Summary
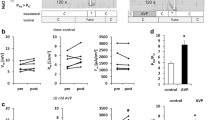
Cellular potential and pH measurements (pH i ) were carried out in the perfused kidney ofNecturus on proximal tubules with standard and recessed-tip glass microelectrodes under control conditions and after stimulation of tubular bicarbonate reabsorption. Luminal pH and net bicarbonate reabsorption were measured in parallel experiments with recessed-tip glass or antimony electrodes, both during stationary microperfusions as well as under conditions of isosmotic fluid transport. A mean cell pH of 7.15 was obtained in control conditions. When the luminal bicarbonate concentration was raised to 25 and 50mm, pH i rose to 7.44 and 7.56, respectively. These changes in pH i were fully reversible. Under all conditions intracellular H+ was below electrochemical equilibrium. Thus the maintenance of intracellular pH requires “active” H+ extrusion across one or both of the cell membranes. The observed rise in pH i and the peritubular depolarization after stimulation of bicarbonate reabsorption are consistent with enhanced luminal hydrogen ion secretion and augmentation of peritubular bicarbonate exit via an anion-conductive transport pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry, C.A. 1981. Electrical effects of acidification in the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule.Am. J. Physiol. 240:F459-F470
Bichara, M., Paillard, M., Leviel, F., Gardin, J.P. 1980. Hydrogen transport in rabbit kidney proximal tubules—Na∶H exchange.Am. J. Physiol. 238:F445-F451
Boron, W.F., Boulpaep, E.L. 1980a. Intracellular pH in isolated, perfused proximal tubules of amphibian kidney.Fed. Proc. 39:713
Boron, W.F., Boulpaep, E.L. 1980b. Intracellular pH regulation in the salamander renal proximal tubule.Kidney Int. 18:126A
Boron, W.F., Boulpaep, E.L. 1981. Hydrogen and bicarbonate transport by salamander proximal tubule cells.In: Intracellular pH. R. Nucchitelli and D. Deamer, editors. Liss, New York (in press)
Boron, W.F., DeWeer, P. 1976. Intracellular pH transients in squid giant axon caused by CO2, NH3 and metabolis inhbitors.J. Gen. Physiol. 67:91–112
Bott, P.A. 1962. A micropuncture study of renal excretion of water, K, Na and Cl inNecturus.Am. J. Physiol. 203:662–666
Boulpaep, E. 1976a. Electrical phenomena in the nephron.Kidney Int. 9:88–102
Boulpaep, E. 1976b. Recent advances in electrophysiology of the nephron.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 38:20–36
Burckhardt, B.-Ch., Frömter, E. 1980. Bicarbonate transport across the peritubular membrane of rat kidney proximal tubule.In: Hydrogen Transport in Epithelia. J. Schultz, G. Sachs, J.G. Forte, and K.J. Ullrich, editors. pp. 277–286. Elsevier-North Holland, Amsterdam-New York-Oxford
Cassola, A.C., Giebisch, G., Malnic, G. 1977. Mechanisms and components of renal tubular acidification.J. Physiol. (London) 267:601–624
Chan, Y.L., Giebisch, G. 1981. Relationship between sodium and bicarbonate transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule.Am. J. Physiol. 240:F222-F230
Dole, W. 1941. The Glass Electrode: Methods, Applications, and Theory, p. 131. J. Wiley & Sons, New York
Edelman, A., Bouthier, M., Anagnostopoulos, T. 1981. Chloride distribution in the proximal convoluted tubule ofNecturus kidney.J. Membrane Biol. 62:7–18
Giebisch, G. 1956. Measurement of pH, chloride and inulin concentrations in proximal tubule fluid ofNecturus.Am. J. Physiol. 185:171–175
Giebisch, G. 1961. Measurement of electrical potential difference on single nephrons of the perfusedNecturus kidney.J. Gen. Physiol. 44:659
Giebisch, G., Malnic, G., Mello, G.B. de, Mello-Aires, M. de. 1977. Kinetics of luminal acidification in cortical tubules of the rat kidney.J. Physiol. (London) 267:571–559
Giebisch, G., Sullivan, L.P., Whittembury, G. 1973. Relationship between tubular net sodium transport and peritubular potassium uptake in the perfusedNecturus kidney.J. Physiol. (London) 230:51–73
Guggino, W.B., London, R., Boulpaep, E.L., Giebisch, G. 1981. Regulation of intracellular chloride in theNecturus proximal tubule cell.Fed. Proc. 40:706
Hodgkin, A.L., Katz, B. 1949. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid.J. Physiol. (London) 108:37–77
Hoshiko, T., Lindley, B.D. 1967, Phenomenological description of active transport of salt and water.J. Gen. Physiol. 50:729–758
Isard, J.O. 1967. The dependence of glass-electrode properties on composition.In: Glass Electrodes Hydrogen and Other Cations. G. Eisenman, editor. pp. 51–100. Marcel Dekker, New York
Kedem, O., Katchalsky, A. 1963. Permeability of composite membranes. I. Electric current, volume flow and flow of solute through membranes.Trans. Faraday Soc. 59:1918–1930
Khuri, R.N., Agulian, S.K., Bogharian, K., Nassar, R., Wise, W. 1974. Intracellular bicarbonate in single cells ofNecturus proximal tubule.Pfluegers Arch. 349:295–299
Kimura, G., Spring, K.R. 1978. Transcellular and paracellular tracer chloride fluxes inNecturus proximal tubule.Am. J. Physiol. 235:F617–625
Kinsella, J.L., Aronson, P.S. 1980. Properties of the Na+−H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles.Am. J. Physiol. 238:F461–469
Malnic, G., Giebisoh, G. 1979. Cellular aspects of renal tubular acidification.In: Membrane Transport in Biology. G. Giebisch, D.C. Tosteson, and H.H. Ussing, editors. Vol. 4A, pp. 229–355. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York
Malnic, G., Mello-Aires, M. de 1972. Kinetic study of the bicarbonate reabsorption in proximal tubule of the rat.Am. J. Physiol. 220:1759–1767
Malnic, G., Steinmetz, P.R. 1976. Transport process in urinary acidification.Kidney Int. 9:172–188
Maren, T.H. 1967. Carbonic anhydrase: Chemistry, physiology and inhibition.Physiol. Rev. 47:595–781
Matsumura, Y., Guggino, W.B., Giebisch, G. 1981. Electrical effects of potassium and bicarbonate on proximal tubule cell ofNecturus: Intracellular K affects K conductance.Kidney Int. 21:281
Montgomery, H., Pierce, J.A. 1937. The site of acidification of the urine within the renal tubule of amphibia.Am. J. Physiol. 118:144–152
Roos, A., Boron, W.F. 1981. Intracellular pH.Physiol. Rev. 61:296–434
Sacktor, B. 1977. Transport in membrane vesicles isolated from the mammalian kidney and intestine.In: Current Topics in Bioenergetics. R. Sanadi, editor. Vol. VI, pp. 39–81. Academic Press, New York
Shindo, T., Spring, K.R. 1981. Chloride movement across the basolateral membrane of proximal tubule cells.J. Membrane Biol. 58:35–42
Struyvenberg, A., Morrison, R.B., Relman, A.S. 1968. Acid-base behavior of separated canine renal tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 214:1155–1162
Thomas, R.C. 1974. Intracellular pH of snail neurones measured with a new pH-sensitive glass microelectrode.J. Physiol. (London) 238:159–180
Thomas, R.C. 1978. Ion-sensitive Intracellular Microelectrodes. Academic Press, London-New York-San Francisco
Ullrich, K.J. 1973. Permeability characteristics of the mammalian nephron.In: Handbook of Physiology, Section 8: Renal Physiology. J. Orloff, R.W. Berliner, and S.R. Geiger, editors. pp. 377–414. American Physiological Society, Washington, D.C.
Ullrich, K.J., Rumrich, G., Baumann, K. 1975. Renal proximal tubular buffer (glycodiazine) transport. Inhomogeneity of local transport dependence or sodium effect of inhibitors and chronic adaptation.Pfluegers Arch. 357:140–163
Vieira, F.L., Malnic, G. 1968. Hydrogen ion secretion by rat renal cortical tubules as studied by the antimony microelectrode.Am. J. Physiol. 214:710–718
Warnock, D.G., Rector, F.C., Jr. 1979. Proton secretion by the kidney.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 41:197–210
Warnock, D., Rector, F.C., Jr. 1981. Renal acidification mechanism.In: The Kidney. B.M. Brenner and F.C. Rector, Jr., editors. pp. 440–494. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia-London-Toronto
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Regan, M.G., Malnic, G. & Giebisch, G. Cell pH and luminal acidification inNecturus proximal tubule. J. Membrain Biol. 69, 99–106 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872269
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872269