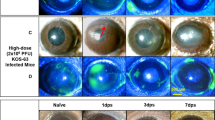
Summary
Mixed infections with different strains of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) may result in more severe disease than infection with either strain alone. This phenomenon is important because it may facilitate the identification of virulence genes through the transfer of virulence determinants between complementing strains, and it may pose a problem in the use of attenuated HSV strains for vaccines and gene delivery vectors. In this study, we have compared the percentage of recombinants present after mixed infection with HSV-1 strains OD4 and 994 in vitro and in vivo. After corneal inoculation, we found that 74% of randomly picked isolates from the trigeminal ganglia were recombinants, compared with 59% from the cornea. Twenty-six percent of randomly picked isolates were recombinant following mixed infection of Vero cells in vitro. Seventeen recombinant strains isolated from the in vivo mixed infections were assayed for ocular virulence, and they were found to exhibit a wide range of virulence phenotypes. The presence of virulent recombinants suggests that recombination plays a role in the increased disease observed in this mixed infection, and the broad range of virulence indicates that there may be multiple genetic factors involved in the increased virulence observed after mixed infection with these two strains. The recombinants were also tested for their ability to grow in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts, and though some correlation was observed between growth in vitro and ability to cause ocular disease, improved growth in murine cells does not sufficiently explain the increased virulence observed in some recombinants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandt CR (1991) Mixed ocular infections identify strains of herpes simplex virus for use in genetic studies. J Virol Methods 35: 127–135
Brandt CR, Coakley LM, Grau DR (1992) A murine model of herpes simplex virus-induced ocular disease for antiviral drug testing. J Virol Methods 36: 209–222
Brandt CR, Grau DR (1990) Mixed infection with herpes simplex virus type 1 generates recombinants with increased ocular and neurovirulence. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 31: 2214–2223
Breakefield XO, DeLuca NA (1991) Herpes simplex virus for gene delivery to neurons. New Biol 3: 203–218
Brown SM, Subak-Sharpe JH, Harland J, MacLean AR (1992) Analysis of intrastrain recombination in herpes simplex virus type 1 strain 17 and herpes simplex virus type 2 strain HG52 using restriction endonuclease sites as unselected markers and temperature-sensitive lesions as selected markers. J Gen Virol 73: 293–301
Dix RD, McKendall RR, Baringer JR (1983) Comparative neurovirulence of herpes simplex virus type 1 strains after peripheral or intracerebral inoculation of BALB/c mice. Infect Immun 40: 103–112
Efstathiou S, Kemp S, Darby G, Minson AC (1989) The role of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase in pathogenesis. J Gen Virol 70: 869–879
Foster CS (1989) Herpes simplex virus-induced destructive corneal disease. Eye 3: 194–203
Grau DR, Visalli RJ, Brandt CR (1989) Herpes simplex virus stromal keratitis is not titer-dependent and does not correlate with neurovirulence. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 30: 2474–2480
Henderson LM, Katz JB, Erickson GA, Mayfield JE (1990) In vivo and in vitro genetic recombination between conventional and gene-deleted vaccine strains of pseudorabies virus. Am J Vet Res 51: 1656–1662
Izumi KM, Stevens JG (1990) Molecular and biological characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) neuroinvasiveness gene. J Exp Med 172: 487–496
Javier RT, Sedarati F, Stevens JG (1986) Two avirulent herpes simplex viruses generate lethal recombinants in vivo. Science 234: 746–748
Kintner RL, Brandt CR (1994) Rapid small-scale isolation of herpes simplex virus DNA. J Virol Methods 48: 189–196
Liesegang TJ (1992) Biology and molecular aspects of herpes simplex and varicellazoster virus infections. Ophthalmology 99: 781–799
Nishiyama Y, Kimura H, Daikoku T (1991) Complementary lethal invasion of the central nervous system by nonneuroinvasive herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol 65: 4520–4524
Rajcani J (1992) DNA regions and genes determining the virulence of herpes simplex virus. Acta Virol 36: 208–222
Sedarati F, Javier RT, Stevens JG (1988) Pathogenesis of a lethal mixed infection in mice with two nonneuroinvasive herpes simplex virus strains. J Virol 62: 3037–3039
Steiner I, Kennedy PG (1993) Molecular biology of herpes simplex virus type 1 latency in the nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 7: 137–159
Stulting RD, Kindle JC, Nahmias AJ (1985) Patterns of herpes simplex keratitis in inbred mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 26: 1360–1367
Wander AH, Centifanto YM, Kaufman HE (1980) Strain specificity of clinical isolates of herpes simplex virus. Arch Ophthalmol 98: 1458–1461
Whitley RJ, Meignier B (1992) Herpes simplex vaccines. Biotechnology 20: 223–254
Yamada Y, Kimura H, Morishima T, Daikoku T, Maeno K, Nishiyama Y (1991) The pathogenicity of ribonucleotide reductase-null mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in mice. J Infect Dis 164: 1091–1097
Yirrell DL, Rogers CE, Blyth WA, Hill TJ (1992) Experimental in vivo generation of intertypic recombinant strains of HSV in the mouse. Arch Virol 125: 227–238
Yuhasz SA, Stevens JG (1993) Glycoprotein B is a specific determinant of herpes simplex virus type 1 neuroinvasiveness. J Virol 67: 5948–5954
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kintner, R.L., Allan, R.W. & Brandt, C.R. Recombinants are isolated at high frequency following in vivo mixed ocular infection with two avirulent herpes simplex virus type 1 strains. Archives of Virology 140, 231–244 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01309859
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01309859