Summary
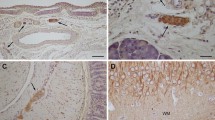
Taxol, a compound that enhances microtubule polymerization, was injected locally into the sciatic nerve of the rat and its effects examined by electron microscopy up to 21 days postinjection. The drug did not have a degenerative effect upon the P.N.S. but caused a slow accumulation of microtubules, first seen within Schwann cells and shortly thereafter, in axons. Within Schwann cells, microtubule aggregates evolved at the expense of rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and microtubule arrays were frequently encountered in relationship to smooth ER cisterns. Arrested mitoses were seen, there was no proliferation of Schwann cells and long stretches of axon were naked. Within axons, microtubules predominated over intermediate filaments and displayed a tendency to cluster around mitochondria. The lesion appeared to be focal and to be related to a local axonal stasis. These experiments provide yet another tool for the examination of Schwann cell-axon interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner, S. L. &Brikley, B. R. (1982) Tubulin assembly sites and the organization of microtubule arrays in mammalian cells.Cold Spring Harbor Symposium on Quantitative Biology 46, 21–154.
Davenport, J. G., Farrell, C. &Siemi, S. M. (1976) ‘Giant axonal neuropathy’ caused by industrial chemicals: Neurofilamentous masses in man.Neurology 26, 919–23.
DeBrabander, M., Geuens, G., Nuydens, R., Willebrords, R. &DeMey, J. (1981) Taxol induces the assembly of free microtubules in living cells and blocks the organizing capacity of the centrosomes and the kinetochores.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sdences, USA 78, 5608–12.
Donat, J. R. &Wisniewski, H. M. (1973) The spatio-temporal pattern of Wallerian degeneration in mammalian peripheral nerves.Brain Research 53, 41–53.
Epstein, L. G., Prineas, J. W. &Raine, C. S. (1983) Attachment of myelin to coated pits in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.Journal of the Neurological Sciences 61, 341–8.
Griffin, J. W. &Price, D. L. (1981) Demyelination in experimental B,B′-iminodipropionitide and hexacarbon neuropathies. Evidence of an axonal influence.Laboratory Investigation 45, 130–41.
Heath, J. W., Ueda, S., Bornstein, M. B., Davis, G. D. &Raine, C. S. (1982) Buckthorn neuropathy in vitro: Evidence for a primary neuronal effect.Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 41, 204–20.
Kumar, N. (1981) Taxol induced polymerization of purified tubulin.Journal of Biological Chemistry 256, 10435–41.
Manfredi, J. J., Parness, J. &Horwitz, S. B. (1982) Taxol binds to cellular microtubules.Journal of Cell Biology 94, 688–96.
Masurovsky, E. G., Peterson, E. R., Crain, S. M. &Horwitz, S. B. (1981a) Microtubule arrays in taxol-treated mouse dorsal root ganglion-spinal cord cultures.Brain Research 217, 392–8.
Masurovsky, E. B., Peterson, E. R., Crain, S. M. &Horwitz, S. B. (1981b) Morphologic alterations in satellite and Schwann cells after exposure of fetal mouse dorsal root ganglia-spinal cord cultures to taxol.International Research Communications Service: Medical Science 9, 968–9.
Masurovsky, E. G., Peterson, E. R., Crain, S. M. &Horwitz, S. B. (1983) Morphological alterations in dorsal root ganglion neurons and supporting cells of organotypic mouse spinal cord — ganglion cultures exposed to taxol.Neuroscience 10, 491–509.
Parness, J. &Horwitz, S. B. (1981) Taxol binds to polymerized tubulin in vitro.Journal of Cell Biology 91, 479–87.
Peterson, E. R. &Crain, S. M. (1982) Nerve growth factor attenuates neurotoxic effects of Taxol on spinal cord-ganglion explants from fetal mice.Science 217, 377–9.
Prineas, J. W., Ouvrier, R. A., Wright, R. G., Walsh, J. C. &McLeod, J. G. (1976) Giant axonal neuropathy. A generalized disorder of cytoplasmic microfilament formation.Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 35, 458–70.
Raine, C. S. (1977) Schwann cell responses during recurrent demyelination and their relevance to onion-bulb formation.Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 3, 453–70.
Raine, C. S. (1982) Differences in the nodes of Ranvier of large and small diameter fibres in the P.N.S.Journal of Neurocytology 11, 935–47.
Raine, C. S., Finch, H. &Masone, A. (1983) Axoplasmic asymmetry at the node of Ranvier.Journal of Neurocytology 12, 533–6.
Raine, C. S., Ghetti, B. &Shelanski, M. L. (1971) On the association between microtubules and mitochondria within axons.Brain Research 34, 389–94.
Schiff, P. B., Fant, J. &Horwitz, S. B. (1979) Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol.Nature 277, 665–7.
Schiff, P. B. &Horwitz, S. B. (1980) Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 77, 1561–5.
Schiff, P. B. &Horwitz, S. B. (1981) Taxol assembles tubulin in the absence of exogenous guanosine 5′-triphosphate or microtubule-associated proteins.Biochemistry 20, 3242–52.
Singer, M. &Steinberg, M. C. (1972) Wallerian degeneration. A reevaluation based on transected and colchicine-poisoned nerves in the amphibian, Triturus.American Journal of Anatomy 133, 51–63.
Spencer, P. S. &Schaumburg, H. H. (1976) Central-peripheral distal axonopathy. The pathology of dying-back polyneuropathies. InProgress in Neurapathology, Vol. 3 (edited byZimmerman, H. M.), pp. 253–95. New York: Grune and Stratton.
Wani, M. C., Taylor, H. I., Wall, M. E., Coggon, P. &McPhail, A. T. (1971) Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol: a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia.Journal of the American Chemical Society 93, 2325–7.
Zelena, J., Lubinska, L. &Guttman, E. (1968) Accumulation of organelles at the ends of interrupted axons.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 91, 200–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Röyttä, M., Horwitz, S.B. & Raine, C.S. Taxol-induced neuropathy: short-term effects of local injection. J Neurocytol 13, 685–701 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148489
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148489