Abstract
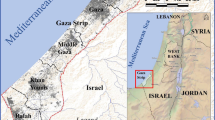
A two-dimensional finite element model is applied to the San Mateo Basin, California in order to investigate feasible and efficient management alternatives to enhance the basin yield and preserve the basin water quality. The model utilizes lumped approximation methods for the determination of its subsurface boundary conditions, and incorporates a variety of hydrological processes. The model solves uncoupled flow and transport equations using a nodal domain integration technique for the flow model and an integrated finite difference method for the transport model. The model incorporates the basin inputs and outputs as ocean flux, well and phreatophyte extractions, subsurface inflow, precipitation and streambed percolation. Modeling results indicate that the substained yield may be maximized by interception of ocean outflow from the basin. An improvement of about four times of the historical sustained yield was achieved. This strategy required relocation of existing wastewater recharge ponds and increasing basin extractions. In order to intercept most of the ocean outflow by increasing basin extractions, simulated subsurface seawater intrusion was observed. The water quality study indicated that the basin yield could be increased significantly by moderately relaxing the water quality criteria near the ocean.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bear, J., 1979,Hydraulics of Groundwater, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Freeze, R. A. and Cherry, J. A., 1979,Groundwater, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
Domenico, P. A., 1972,Concepts and Models in Groundwater Hydrology, McGraw Hill, New York.
Guymon, G. L., and Yen, C. C., 1990, An efficient deterministic-probabilistic approach to modeling regional groundwater flow, 2. Application to Owens Valley, California,Water Resour. Res. 26(7), 1569–1581.
Guymon, G. L., Bagtzoglou, A. C., and Welch, M. R., 1992, A lumped stream-aquifer model to assess reclaimed water impacts,Water Resour. Bull. 28(2), 361–370.
Hromadka II, T. V., Guymon, G. L., and Pardeon, G. C., 1981, Nodal domain integration model of two-dimensional unsaturated soil water flow: Development,Water Resour. Res. 17(5), 1425–1430.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagtzoglou, A.C., Khan, M.N., Guymon, G.L. et al. Groundwater quality management of a low inertia basin: Application to the San Mateo Basin, California. Water Resour Manage 7, 189–205 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01675303
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01675303