Abstract
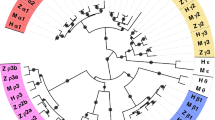
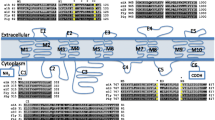
Molecular cloning of GABA transporter-homologous cDNAs from aDrosophila melanogaster headspecific library was accomplished using a conserved oligomer from a highly conserved domain within the mammalian GABA transporters. Partial DNA sequencing of these cDNAs demonstrated homology with the mammalian transporters, indicating these are ancient, evolutionarily conserved molecules. Although theDrosophila cDNAs had distinct restriction enzyme patterns, they recognized the same locus inDrosophila genomic DNA, suggesting that the multiple isoforms might arise via alternative splicing. Antibodies specific for the mammalian GABA transporters GAT1, GAT2 and GAT3 recognized non-overlapping and developmentally distinct patterns of expression inDrosophila neuronal tissues. Treatment of larval instars with nipecotic acid, a generalized GABA reuptake inhibitor, revealed specific, dose-dependent alterations in behavior consistent with the presence of multiple transporter molecules with differing affinities for this drug. Synaptic current recordings revealed that nipecotic acid treated larvae have an increase in latency jitter of evoked quantal release, resulting in a broader average excitatory junctional current which was manifested in a broader EJP. These results imply that alterations in the development of the CNS occur if GABAergic neurotransmission is protentiated during development. The data suggest that, as in mammals, there are multiple GABA transporters inDrosophila whose expression is differentially regulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwood, H. L., Govind, C. K. and Wu, C.-F. (1993) Differential ultrastructure of synaptic terminals on ventral longitudinal abdominal muscles inDrosophila larvae.J. Neurobiol.,24, 1008–1024.
Atwood, H. L. and Cooper, R. L. (1995) Functional and structural parallels in crustaceans andDrosophila neuromuscular systems.American Zool.,35, 556–565.
Atwood, H. L. and Cooper, R. L. (1996a) Ultrastructure of crustacean and insect neuromuscular junctions.J. Neurosci. Methods,69, 51–58.
Atwood, H. L. and Cooper, R. L. (1996b) Synaptic diversity and differentiation: crustacean neuromuscular junctions.Invertebrate Neuroscience,1, 291–307.
Blakely, R., Berson, H., Fremeau, R., Caron, M., Peek, M., Prince, H. and Bradley, C. (1991) Cloning and expression of a functional serotonan transporter from rat brain.Nature,354, 66–70.
Buchner, E., Bader, R., Buchner, S. and Cox, J. (1988) Cell specific immuno-probes for the brain of normal and mutantDrosophila melanogaster. l. Wildtype visual system.Cell and Tiss. Res.,253, 357–370.
Campos-Ortega, J. and Hartenstein, V. (1985)The Embryonic Development of Drosophila melanogaster. Springer Verlag, Berlin.
Chen, P. and Widmer, B. (1968) Content and synthesis of λ-aminobutyric acid in the larval brain ofDrosophila melanogaster.Experientia,24, 516–517.
Cherubini, E., Gaiarsa, J. L. and Ben-Ari, Y. (1991) GABA: an excitatory transmitter in early postnatal life.Trends Neurosci.,14, 515–519.
Clark, J. A., and Amara, S. G. (1994) Stable expression of a neuronal λ-aminobutyric acid transporter, GAT-3, in mammalian cells demonstrates unique pharmacological properties and ion dependence.Mol. Pharmacol.,46, 550–557.
Clark, J. A., Deutch, A. Y., Gallipoli, P. Z. and Amara, S. G. (1992) Functional expression and CNS distribution of β-alanine sensitive neuronal GABA transporter.Neuron,9, 337–347.
Cobb, M., Bruneau, S. and Jallon, J.-M. (1992) Genetic and developmental factors in the olfactory response ofDrosophila melanogaster larvae to alcohols.Proc. R. Soc. London B.,248, 103–109.
Cooper, R. L., Stewart, B. A., Wojtowicz, J. M., Wang, S. and Atwood, H. L. (1995a) Quantal measurement and analysis methods compared for crayfish andDrosophila neuromuscular junctions and rat hippocampus.J. Neurosci. Methods,61, 67–79.
Cooper, R. L., Marin, L. and Atwood, H. L. (1995b). Synaptic differentiation of a single motor neuron: conjoint definition of transmitter release, presynaptic calcium signals, and ultrastructure.J. Neuroscience,15, 4209–4222.
Cooper, R. L., Hampson, D. and Atwood, H. L. (1996a) Synaptotagmin-like expression in the motor nerve terminals of crayfish.Brain Res.,703, 214–216.
Cooper, R. L., Harrington, C. C., Marin, L. and Atwood, H. L. (1996b) Quantal release at visualized terminals of a crayfish motor axon: intraterminal and regional differences.J. Comp. Neurol.,375, 583–600.
Cooper, R. L., Winslow, J., Govind, C. K. and Atwood, H. L. (1996c) Synaptic structural complexity as a factor enhancing probability of calcium-mediated transmitter release.J. Neurophysiol.,75, 2451–2466.
DeFeudis, F. (1982) GABA binding processes and behavior.Gen. Pharmacol.,14, 313–319.
Dodge, F. A. and Rahamimoff, R. (1967) Cooperative action of calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction.J. Physiol.,193, 419–432.
Engles, W., Preston, C., Thompson, P. and Eggelston, W. (1986)In situ hybridization toDrosophila salivary chromosomes with biotinylated DNA probes and alkaline pohosphatase.BRL Focus,8, 6–8.
Guastella, J., Nelson, H., Cayzyk, L., Keynan, S., Miedel, M., Davidson, N., Lester, H. and Kanner, B. (1990) Cloning and expression of a rat GABA transporter.Science,249, 1303–1306.
Guimbal, C., Klostermann, A. and Kilimann, M. (1995) Phylogeneyic conservation of 4-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporter isoforms: cloning and pharmacological characterization of a GABA/β-alanine transporter from Torpedo.Eur. J. Biochem.,234, 794–800.
Honda, S., Yamamoto, M. and Salto, N. (1995) Immunocytochemical localization of 3 subtypes of GABA transporter isoforms.Mol. Brain Res.,33, 319–325.
Ikegaki, N., Saito, N., Hashima, M. and Tanaka, C. (1994) Production of specific antibodies against GABA transporter subtypes (GAT-1, GAT-2, GAT-3) and their application to immunocytochemistry.Mol. Brain Res.,26, 47–54.
Itoh, N., Salvaterra, P. and Itakura, K. (1985) Construction of an adultDrosophila head cDNA expression library with γgt11.Dros. Inf. Serv.,61, 89.
Iverson, L. and Kravitz, E. (1968) The metabolism of GABA in the lobster nervous system. Uptake of GABA the nerve-muscle preparations.J. Neurochem.,15, 1141–1149.
Jursky, F. and Nelson, N. (1994) Developmental expression of GABA transporters GAT-1 and GAT-4 suggests involvement in brain maturation.J. Neurochem.,67, 857–867.
Katz, B. and Miledi, R. (1968) The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation.J. Physiol.,195, 481–492.
Krause, D., Ikeda, K. and Roberts, E. (1981) Dose-conductance relationships for GABA agonists and the effect of uptake inhibitors in crayfish stretch receptor neurons.Brain Res.,225, 319–332.
Kurdyak, P., Atwood, H. L., Stewart, B. A. and Wu, C.-F. (1994) Differential physiology and morphology of motor axons to ventral longitudinal muscles in larvalDrosophila.J. Comp. Neurol.,350, 463–472.
Lilly, M. and Carslon, J. (1990).smellblind, a gene required forDrosophila olfaction.Genetics,124, 293–302.
Liu, Q., Mandiyan, S., Lopez-Corcuera, B., Nelson, H. and Nelson, N. (1993) A rat brain cDNA encoding the neurotransmitter transporter with an unusual structure.FEBS Lett.,315, 114–118.
Mbungu, D., Ross, L. and Gill, L., (1995) Cloning, functional expression and pharmacology of a GABA transporter fromManduca sexta.Arch. Biochem. Biophys.,318, 489–497.
Meier, E., Hertz, L. and Schousboe, A. (1991) Neurotransmitters as developmental signals.Neurochem. Int.,19, 99–102.
Minelli, A., Brecha, N., Karschin, C., DeBiasi, S. and Conti, F. (1995) GAT-1, a high-affinity GABA plasma membrane transporter, is localized to neurons and astroglia in the cerebral cortex.J. Neurosci.,15, 7754–7736.
Muller, K. J., Nicholls, J. G. and Stent, G. S. (1981)Neurobiology of the Leech, p. 254. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Neckameyer, W. (1996) Multiple roles for dopamine inDrosophila development.Dev. Biol.,176, 209–219.
Paredes, R. and Agmo, A. (1992) GABA and behavior: the role of receptor subtypes.Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Rev.,16, 145–170.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A. (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,74, 5463–5467.
Sewell, D., Burnet, B. and Connolly, K. (1975) Genetic analysis of larval feeding behavior inDrosophila melanogaster.Genet. Res. Camb.,24, 163–173.
Shepherd, D. and Tyrer, N. (1985) Inhibition of GABA uptake potentiates the effects of exogenous GABA on locust skeletal muscle.Comp. Biochem. Physiol.,82C, 315–321.
Shimada, S., Kitayama, S., Lin, C., Patel, A., Nanthakumar, E., Gregor, P., Kuhar, M. and Uhl, G. (1991) Cloning and expression of a cocaine-sensitive dopamine transporter complementary cDNA.Science,254, 576–578.
Southern, E. (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis.J. Mol. Biol.,98, 503–517.
Stewart, B. A., Atwood, H. L., Renger, J. J., Wang, J. and Wu, C.-F. (1994) Improved stability ofDrosophila larval neuromuscular preparation in haemolymph-like physiological solutions.J. Comp. Physiol. A,175, 179–191.
Stewart, B. A., Schuster, C. M., Goodman, C. S. and Atwood, H. L. (1996) Homeostasis of synaptic transmission inDrosophila with genetically altered nerve terminal morphology.J. Neurosci.,16, 3877–3886.
Takahashi, K.-I., Miyoshi, S.-I., Kaneko, A. and Copenhagen, D. (1995) Actions of nipecotic acid and SKF89976A on GABA transporter in cone-driven horizontal cells dissociated from the catfish retina.Jap. J. Physiol.,45, 457–473.
Zucker, R. S. and Lara-Estrella, L. O. (1983) Post-tetanic decay of evoked and spontaneous transmitter release and a residual calcium model of synaptic facilitation at crayfish neuromuscular junctions.J. Gen. Physiol.,81, 355–372.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neckameyer, W.S., Cooper, R.L. GABA transporters inDrosophila melanogaster: molecular cloning, behavior, and physiology. Invertebrate Neuroscience 3, 279–294 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577688
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577688