Summary
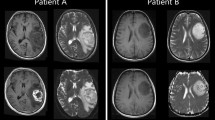
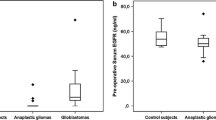
Proteases and their inhibitors have been shown to play roles in tumor invasion and metastasis in a number of experimental models. Recently, relative increases in the amounts of urokinase type plasminogen activator (uPA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) in tumor samples have been correlated with poorer pathological grade, shorter disease-free interval, and shorter survival. To date, all studies investigating the prognostic significance of proteases and their inhibitors have been limited to extracranial cancer. In this article, we review the literature and present our data on the prognostic significance of proteases in human brain tumors. High levels of uPA were seen in malignant glioma and metastatic tumors (n=82), whereas normal levels of uPA were found in low-grade gliomas. Analysis with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated a significant correlation between high levels of uPA and necrosis and edema (n=50; P < 0.05). Similarly, patients with high levels of uPA had shorter survival than did patients with low levels of uPA.
Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA), which was virtually absent in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), colon, lung, and breast metastasis, was found in normal quantities in anaplastic astrocytoma (AA), low-grade glioma (LGG), and meningioma. Melanoma had significantly more tPA activity than normal brain did. A reverse correlation was found between tPA and MRI findings of necrosis, enhancement, and edema. Similarly, patients with no detectable tPA activity had shorter survival than did patients with detectable tPA activity. We conclude that high levels of uPA and absent tPA activity correlate with histologically malignant brain tumors, aggressive characteristics, and shorter survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly PJ, Daumas-Duport C, Kispert DB, Kall BA, Scheithauer BW, Illig JJ: Imaging-based stereotaxic serial biopsies in untreated intracranial glial neoplasms. J Neurosurg 66: 865–874, 1987
Pederson PH, Marienhagen K, Mork S, Bjerkvig R: Migratory pattern of fetal rat brain cells and human glioma cells in the adult rat brain. Cancer Res 53: 5158–5165, 1993
Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Stetler-Stevenson WG: Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: An imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 64: 327–336, 1991
Ellis V, Danø K: Plasminogen activation by receptor-bound urokinase. Semin Thromb Haemostat 17: 194–200, 1991
Mohanam S, Sawaya R, McCutcheon I, Ali-Osman F, Boyd D, Rao JS: Modulation ofin vitro invasion of human glioblastoma cells by urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor antibody. Cancer Res 53: 4143–4147, 1993
Andreasen PA, Nielsen LS, Kristensen P, Grondahl-Hansen J, Skriver L, Danø K: Plasminogen activator inhibitor from human fibrosarcoma cells binds urokinase-type plasminogen activator, but not its proenzyme. J Biol Chem 261: 7644–7651, 1986
Cubellis MV, Andreasen P, Ragno P, Mayer M, Danø K, Blasi F: Accessibility of receptor-bound urokinase to type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 4828–4832, 1989
Olson D, Pollanen J, Hoyer-Hansen G, Ronne E, Sakaguchi K, Wun TC, Apella E, Danø K, Blasi F: Internalization of the urokinase: Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complex is mediated by the urokinase receptor. J Bio Chem 267: 9129–9133, 1992
Ossowski L, Reich E: Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell 35: 611–619, 1983
Achbarou A, Kaiser S, Tremblay G, Ste-Marie LG, Brodt P, Goltzman D, Rabbani SA: Urokinase over production results in increased skeletal metastasis by prostate cancer cellsin vivo. Cancer Res 54: 2372–2377, 1994
Pyke C, Kirstensen P, Ralfkiaer E, Eriksen J, Danø K: The plasminogen activation system in human colon cancer: Messenger RNA for the inhibitor PAI-1 is located in endothelial cells in the tumor stroma. Cancer Res 51: 4067–4071, 1991
Danø K, Andreasen PA, Grondahl-Hansen J, Kristensen P, Nielsen LS, Skriver L: Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 44: 139–266, 1984
Ausprunk DH, Folkman J: Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during angiogenesis. Microvasc Res 14: 53–65, 1977
Reilly D, Christensen L, O'Sullivan C, O'Higgins N, Fennelly JJ, Andreasen PA: Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in human breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer 50: 208–214, 1992
Alvord EC Jr: Is necrosis helpful in the grading of gliomas? Editorial opinion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 51: 127–132, 1992
Nelson JS, Tsukada Y, Schoenfeld D, Fulling K, Lamarche J, Peress N: Necrosis as a prognostic criterion in malignant supratentorial astrocytric gliomas. Cancer 52: 550–554, 1983
Sawaya R: The fibrinolytic enzymes in the biology of brain tumors. In: Sawaya R (ed) Fibrinolysis and the Central Nervous System. Hanley and Belfus, Inc., Philadelphia, 1990, pp 106–126
Sawaya R, Rämö J, Shi ML, Mandybur G: Biological significance of tissue plasminogen activator content in brain tumors. J Neurosurg 74: 480–486, 1991
Sawaya R, Yamamoto M, Ramo OJ, Shi ML, Rao JS: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in brain tumors: Relation to malignancy and necrosis. Neurosurgery (in press), 1994
Colucci M, Parmo JA, Collen D: Inhibition of one-chain and two-chain forms of human tissue-type plasminogen activator by the fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activatorin vitro andin vivo. J Lab Clin Med 198: 53–59, 1986
Medcalf RL, Kruithof EKO, Schleuning WF: Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and 2 are tumor necrosis factor/cachectin-responsive genes. J Exp Med 168: 751–759, 1988
van Hinsbergh VWM, Kooistra T, van den Berg EA, Princen HM, Fiers W, Emeis JJ: Tumor necrosis factor increases the production of plasminogen activator inhibitor in human endothelial cellsin vitro and in ratsin vivo. Blood 72: 1467–1473, 1988
Engel U: The morphology of hemostasis failure in glial brain tumors. Acta Histochem (Suppl) 42: 201–210, 1992
Caillé JM, Guibert-Tranier F, Calabet A, Billerey J, Piton J: Abnormal enhancements after contrast injection. In: Caillé JM, Salmon G (eds) Computerized Tomography. Springer, Berlin, 1980, pp 166–171
Nyström S: Pathological changes in blood vessels of human glioblastoma multiforme. Comparative studies using plastic casting, angiography, light microscopy, and electron microscopy, and with reference to some other brain tumors. Acta Pathol Microbiol 49 (Suppl): 137, 1960
Long DM: Capillary ultrastructure and the blood-brain barrier in human malignant brain tumors. J Neurosurg 32: 127–144, 1970
Pepper MS, Belin D, Montesano R, Orci L, Vassalli JD: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteolytic and angiogenic properties of endothelial cellsin vitro. J Cell Biol 11: 743–755, 1990
Quindlen EA, Bucher PB: Correlation of tumor plasminogen activator with peritumoral cerebral edema. J Neurosurg 66: 729–733, 1987
Unterberg A, Baethmann AJ: The kallikrein-kinin system as mediator in vasogenic brain edema. Part 1: Cerebral exposure to bradykinin and plasma. J Neurosurg 61: 87–96, 1984
Maier-Hauff K, Baethmann AJ, Lange M, Schürer L, Unterberg A: The Kauikrien-Kinin system as a mediator in vasogenic brain edema. J Neurosurg 61: 97–106, 1984
Duffy MJ, Reilly D, O'Sullivan C, O'Higgins N, Fennelly JJ, Andreasen P: Urokinase-plasminogen activator, a new and independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer Res 50: 6827–6829, 1990
Grondahl-Hansen J, Christensen U, Rosenquist C, Brunner N, Mouridsen HT, Danø K, Blichert-Toft M: High levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its inhibitor PAI-1 in cytosolic extracts of breast carcinomas are associated with poor prognosis. Cancer Res 53: 2513–2521, 1993
Foekens JA, Schmitt M, van Putten WLJ, Peters HA, Bontenbal M, Janicke F, Klijn JGM: Prognostic value of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in 671 primary breast cancer patients. Cancer Res 52: 6101–6105, 1992
Kono S, Rao JS, Bruner JM, Sawaya R: Immunohistochemical localization of plasminogen activator inhibitors-1 (PAI-1) in human brain tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurology 53: 256–262, 1994
Yamamoto M, Sawaya R, Loskutoff DJ, Bruner JM, Oka K, Tomonaga M, Nicolson GL, Rao JS: Expression and cellular localization of messenger RNA for plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in human astrocytomasin vivo. Cancer Res 54: 3329–3332, 1994
Oka T, Ishida T, Nishino T, Sugimachi K: Immunohistochemical evidence of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in primary and metastatic tumors of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 51: 3522–3525, 1991
Frank AJ, Ellis E: Immunohistochemical localization of tissue plasminogen activator in human brain tumors. Br J Cancer 59: 462–466, 1989
Pedersen H, Grondahl-Hansen J, Francis DKO, Hansen HH, Danø K, Brunner N: Urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 54: 120–123, 1994
Landau BJ, Kwaan HC, Verrusio EN, Brem SS: Elevated levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in malignant brain tumor. Cancer Res 54: 1105–1108, 1994
Rutka JT, Myatt CA, Giblin JR, Davis RL, Rosenblum ML: Distribution of extracellular matrix proteins in primary human brain tumors: An immunohistochemical analysis. Can J Neurol Sci 14: 25–30, 1987
Gladson CL, Cheresh DA: Glioblastoma expression of vitronectin and the a2b3 integrin. J Clin Invest 88: 1924–1932, 1991
Yamamoto M, Sawaya R, Mohanam S, Bindal AK, Bruner JM, Oka K, Rao VH, Tomonaga M, Nicolson GL, Rao JS: Expression and localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human astrocytomasin vivo. Cancer Res 54: 3654–3661, 1994
Russel DC, Rubinstain LJ: Pathology of tumors of the nervous system (5th ed), Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1989
Roblin R, Young PL: Dexamethasone regulation of plasminogen activator in embryonic and tumor-derived human cells. Cancer Res 40: 2706–2713, 1980
Coleman PL, Patel PD, Cwikel BJ, Rafferty UM: Characterization of the dexamethasone-induced inhibitor of plasminogen activator in HTC hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 261: 4352–4357, 1986
Laug WE: Glucocorticoids inhibit plasminogen activator production by endothelial cells. Thromb Haemostat 50: 888–892, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bindal, A.K., Hammoud, M., Shi, W.M. et al. Prognostic significance of proteolytic enzymes in human brain tumors. J Neuro-Oncol 22, 101–110 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052886
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052886