change across trials in SCR to CS+ probes and CS− stimuli. The results suggest that different processes influence levels of constraint in non-alcoholics and alcoholics. The data indicate that low constraint in non-alcoholics is associated with allocating fewer processing resources to potentially significant stimuli, rather than being associated with a specific deficit in aversive conditioning per se.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (1994).Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, D.C.: Author.
Booth, M.L., Siddle, D.A.T., & Bond, N.W. (1989). Effects of conditioned stimulus fear-relevance and preexposure on expectancy and electrodermal measures of human pavlovian conditioning.Psychophysiology, 26, 281–291.
Bucholz, K., Cadoret, R., Cloninger, C. R., Dinwiddie, S., Hesselbrock, V., Nurberger, J., Reich, T., Schmit, I. & Schuckit, M. (1994). A new, semistructured psychiatric interview for use in genetic linkage studies: A report of the reliability of the SSAGA.Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 55, 149–158.
Caspi, A., Moffitt, T. E., Newman, D. L., & Silva, P. A. (1996). Behavioral observations at age 3 years predict adult psychiaric disorders.Archives of General Psychiatry, 53, 1033–1039.
Chassin, L., Pitts, S. C., DeLucia, C., Todd, M. (1999). A longitudinal study of children of alcoholics: Predicting young adult substance abuse disorders, anxiety, and depression.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 108, 106–119.
Cloninger, C. R. (1987). Neurogenetic adaptive mechanisms in alcoholism.Science, 236, 410–416.
Cloninger, C. R., Sigvardsson, S., Bohman, M. (1988). Childhood personality predict alcohol abuse in young adults.Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 12, 494–505.
Finn, P. R., Kessler, D. N., & Hussong, A. M. (1994). Risk for alcoholism and classical conditioning to signals for punishment: Evidence for a weak behavioral inhibition system.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 103, 293–301.
Finn, P. R., Sharkansky, E. J., Brandt, K. M., & Turcotte, N. (2000). The effects of familial-risk, personality, and expectancies on alcohol use and abuse.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109, 122–133.
Finn, P.R., Sharkansky, E., Viken, R., West, T.L., Sandy, J., & Bufferd, G. (1977). Heterogeneity in the families of sons of alcoholics: The impact of familial vulnerability type on offspring characteristics.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 106, 26–36.
Fowles, D.C. (1980). The three arousal model: Implications of Gray’s two-factor learning theory for heart rate, electrodermal activity, and psychopathy.Psychophysiology, 17, 87–104.
Fowles, D.C., Christie, M.J., Edelberg, R., Grings, W.W., Lykken, D.T., & Venables, P.H. (1981). Publication recommendations for electrodermal measurements.Psychophysiology, 18, 232–239.
Gorenstein, E.E., & Newman J.P. (1980). Disinhibitory psychopathology: A new perspective and a model for research.Psychological Review, 87, 301–315.
Gough, H.G. (1969).Manual for the California Psychological Inventory. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, CA.
Gray, J.A. (1972). The psychophysiological nature of introversion-extraversion: A modification of Eysenck’s theory. In J.A. Gray & V.D. Nebylitsyn (Eds.)Biological bases of individual behavior. New York: Academic Press.
Gray, J. A. (1975).Elements of a two-process theory of learning. New York: Academic Press.
Gray, J. A. (1987). Perspectives on anxiety and impulsivity: a commentary.Journal of Research in Personality, 21, 493–509.
Hare, R.D. (1965). Acquisition and generalization of a conditioned fear response in psychopathic and non-psychopathic criminals.Journal of Psychology, 59, 367–370.
Hare, R.D. (1970).Psychopathy: Theory and research. New York, Wiley.
Hare, R.D., Frazelle, J., & Cox, D.N. (1978). Psychopathy and physiological responses to threat of an aversive stimulus.Psychophysiology, 15, 165–172.
Hare, R.D., & Quinn, M.J. (1971). Psychopathy and autonomic conditioning.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 77, 223–235.
Iacono, W.G. (1998). Identifying psychophysiological risk for psychopathology: Examples from substance abuse and schizophrenia research.Psychophysiology, 35, 621–637.
Iacono, W.G., Carlson, S.R., Taylor, J., Elkins, I.J., & mcGue, M. (1999) Behavioral disinhibition and the development of substance abuse disorders: Findings from the Minnesota Twin Family Study.Development and Psychopathology, 11, 869–900.
Justus, A.N., Finn, P.R., Steinmetz, J.E. (2000). The influence of traits of disinhibition on the association between alcohol use and risky sexual behavior.Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research, 24, 1028–1035.
Krueger, R.F., Caspi, A., Moffitt, T.E., Silva, P.A., McGee, R. (1996). Personality traits are differentially linked to mental disorders: A multitrait-multidiagnosis study of an adolescent birth cohort.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 105, 299–312.
Lachnit, H., & Kimmel, H.D. (1993). Positive and negative patterning in human classical skin conductance response conditioning.Animal Learning and Behavior, 21, 314–326.
Lykken, D.T. (1957). A study of anxiety in the sociopathic personality.Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 55, 6–10.
Lykken, D.T. (1997). The American crime factory.Psychological Inquiry, 8, 261–270.
Masse, L.C., Tremblay, R.E. (1997). Behavior of boys in kindergarten and the onset of substance use during adolescence.Archives of General Psychiatry, 54, 62–68. Mazas, C., Finn, P.R., & Steinmetz, J.E. (2000). Decision making biases, antisocial personality, and early-onset Alcoholism.Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research, 24, 1036–1040.
McGue, M., Slutske, W., Taylor, J., & Iacono, W.G. (1997). Personality and substance abuse disorders: I. Effects of gender and alcoholism subtype.Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research, 21, 513–520.
Nigg, J.T., (2000). On inhibition/disinhibition in developmental psychopathology: Views from cognitive and personality psychology and a working inhibition taxonomy.Psychological Bulletin, 126, 220–246.
Raine, A., & Venables, P.H. (1981). Classical conditioning and socialization—A biosocial interaction.Personality and Individual Differences, 2, 273–283.
Tellegen, A. (1982).Brief Manual of the Multi-dimensional Personality Questionnaire. Unpublished manuscript, University of Minnesota.
Waid, W.M. (1976). Skin conductance response to both signalled and unsignalled noxious stimulation predicts level of socialization.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 34, 923–929.
Waid W.M., & Orne, M.T. (1982). Reduced electodermal response to conflict, failure to inhibit dominant behaviors, and deliquency proneness.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 43, 769–774.
Ziskind, E., Syndulko, K., & Maltzman, I. (1977). Evidence for a neurologic disorder in the sociopath syndrome: Aversive conditioning and recidivism. In C. Shagrass, S. Gershon and A.I. Friedhoff (Eds.)Psychopathology and Brain Dysfunction. New York: Raven Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finn, P.R., Justus, A.N., Mazas, C. et al. Constraint, alcoholism, and electrodermal response in aversive classical conditioning and mismatch novelty paradigms. Integr. psych. behav. 36, 154–167 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02734048
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02734048