Summary
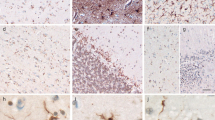
Neuroaxonal spheroids became evident microscopically after the autopsy of a 45-year-old woman with pigmentation of the globus pallidus suggesting Hallervorden-Spatz disease. In our opinion the fine floccular pigment seen electron-microscopically in many of the axonal spheroids is melanin, an end product of catecholamine metabolism. Neurofibrillary degeneration, senile plaques, and granulovacuolar degeneration in the hippocampus produced a picture of Alzheimer's disease. Pontocerebellar degeneration and motor neuron disease were also observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aicardi J, Castelein P (1979) Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. Brain 102:727–748
Borit A, Rubinstein JL, Urich H (1975) The striatonigral degenerations. Brain 98:101–112
Bots GT, Staal A (1973) Amyothrophic lateral sclerosis-dementia complex, neuroaxonal dystrophy and Hallervorden-Spatz disease. Neurology (Minn) 23:35–39
Bronson RT, Schoene WC (1980) Spontaneous pallido-nigral accumulation of iron pigment and spheroid-like structures in Macaque monkeys. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 39:181–196
Cowen D, Olmstead EV (1963) Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 22:175–236
Dooling EC, Schoene WC, Richardson EP (1974) Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome. Arch Neurol 30:70–82
Fischer O (1910) Die presbyophrene Demenz, deren anatomische Grundlage und klinische Abgrenzung. Z Ges Neurol Psychiat 3:371–471
Glenner GG (1980) Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 302:1283–1293
Grol CJ (1980) The chemistry of dopamine. In: Horn AS, Korf J, Westerink BHC (eds) The neurobiology of dopamine. Academic Press, London, pp 7–27
Hallervorden J, Spatz H (1922) Eigenartige Erkrankung im extrapyramidalen System mit besonderer Beteiligung des Globus pallidus und der Substantia nigra. Z Ges Neurol Psychiat 79:254–302
Helfand M (1935) Status pigmentatus. Its pathology and its relation to Hallervorden-Spatz disease. J Nerv Ment Dis 81:662–675
Hornykiewicz O (1979) Brain dopamine in Parkinson's disease and other neurological disturbances. In: Horn AS, Korf J, Westerink BHC (eds) The neurobiology of dopamine. Academic Press, London, pp 633–654
Iversen LL (1979) The chemistry of the brain. Sci Am 241:134–149
Marsden CD (1969) Brain melanin. In: Wolman M (ed) Pigments in pathology. Academic Press, New York, pp 395–420
Park BE, Netsky MG, Betsill WL (1975) Pathogenesis of pigment and speroid formation in Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome and related disorders. Neurology (Minn) 25:35–39
Scheithauer BW, Forno LS, Dorfman LJ, Kane CA (1978) Neuroaxonal dystrophy (Seitelberger's disease) with late onset, protracted course and myoclonic epilepsy. J Neurol Sci 36:247–258
Schochet SS, McCormick (1972) Ultrastructure of Hirano bodies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 21:50–60
Seitelberger F (1957) Zur Morphologie und Histochemie der generativen Axonveränderungen im Zentralnervensystem. Proceedings of the IIIrd International Congress of Neuropathology, Bruxelles, pp 127–147
Seitelberger F (1976) Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome. In: Blackwood W, Corsellis JAN (eds) Greensfield's neuropathology, 3rd edn. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, pp 178–180
Toga M, Bérard-Badier M, Gamberelli-Dubois D (1970) La dystrophie neuroaxonale infantile ou maladie de Seitelberger. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 15:327–350
VanWoert MN, Prasad KN, Borg DC (1967) Spectroscopic studies of substantia nigra pigment in human subjects. J Neurochem 14:706–716
Wiliamson K, Sima AAF, Curry B, Ludwin SK (1982) Neuroaxonal dystrophy in young adults. A clinicopathological study of two unrelated cases. Ann Neurol 11:335–343
Wisniewski K, Jervis GA, Moretz RC, Wisniewski HM (1979) Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles in diseases other than senile and presenile dementia. An Neurol 5:288–294
Wohlfart G (1959) Degenerative and regenerative axonal changes in the ventral horn, brain stem and cerebral cortex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Univ Lundens 56:1–13
Yanagisawa N, Shiraki H, Minakawa M, Narabayashi H (1966) Clinicopathological and histochemical studies of Hallervorden-Spatz disease with torsion dystonia with special reference to diagnostic criteria of the disease from the clinicopathological view point. Prog Brain Res 21B:373–425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartmann, H.A., White, S.K. & Levine, R.L. Neuroaxonal dystrophy with neuromelanin deposition, neurofibrillary tangles, and neuronal loss. Acta Neuropathol 61, 169–172 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691981
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691981