Abstract
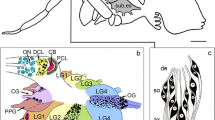
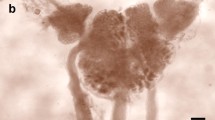
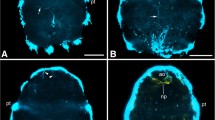
A search for genes specifically expressed in the giant interneurons of parietal ganglia of the snailHelix lucorum yielded, among others, two genes named HDS1 and HDS2. According to data obtained by Northern hybridization and whole-mountin situ hybridization, both genes are neurospecific and expressed almost exclusively in the peptidergic D-group neurons (Sakharov, 1974) located in the right parietal ganglion.In situ hybridization of the HDS1 and HDS2 probes with CNS of several related species of the Helicoidea superfamily identified in all cases similarly located homologous groups of neurons. Sequencing of the near full-length cDNA copies of the HDS1 and HDS2 genes revealed open reading frames 107 and 102 amino acids long for HDS1 and HDS2, respectively. Both putative proteins contain a hydrophobic leader peptide and putative recognition sites for furin-like and PC-like endopeptidases. Predicted amino acid sequences of the HDS1 and HDS2 proteins were found to be moderately homologous to each other, as well as to the LYCP preprohormone expressed by the light yellow cells of the freshwater snailLymnaea stagnalis. These results confirm an earlier hypothesis that the D-group of theHelix family and the light yellow cells ofLymnaea stagnalis represent homologous neuronal groups. Our data suggest that the HDS1 and HDS2 genes encode precursors of secreted molecules, most likely neuropeptides or neurohormones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angerer, L. M. and Angerer, R. C. (1993)In situ hybridization to cellular RNA with radiolaheled RNA probes. InIn situ Hybridization. A Practical Approach, ed. D. G. Williamson, pp 15–32. Oxford: IRL Press.
Barr, P. J. (1991) Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases.Cell,66, 1–3.
Belyavsky, A. V., Vinogradova, T. V. and Rajewsky, K. (1989) PCR-based cDNA library construction: General cDNA libraries at the level of a few cells.Nucleic Acids Res.,17, 2919–2932.
Bogdanov, Yu. D., Ovchinnikov, D. A., Balaban, P. M. and Belyavsky, A. V. (1994) Novel gene HCS1 is specifically expressed in the giant interneurons of the terrestrial snail.Neuroreport,5, 589–592.
Cash, D. and Carew, T. J. (1989) A quantitative analysis of the development of the central nervous system in juvenileAplysia californica.J. Neurobiol.,20, 25–47.
Chomczynsky, P. and Sacchi, N. (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction.Anal. Biochem.,162, 156–159.
Feinberg, A. P. and Vogelstein, B. (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity.Anal. Biochem.,132, 6–13.
Frank, D. and Harland R. M. (1991) Transient expression of XMyoD in non-somitic mesoderm ofXenopus gastrulae.Development,113, 1387–1393.
Hemmatti-Brivanlou, L., Frank, D., Bolce, M. E., Brown, B. D., Sive, H. L. and Harland, R. M. (1990) Localisation of specific mRNAs inXenopus embryos by whole-mountin situ hybridization.Development,110, 325–330.
Hosaka, M., Nagahama, M., Kim, W. S., Watanabe, T., Hatsuzawa, K., Ikemizu, J., Murakami, K. and Nakayama, K. (1991) Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway.J. Biol. Chem.,266, 12127–12130.
Hunt, P., Wilkinson, D. and Krumlauf, R. (1991) Patterning the vertebrate head: murine Hox 2 genes mark distinct subpopulations of premigratory and migrating cranial neural crest.Development,112, 43–50.
Jung, L. J. and Scheller, R. H. (1991) Peptide processing and targeting in the neuronal secretory pathway.Science,251, 1330–1335.
Kelly, R. B. and Grote, E. (1993) Protein targeting in the neuron.Annu. Rev. Neurosci.,16, 95–127.
Kelly, R. B. (1993) Storage and release of neurotransmitters.Cell,72/Neuron, 10 (Suppl.), 43–53.
Korner, J., Chun, J., O'Bryan, L. and Axel, R. (1991) Prohormone processing inXenopus oocytes: characterization of cleavage signals and cleavage enzymes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,88, 11393–11397.
Ono, J. K. and McCaman, R. E. (1992)In situ hybridization of whole-mounts ofAplysia ganglia using non-radioactive probes.J. Neurosci. Methods,44, 71–79.
Orci, L., Ravazzola, M., Storch, M. -J., Anderson, R. G. W., Vassali, J.-D. and Perrellet, A. (1987) Proteolytic maturation of insulin is a post-Golgi event which occurs in acidifying clathrin-coated secretory vesicles.Cell,49, 865–868.
Pfeffer, S. R. and Rothman, J. E. (1987) Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi.Annu. Rev. Biochem.,56, 829–852.
Sakharov, D. A. (1974)Genealogy of a neuron. Moscow: Nauka.
Sakharov, D. A. and Salanki, J. (1969) Physiological and pharmacological identification of neurons in the central nervous system ofHelix pomatia L.Acta Physiol. Hung.,35, 19–30.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. and Maniatis, T. (1989) Molecular Cloning: ALaboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A. R. (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,74, 5463–5467.
Sive, H. L. and St John, T. (1988) A simple subtractive hybridization technique employing photoactivable biotin and phenol extraction.Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 10937.
Smit, A. B., Hoek, R. M. and Geraerts, W. P. M. (1993) The isolation of a cDNA encoding a neuropeptide prohormone from the light yellow cells ofLymnaea stagnalis.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol.,13, 263–270.
Vassar, R., Ngai, J. and Axel, R. (1993) Spatial segregation of odorant receptor expression in the mammalian olfactory epithelium.Cell,74, 309–318.
von Heijne, G. (1986) A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites.Nucleic Acids Res.,14, 4683–4690.
Wendelaar Bonga, S. E. (1970) Ultrastructure and histochemistry of neurosecretory cells and neurohaemal areas in the pond snailLymnaea stagnalis L.Z. Zellforsch.,108, 190–225.
Wilkinson, D. G. (1993)In situ hybridization. In EssentialDevelopmental Biobgy. A Practical Approach, ed. C. L. Stern and P. W. Holland, pp. 257- 274. Oxford: IRL Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogdanov, Y.D., Balaban, P.M., Zakharov, I.S. et al. Identification of two novel genes specifically expressed in the D-group neurons of the terrestrial snail CNS. Invertebrate Neuroscience 2, 61–69 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02336661
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02336661