Abstract
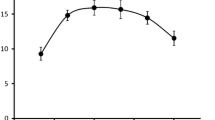
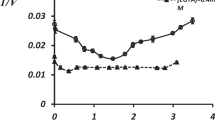
Procedures were developed for measurement of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in resealed plasma membrane vesicles from postmortem human brain. The vesicle preparation method permits use of stored frozen tissue with minimal processing required prior to freezing. Vesicles prepared in this manner transport Ca2+ in the presence of a Na+ gradient. The kinetic characteristics of the Na+/Ca2+ exchange process were determined in membrane vesicles isolated from hippocampus and cortex. The Kact for Ca2+ was estimated to be 32 μM for hippocampal and 17 μM for cortical tissue. The maximal rate of Ca2+ uptake (Vmax) was 3.5 nmol/mg protein/15 sec and 3.3 nmol/mg protein/15 sec for hippocampal and cortical tissue, respectively. Exchange activity was dependent on the Na+ gradient, and was optimal in the high pH range. Therefore, membranes in which Na+-dependent o Ca2+ transport activity is preserved can be isolated from postmortem human brain and could be used to determine the influence of pathological conditions on this transport system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaustein, M. P. 1988. Calcium and synaptic function. Pages 275–304,in Baker, P. F. (ed.), Calcium in Drug Action, Springer-Verlag Inc., Berlin.
Blaustein, M. P., and Oborn, C. J. 1975. The influence of sodium on calcium fluxes in pinched-off nerve terminalsin vitro. J. Physiol. Lond. 247:657–686.
Michaelis, M. L., and Michaelis, E. K. 1981. Ca++ fluxes in resealed synaptic plasma membrane. Life Sci. 28:37–45.
Hakim, G., Itano, T., Verma, A. K., and Penniston, J. T. 1982. Purification of the Ca2+ and Mg2+-requiring ATPase from rat brain synaptic plasma membrane. Biochem. J. 207:225–231.
Michaelis, M. L., Kitos, T. E., Nunley, E. W., Lecluyse, E., and Michaelis, E. K. 1987. Characteristics of Mg2+-dependent, ATP-activated Ca2 transport in synaptic and microsomal membranes and in permeabilized synaptosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 262:4182–4189.
Kaczorowski G. J. 1985. Sodium/calcium exchange and calcium homeostasis in excitable tissue. Pages 215–226,in Egan, R. W. (ed.), Ann. Reports Med. Chem., Academic Press, Inc., New York.
DiPolo, R. and Beauge, L. 1988. Ca2+ transport in nerve fibers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 947:549–569.
Rahamimoff, H., and Spanier, R. 1979. Sodium-dependent calcium uptake in membrane vesicles derived from rat brain synaptosomes. FEBS Lett. 104:111–114.
Michaelis, M. L., and Michaelis, E. K. 1983. Alcohol and local anesthetic effects on Na+-dependent Ca2+ fluxes in brain synaptic membranc vesicles. Biochem. Pharmacol. 32:963–969.
Reynolds, G. P. 1985. Neurochemical studies in human postmortem brain tissue. Pages 477–496,in Boulton, A. D., and Baker, G. B. (ed.), Neuromethods Vol. 2, General Neurochemical Techniques, Humana Press, Clifton, NJ.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–208.
Atkinson, A., Gatenby, A. D., and Lowe, A. G. 1973. The determination of inorganic orthophosphate in biological systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 320:205–209.
Michaelis, M. L., Johe, K., and Kitos, T. E. 1984. Age-dependent alterations in synaptic membrane systems for Ca2+ regulation. Mech. Ageing Devel. 25:215–225.
Philipson, K. D., Bersohn, M. M., and Nishimoto, A. Y. 1982. Effects of pH on Na+−Ca2+ exchange in canine cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Circ. Res. 50:287–293.
Michaelis, M. L., Jayawickreme, C., and Joachims, B. 1989. Chromatographic procedures in the isolation of the Na+−Ca2+ antiporter from brain synaptic membranes. J. Cell. Biol. 107:127a.
Siegel, P. K. S., Cragoe, E. J., Jr., Trumble, M. J., and Kaczorwski, G. J. 1984. Inhibition of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in membrane vesicles and papillary muscle preparations from guinea pig heart by analogs of amiloride. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81:3238–3242.
Sanchez-Armass, S., and Blaustein, M. P. 1987. Role of sodium/calcium exchange in the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ in nerve terminals. Am. J. Physiol. 252:C595-C603.
Nachshen, D. A., Sanchez-Armass, S., and Weinstein, A. M. 1986. The regulation of cytosolic calcium in rat brain synaptosomes by sodium-dependent calcium efflux. J. Physiol. 381:17–28.
Reeves, J. P., Bailey, C. A. and Hale, C. C. 1986. Redox modification of sodium-calcium exchange activity in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 261:4948–4955.
Slaughter, R. S., Garcia, M. L., Cragoe, E. J., Jr., Reeves J. P., and Kaczorowski, G. J. 1988. Inhibition of sodium-calcium exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal membrane vesicles. 1. Mechanism of inhibition by amiloride analogues. Biochemistry 27:2403–2409.
Hardy, J. A., Dodd, P. R., Oakley, A. E., Perry, R. H., Edwardson, J. A., and Kidd, A. M. 1983. Metabolically active synaptosomes can be prepared from frozen rat and human brain. J. Neurochem. 40:608–614.
Michaelis, M. L., Michaelis, E. K., and Tehan, T. 1983. Alcohol effects on synaptic membrane calcium ion fluxus. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 18:19–23.
Michaelis, M. L., Kitos, T. E., and Tehan, T. 1985. Differential effects of ethanol on two synaptic membrane Ca2+ transport systems. Alcohol 2:129–132.
Slaughter, R. S., Shevell, J. L., Felix, J. P., Garcia, M. L., and Kaczorowski, G. J. 1989. High levels of sodium-calcium exchange in vascular smooth muscle sarcolemmal membrane vesicles. Biochemistry 28:3995–4002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoel, G., Michaelis, M.L., Freed, W.J. et al. Characterization of Na+−Ca2+ exchange activity in plasma membrane vesicles from postmortem human brain. Neurochem Res 15, 881–887 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00965907
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00965907