Abstract
Transformation of cereal protoplasts has been reported using several methods; however, the efficiencies of transformations are still very low. We have evaluated a number of parameters that influence electroporation-mediated DNA uptake and have also compared the efficiency of transient GUS activity and stable transformation obtained using an optimized electroporation method with that of the PEG method. The electroporation conditions tested were ionic composition of buffer, ionic strength, resistivity of buffer, type of anions, voltage, and capacitance.
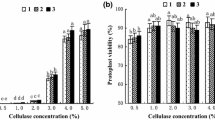
Protoplasts isolated from suspension cultures derived from immature embryos of rice (cvs Radon and IR-54) were used for this study. Stable transformation or transient GUS expression experiments were carried out using a plasmid construct containing the CaMV 35S promoter driving thebar gene and a rice actin promoter driving thegus A (uid A) gene (pAG35bar). Electroporation under optimized conditions resulted in about 13-fold higher GUS activities compared to the PEG method. Protoplast survival following optimized electroporation conditions was 55–60%, compared to 35–40% with the PEG treatment. Protoplasts isolated from a suspension culture at different ages gave substantially different levels of transient GUS expression following electroporation-mediated DNA uptake. In contrast, the age of the suspension culture did not influence PEG-mediated DNA uptake and transient GUS activities, which remained low throughout the culture period examined (21 months). Putatively transformed calluses were selected after three to four weeks on medium containing phosphinothricin as the selection agent. The transformation frequencies ranged from 6.2×10−5 to 5.4×10−4 with the electroporation method compared to 1.3×10−5 to 5.3×10−5 with the PEG method. Southern blot analysis of PPT-resistant calluses obtained by the electroporation-mediated transformation showed simple intergration patterns of integrated DNA in most of the transformants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boggs, S.S., Gregg, R.G., Borenstein, N. and Smithies, O. (1986) Efficient transformation and frequent single-site, single-copy insertion of DNA can be obtained in mouse erythroleukemia cells transformed by electroporation.Exp. Hematol. 14, 988–94.
Cornejo, M.J., Luth, D., Blankenship, K.M., Anderson, O.D. and Blechl, A.E. (1993) Activity of a maize ubiquitin promoter in transgenic rice.Plant Mol. Biol. 23, 567–81.
Datta, S.K., Peterhans, A., Datta, K. and Potrykus, I. (1990) Genetically engineered fertile indica-rice recovered from protoplasts.Bio/Technology 8, 736–40.
Feldhaus, A.L., Klug, C.A., Arvin, K.L. and Singh, H. (1993) Targeted disruption of the Oct-2 locus in a B cell provides genetic evidence for two distinct cell type-specific pathways of octamer element-mediated gene activation.EMBO J. 12, 2763–72.
Frearson, E.M., Power, J.B. and Cocking, E.C. (1973) The isolation, culture and regeneration of petunia leaf protoplasts.Devel. Biol. 33, 130–7.
Gallie, R.D., Lucas, W.J. and Walbot, V. (1989) Visualizing mRNA expression in plant protoplasts: factors influencing efficient mRNA uptake and translation.Plant Cell 1, 301–11.
Hayashimoto, A., Li, Z. and Murai, N. (1990) A polyethylene glycol-mediated protoplast transformation system for production of fertile transgenic rice plants.Plant Physiol 93, 857–63.
Gu, H., Marth, J.D., Orban, P.C., Mossmann, H. and Rajewsky, K. (1994) Deletion of a DNA polymerase β gene segment in T cells using cell type-specific gene targeting.Science 265, 103–6.
Jefferson, R.A. (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system.Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 5, 387–405.
Joersbo, M. and Brunstedt, J. (1991) Electroporation: mechanism and transient expression, stable transformation and biological effects in plant protoplasts.Physiol. Plant. 81, 256–64.
Kao, K.N. (1977) Chromosomal behavior in somatic hybrids of soybean-Nicotiana glauca.Mol. Gen. Genet. 150, 225–30.
Krens, F.A., Molendijik, L., Wullems, G.J. and Schilperoort, R.A. (1982)In vitro transformation of plant protoplasts with Ti-plasmid DNA.Nature 296, 72–4.
Lee, L., Schroll, R.E., Grimes, H.D. and Hodges, T.K. (1989) Plant regeneration from indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) protoplasts.Planta 178, 325–33.
Linsmaier, E.M. and Skoog, F. (1965) Organic growth factor requirement of tobacco tissue culture.Physiol. Plant. 18, 100–27.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 256–75.
Lyznik, L.A., Kamo, K.K., Grimes, H.D., Ryan, R., Chang, K.L. and Hodges, T.K. (1989) Stable transformation of maize: the impact of feeder cells on protoplast growth and transformation efficiency.Plant Cell Rep. 8, 292–5.
Maas, C. and Werr, W. (1989) Mechanism and optimized conditions for PEG mediated DNA transfection into plant protoplasts.Plant Cell Rep. 8, 148–51.
Meijer, E.G.M., Schilperoort, R.A., Rueb, S., Os-Ruygrok, P.E. van and Hensgens, L.A.M. (1991) Transgenic rice cell lines and plants: expression of transferred chimeric genes.Plant Mol. Biol. 16, 807–20.
Mettler, I.J. (1987) A simple and rapid method for minipreparation of DNA from tissue cultured plant cells.Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 5, 346–9.
Nagata, T. (1989) Cell biological aspects of gene delivery into plant protoplasts by electroporation.Int. Rev. Cytol. 116, 229–55.
Peng, J., Kononowicz, H. and Hodges, T.K. (1992) Transgenic indica rice plants.Theor. Appl. Genet. 83, 855–63.
Perucho, M., Hanahan, D. and Wigler, M. (1980) Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells.Cell 22, 309–17.
Rathore, K.S., Chowdhury, V.K. and Hodges, T.K. (1993) Use ofbar gene as a selectable marker gene and for the production of herbicide-resistant rice plants from protoplasts.Plant. Mol. Biol. 21, 871–84.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. (1989)Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Pres.
Smithies, O., Gregg, R.G., Boggs, S., Koralewski, M.A. and Kucherlapati, R.S. (1985) Insertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal B-globulin locus by homologous recombination.Nature 317, 230–4.
Tada, Y., Sakamoto, M. and Fujimura, T. (1990) Efficient gene introduction into rice by electroporation and analysis of transgenic plants: use of electroporation buffer lacking chloride ions.Theor. Appl. Genet 80, 475–80.
Thomas, K.R. and Capecchi, M.R. (1987) Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells.Cell 51, 503–12.
Toneguzzo, F., Keating, A., Glynn, S. and McDonald, K. (1988) Electric field-mediated gene transfer: characterization of DNA transfer and patterns of integration in lymphoid cells.Nucl. Acids Res. 16, 5515–32.
Tyagi, S., Sporlein, B., Tyagi, A.K., Hermann, R.G. and Koop, H.U. (1989) PEG- and electroporation-induced transformation inNicotiana tabacum: influence of genotype on transformation frequencies.Theor. Appl. Genet. 78, 287–92.
Yang, H., Zhang, Z.M., Davey, M.R., Mulligan, B.J. and Cocking, E.C. (1988) Production of kanamycin resistant rice tissues following DNA uptake into protoplasts.Plant Cell Rep. 7, 421–5.
Zhen, L., King, A.A.J., Xiao, Y., Chanock, S.J., Orkin, S.H. and Dinauer, M.C. (1993) Gene targeting of X chromosome-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus in a human myeloid leukemia cell line and rescue by expression of recombinant gp91phox.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 9832–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, K.V., Rathore, K.S. & Hodges, T.K. Physical, chemical and physiological parameters for electroporation-mediated gene delivery into rice protoplasts. Transgenic Research 4, 361–368 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973754
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973754