Abstract
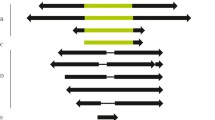
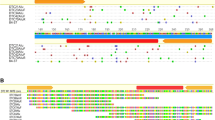
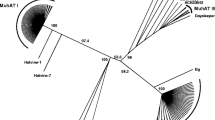
The cloning and characterization ofGandalf, a new DNA-transposing mobile element obtained from theDrosophila koepferae (repleta group) genome is described. A fragment ofGandalf was found in a middle repetitive clone that shows variable chromosomal localization. Restriction, Southern blot, PCR and sequencing analyses have shown that mostGandalf copies are about 1 kb long, are flanked by 12 by inverted terminal repeats and contain subterminal repetitive regions on both sides of the element. As with other elements of the DNA-transposing type (known as the ‘Ac family’), theGandalf element generates 8 by direct duplications at the insertion point. Coding region analysis has shown that the longer open reading frame found inGandalf copies could encode part of a protein. However, whether or not the 1 kb copies of the element are actually the active transposons remains to be elucidated.Gandalf shows a very low copy number inD. buzzatii, a sibling species ofD. koepferae. An attempt to induce interspecific hybrid dysgenesis in hybrids of these two species has been unsuccessful.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackman RK, Grimalia R, Koehler MMD, Gelbart WM (1987) Mobilization ofhobo elements residing within thedecapentaplegic gene complex: suggestion of a new hybrid dysgenesis system inDrosophila melanogaster. Cell 49:497–505
Blackman RK, Koehler MMD, Grimalia R, Gelbart WM (1989) Identification of a fully-functionalhobo transposable element and its use for germ-like transformation ofDrosophila. EMBO J, 8:211–217
Brennan MD, Rowan RG, Dickinson WJ (1984) Introduction of a functionalP element into the germ-line ofDrosophila hawaiiensis. Cell 38:147–151
Brezinsky L, Wang GLV, Humphreys T, Hunt J (1990) The transposable element Uhu from HawaiianDrosophila — member of the widely dispersed class ofTcl-like transposons. Nucleic Acids Res 18:2053–2059
Bucheton A, Paro R, Sang HM, Pelisson A, Finnegan DJ (1984) The molecular basis of I-R hybrid dysgenesis inDrosophila melanogaster: identification, cloning and properties of the 1 factor. Cell 38:153–163
Bullock P, Miller J, Botchan M (1986) Effects of poly(d(pGpT)d(pApC)) and poly(d(pCpG)-d(pCpG)) repeats on homologous recombination in somatic cells. Mol Cell Biol 6:3948–3953
Calvi BR, Hong TJ, Findley SD, Gelbart WM (1990) Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of inverted repeat transposons inDrosophila and plants:hobo, Activator andTam3. Cell 66:465–471
Capy P, Koga A, David JR, Hard DL (1992) Sequence analysis of active mariner elements in natural populations ofDrosophila simulans. Genetics 130:499–506
Charlesworth B, Langley CH, Stephen W (1986) The evolution of restricted recombination and the accumulation of repeated sequences. Genetics 112:947–962
Chomet P, Lisch D, Hardeman KJ, Chandler VL, Freeling M (1991) Identification of a regulatory transposon that controls theMutator transposable element system in maize. Genetics 129: 261–270
Coupland G, Baker B, Schelland J, Starlinger P (1988) Characterization of the maize transposable elementAc by internal deletions. EMBO J 7:3653–3659
Coupland G, Plum C, Chatterjee S, Post A, Starlinger P (1989) Sequences near the termini are required for transposition of the maize transposonAc in transgenic tobacco plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9385–9388
Daniels SB, Strausbaugh LD, Armstrong RA (1985) Molecular analysis ofP element behavior inDrosophila simulans transformants. Mol Gen Genet 200:258–265
Devereux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O (1984) A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res 12:387–395
Doak TG, Doerder FP, Jahn CL, Herrick G (1994) A proposed superfamily of transposase genes: transposon-like elements in ciliated protozoa and a common ‘D35Ers motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:942–946
Engels WR (1989)P elements inDrosophila melanogaster. In: Berg DE, Howe MM (eds) Mobile DNA. American Society for Microbiology, Washington pp 437–484
Fickett JW (1982) Recognition of protein coding regions in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 10:5303–5318
Finnegan DJ (1989) Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution. Trends Genet 5:103–107
Fontdevila A, Pla C, Hasson E, Wasserman M, Sánchez A, Naveira H, Ruíz A (1988)Drosophila koepferae: a new member of theDrosophila serido (Diptera: Drosophilidae) superspecies toxon. Ann Entomol Soc Am 81:380–385
Francino O, Cabre O, Fontdevila A (1994) Distribution of thecopia transposable element in therepleta group ofDrosophila. Genet Sel Evol 25:501–516
Franz G, Sauakis C (1991)Minos, a new transposable element fromDrosophila hydei, is a member of the Tcl-like family of transposons. Nucleic Acids Res 19:6646
Frey M, Reinecke J, Grant S, Saedler H, Gierl A (1990) Excision of the EnISpm transposable element of Zea mays requires two element-encoded proteins. EMBO J 9:4037–4044
Garza D, Medhora M, Koga A, Hartl DL (1991) Introduction of the transposable elementmariner into the germline ofDrosophila melanogaster. Genetics, 128: 303–310
Genetics Computer Group (1991) Program manual for the GCG package, version 7, April 1991, 575 Science Drive, Madison, Wisconsin, USA 53711
Gierl A (1990) How maize transposable elements escape negative selection. Trends Genet 6:155–158
Gierl A, Lütticke S, Saedler H (1988) TnpA product encoded by the transposable elementEn-1 ofZea mays is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J 7:4045–4053
Gierl A, Saedler H, Peterson PA (1989) Maize transposable elements. Annu Rev Genet 23:71–85
Harris LJ, Baillie DL, Rose AM (1988) Sequence identity between an inverted repeat family of transposable elements inDrosophila andCaenorhabditis. Nucleic Acids Res 16: 5991–5998
Hehl R, Nacken WKF, Krause A, Saedler H, Sommer H (1991) Structural analysis ofTam3, a transposable element fromAntirrhinum majus, reveals homologies to theAc element from maize. Plant Mol Biol 16:369–371
Hellman L, Steen M-L, Sundvall M, Pettersson U (1988) A rapidly evolving region in the immunoglobin heavy chain loci of rat and mouse: postulated role of (dC-dA) n -(dG-dT) n sequences. Gene 68:93–100
Jacobson JW, Medhora MM, Hartl DL (1986) Molecular structure of a somatically unstable transposable element inDrosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8684–8688
Karess RE, Rubin GM (1984) Analysis ofP transposable element functions inDrosophila. Cell 38:135–146
Kaufman PD, Doll RF, Rio DC (1989)Drosophila P element transposase recognizes internalP element DNA sequences. Cell 59:359–371
Kaufman PD, Rio DC (1991)Drosophila P-element transposase is a transcriptional repressorin vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2613–2617
Kay BK, Dawid IB (1983) The1723 element: a long, homogeneous, highly repeated DNA unit interspersed in the genome ofXenopus laevis. J Mol Biol 170:583–596
Kozak M (1983) Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes and organelles. Microbiol Rev 47:1–45
Kunze R, Starlinger P (1989) The putative transposase of transposable elementAc fromZea mays L. interacts with subterminal sequences ofAc. EMBO J 8:3177–3185
Labrador M, Fontdevila A (1994) High transposition rates ofOsvaldo, a newDrosophila buzzatii retrotransposon. Mol Gen Genet 245:661–674
Labrador M, Naveira H, Fontdevila A (1990) Genetic mapping of theAdh locus in theRepleta group ofDrosophila byin situ hybridization. J Hered 81: 83–86
Langley CH, Montgomery E, Hudson R, Kaplan N, Charlesworth B (1988) On the role of unequal exchange in the containment of transposable element copy number. Genet Res 52:223–235
Li M-G, Starlinger P (1990) Mutational analysis of the N-terminus of the protein of maize transposable elementAc. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6044–6048
Lowenhaupt K, Rich A, Pardue ML, (1989) Nonrandom distribution of long mono- and dinucleotide repeats inDrosophila chromosomes: correlations with dosage compensation, heterochromatin, and recombination. Mol Cell Biol 9:1173–1182
Marin I, Labrador M, Fontdevila A (1992) The evolutionary history ofD. buzzatii. XXIII. High content of nonsatellite repetitive DNA inD. buzzatii and in its siblingD. koepferae. Genome 35:967–974
Marin I, Ruiz A, Pla C, Fontdevila A (1993) Evolution 47:1616–1624
Maruyama K, Schoor KD, Hartl DL (1991) Identification of nucleotide substitutions necessary for trans-activation ofmariner transposable elements inDrosophila: analysis of naturally occurring elements. Genetics 128:777–784
Medhora MM, MacPeek AH, Hard DL (1988) Excision of theDrosophila transposable elementmariner: identification and characterization of theMos factor. EMBO J 7:2185–2189
Medhora M, Maruyama K, Hard DL (1991) Molecular and functional analysis of the mariner mutator elementMosl inDrosophila. Genetics 128:311–318
Montgomery EA, Huang S-M, Langley CH, Judd BH (1991) Chromosome rearrangement by ectopic recombination inDrosophila melanogaster: genome structure and evolution. Genetics 129:1085–1098
Morgan GT, Middleton KM (1990) Short interspersed repeats fromXenopus that contain multiple octamer motifs are related to known transposable elements. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 5781–5786
Mori I, Moerman DG, Waterston RH (1988) Analysis of a mutator activity necessary for germline transposition and excision of Tel transposable elements inCaenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 120: 397–407
Mount SM, Burks C, Hertz G, Stormo GD, White O, Fields C (1992) Splicing signals inDrosophila: intron size, information content and consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 20:4255–4262
Müllller-Neumann M, Yoder JI, Starlinger P (1984) The DNA sequence of the transposable elementAc ofZea mays L. Mol Gen Genet 198: 19–24
Nacken WKF, Piotrowiak R, Saedler H, Sommer H (1991) The transposable elementTaml fromAnthirrhinum majus shows structural homology to the maize transposonEn/Spm and has no sequence specificity of insertion. Mol Gen Genet 228:201–208
Naveira H, Fontdevila A (1985) The evolutionary history ofDrosophila buzzatii. IX. High frequencies of new chromosome rearrangements induced by introgressive hybridization. Chromosoma 91:87–94
Naveira H, Pla C, Fontdevila A (1986) The evolutionary history ofDrosophila buzzatii. XI. A new method for cytogenetic localization based on asynapsis of polytene chromosomes in interspecific hybrids ofDrosophila. Genetica 71:199–212
O'Brochta DA, Handler AM (1988) Mobility ofP elements in drosophilids and nondrosophilids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6052–6056
O'Brochta DA, Gomez SP, Handler AM (1991)P element excision inDrosophila melanogaster and related drosophilids. Mol Gen Genet 225:387–394
O'Hare K, Rubin GM (1983) Structures ofP transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in theDrosophila melanogaster genome. Cell 34:25–35
Pereira A, Schwarz-Sommer Z, Gierl A, Bertram I, Peterson PA, Saedler H (1985) Genetic and molecular analysis of theEnhancer (En) transposable element system ofZea mays. EMBO J 4:17–23
Prasad SS, Harris LJ, Baillie DL, Rose AM (1991) Evolutionarily conserved regions inCaenorhabditis transposable elements deduced by sequence comparison. Genome 34:6–12
Rhodes PR, Vodkin LO (1988) Organization of theTgm family of transposable elements in soybean. Genetics 120: 597–604
Rio DC (1990) Molecular mechanisms regulatingDrosophila P element transposition. Annu Rev Genet 24: 543–578
Rio DC (1991) Regulation ofDrosophila P element transposition. Trends Genet 7:282–287
Rio DC, Rubin GM (1988) Identification and purification of aDrosophila protein that binds to the terminal 31-base-pair inverted repeats of theP transposable element. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8929–8933
Rio DC, Laski FA, Rubin GM (1986) Identification and immunochemical analysis of biologically activeDrosophila P element transposase. Cell 44:21–32
Rosenzweig B, Liao LW, Hirsh D (1983) Sequence of theC. elegans transposable elementTcl. Nucleic Acids Res 11:4201–4209
Rubin GM, Kidwell MG, Bingham PM (1982) The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the nature of induced mutations. Cell 29:987–994
Ryden TA, Beeman K (1989) Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol 9: 1155–1164
Scavarda NJ, Hard DL (1984) Interspecific DNA transformation inDrosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7515–7519
Schafer DJ, Fredline DK, Knibb WR, Green MM, Barker JSF (1993) Genetics and linkage mapping ofDrosophila buzzatii. J Hered 84:188–194
Sommer H, Carpenter R, Harrison BJ, Saedler H (1985) The transposable elementTam3 ofAntirrhinum majus generates a novel type of sequence alterations upon excision. Mol Gen Genet 199:225–231
Streck RD, MacGaffey JE, Beckendorf SK (1986) The structure ofhobo transposable elements and their insertion sites. EMBO J 5:3615–3623
Templeton NS, Potter SS (1989) Completefoldback transposable elements encode a novel protein found inDrosophila melanogaster. EMBO J 8:1887–1894
Tolkien JRR (1954) The Lord of the Rings. Allen and Unwin, London
Treco D, Arnheim N (1986) The evolutionary conserved repetitive sequence d(TG-AC) n promotes reciprocal exchange and generates unusual recombinant tetrads during yeast meiosis. Mol Cell Biol 6: 3934–3947
Ueda H, Mizuno S, Shimura K (1986) Transposable genetic element found in the 5′-flanking region of the fibroin H-chain in a genomic clone from the silkwormBombyx mori. J Mol Biol 190:319–327
Van Sluys MA, Tempé J, Fedoroff N (1987) Studies on the introduction and mobility of the maizeActivator element inArabidopsis thaliana andDaucus carota. EMBO J 6:3881–3889
Wasserman M (1992) Cytological evolution of theDrosophila repleta species group. In: Krimbas CB, Powell JR (eds)Drosophila inversion polymorphism. CRC Press, Boca Ratón, pp 455–552
Wetmur JG (1991) DNA probes: applications of the principles of nucleic acid hybridization. Crit Rev Biochem Mot Biol 26: 227–259
Wobus U, Bäumlein H, Bogachev SS, Borisevich IV, Panitz R, Kolesnikov NN (1990) A new transposable element inChironomus thummi. Mol Gen Genet 222:311–316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by D. J. Finnegan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marín, I., Fontdevila, A. Characterization ofGandalf, a new inverted-repeat transposable element ofDrosophila koepferae . Molec. Gen. Genet. 248, 423–433 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02191642
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02191642