Abstract
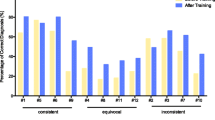
NEONATE is a prototype of an expert system for the Newborn Intensive Care Unit developed at the Primary Children's Medical Center in Salt Lake City, Utah. A pilot study was undertaken to see if the addition of radiological frames to the NEONATE software could aid attending Neonatologists to interpret chest X-ray films. A set of radiological frames was created from rules generated by a radiologist. The performance of these radiological frames was compared to the performance of other radiologists using the Kappa statistic to measure agreement. There is a good agreement between the computer's decisions and the radiologists' decisions. The radiological frames were also tested to see if they help physicians who are not trained in radiology. A system that compares the residents' interpretation and the computer's interpretation to a gold standard interpretation was developed. It shows that the computer helps the first and second year residents, but not the third year residents. This article suggests that NEONATE's interpretation of chest X-ray findings are close to the radiologists' interpretations. While NEONATE's radiological frames help novice physicians in reaching better chest X-ray interpretation, the current study suggests that they are not likely to help a Neonatologist.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warner, H.R., Olmsted, C.M., and Rutherford, B.D., HELP—A Program for Medical Decision-Making,Comput. Biomed. Res. 1972, 5:65–74.
Pryor, T.A., Gardner, R.M., Clayton, P.D., and Warner, H.R., The HELP System.J. Med. Sys. 1983, 7(2):87–101.
Pryor, T.A., The HELP Medical Record System.MD Comput. 1988, 5(5):22–33.
Janik, D.S., Swarner, O.W., Henriksen, K.M., and Wyman, M.L., A computerized single entry system for recording and reporting data on high-risk newborn infants.J. Pediatr. 1978, 93:519–523.
Janik, D.S., Swarner, O.W., Henriksen, K.M., and Wyman, M.L., Computerized newborn intensive care data recording and reporting II: An online system.J. Pediatr. 1979, 94:326–330.
Janik, D.S., Sharp, E.M., Forbush, L., Wyman, M.L., and Jung, A.L., Computerized newborn intensive care data recording, reporting and research III: A practical microcomputer system.J. Pediatr. 1980, 97:497–500.
Franco, A., Farr, F.L., King, J.D., Clark, J.S., and Haug, P.J., NEONATE—An expert application for the HELP system: Comparison of the computer's and the physician's problem list.J. Med. Sys. 1990, 14(5):297–306.
Spitzer, R.I., Cohen, J., Fleiss, J.I., and Endicott, J., Quantification of agreement in psychiatric diagnosis.Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 1967, 17:81–87.
Fleiss, J.I., Measuring nominal scale agreement among many raters.Psychol. Bull. 1971, 76(3):378–382.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franco, A., King, J.D., Farr, F.L. et al. An assessment of the radiological module of NEONATE as an aid in interpreting chest X-ray findings by nonradiologists. J Med Syst 15, 277–286 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999165
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999165