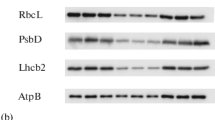
Abstract
We have examined phytochrome effects on the abundance of transcripts from several nuclear and chloroplast genes in buds of dark-grown pea seedlings and primary leaves of dark-grown mung-bean seedlings. Probes for nuclear-coded RNAs were selected from a library of cDNA clones and included those corresponding to the small subunit (SS) of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase and a chlorophyll a/b binding protein (AB). Transcripts from chloroplast genes for RuBP carboxylase large subunit (LS) and a 32,000-dalton photosystem II polypeptide (PII) were assayed with cloned fragments of the chloroplast genome. In addition, we present data on transcripts from a number of other nuclear genes of unknown function, several of which change in abundance during light-induced development. Transcript levels were measured as a proportion of total RNA by a dot blot assay in which RNA from different tissues or stages is fixed to nitrocellulose and hybridized with 32P-labeled probes prepared from cloned DNAs. Several patterns of induction can be seen. For example, although both SS and AB RNAs show positive, red/far-red reversible responses in both pea and mung bean, in pea buds the induction ratio for SS RNA is much higher than that for AB RNA, while just the reverse is true for mung-bean leaves. In addition, treatment with lowfluence red light produces full induction of the pea AB RNA, while SS RNA in the same tissue does not reach a maximum steady-state level until after about 24 h of supplementary high-intensity white light. In pea buds, chloroplast genes (LS, PII) also show clear responses to phytochrome, as measured by the steady-state levels of their RNA products. Chloroplast DNA levels (as a fraction of the total cellular DNA) show the same response pattern, which may indicate that in peas many of the light effects we see are related to a general stimulation of chloroplast development. In mung beans, the levels of plastid DNA and RNA are already quite high in the leaves of 7-d dark-grown seedlings, and light effects are much less pronounced. The results are consistent with the notion that chloroplast development is arrested at a later stage in dark-grown mung-bean leaves than in etiolated pea buds.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AB:
-
chlorophyll a/b polypeptide of the light-harvesting complex
- FR:
-
far-red light
- PII:
-
32,000-dalton photosystem II polypeptide
- R:
-
red light
- SS:
-
small subunit and
- LS:
-
large subunit of ribulosebisphospate carboxylase (RuP2; 3-phospho-D-glycerate carboxylase [dimerizing], EC 4.1.1.39)
References
Apel, K. (1979) Phytochrome-induced appearance of mRNA activity for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Eur. J. Biochem. 97, 183–188
Apel, K. (1981) The protochlorophyllide holochrome of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): phytochrome-induced decrease of translatable mRNA coding for the NADPH: protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase. Eur. J. Biochem. 120, 89–93
Arnon, D. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15
Bedbrook, J.R., Link, G. Coen, D.M., Bogorad, L., Rich, A. (1978) Maize plastid gene expressed during photoregulated development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 3060–3064
Bedbrook, J., Smith, S., Ellis, R. (1980) Molecular cloning and sequencing of cDNA encoding the precursor to the small subunit of chloroplast ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Nature (London) 287, 692–697
Biessmann, H., Craig, E.A., McCarthy, B.S. (1979) Rapid quantitation of individual RNA species in a complex population. Nucleic Acids Res. 7, 981–996
Birnboim, H.D., Doly, J. (1979) A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 7, 1513–1523
Bolivar, F., Rodriguez, R.L., Greene, T.J., Betlach, M.C., Heyneker, H.L., Boyer, H.W. (1977) Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene 2, 95–113
Broglie, R., Bellemare, G., Bartlett, S.G., Chua, N.-H., Cashmore, A.R. (1981) Cloned DNA sequences complementary to mRNAs encoding precursors to the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and a chlorophyll a/b binding polypeptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 7304–7308
Cuellar, R.E. (1982) The structure and evolution of repeated DNA sequences in Pisum sativum: a molecular characterization. Ph.D. thesis, Stanford University. Stanford, Cal., USA
Dagert, M., Ehrlich, S.D. (1979) Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene 6, 23–28
Dyer, T.A., Miller, R.H., Greenwood, A.D. (1971) Leaf nucleic acids characteristics and role in the differentiation of plastids. J. Exp. Bot. 22, 125–136
Eaglesham, A.R.J., Ellis, R.J. (1974) Protein synthesis in chloroplast. II. Light-driven synthesis of membrane proteins by isolated pea chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 335, 396–407
Edelman, M. (1981) Nucleic acids of chloroplasts and mitochondria. In: The biochemistry of plants, vol. 6, pp. 249–301, Marcus, A., ed. Academic Press, New York London
Ellis, J.R. (1981) Chloroplst proteins: synthesis, transport, and assembly. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 32, 111–137
Everett, M., Jorgensen, R.A., Thompson, W.F. (1981) Phytochrome control of transcript abundance in developing pea leaves. Carnegie Inst. Washington Yearb. 80, 79–80
Gallagher, T.F., Ellis, R.J. (1982) Light-stimulated transcription of genes for two chloroplast polypeptides in isolated pea leaf nuclei. EMBO J. 1, 1493–1498
Geiser, M., Doring, H., Wostemeyer, J., Behrens, V., Tillman, E., Starlinger, P. (1980) A cDNA clone from Zea mays endosperm sucrose synthetase mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 8, 6175–6188
Glisin, V., Crkvenjakov, R., Byus, C. (1974) Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry 13, 2633–2637
Gorton, H.L., Briggs, W.R. (1980) Phytochrome responses to end-of-day irradiation in light-grown corn grown in the presence and absence of Sandoz 9789. Plant Physiol. 66, 1024–1026
Grunstein, M.G., Hogness, D.S. (1975) Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72, 3961–3965
Hallick, R.B., Chelm, B.K., Gray, P.W., Orozco, E.M. Jr. (1977) Use of aurintricarboxylic acid as an inhibitor of nucleases during nucleic acid isolation. Nucleic Acids Res. 4, 3055–3064
Heinze, H., Herzfeld, F., Kiper, M. (1980) Light-induced appearance of polysomal poly A-rich messenger RNA during greening of barley plants. Eur. J. Biochem. 111, 137–144
Henshall, J.D., Goodwin, T.W. (1964) The effect of red and far red light on carotenoid and chlorophyll formation in pea seedlings. Photochem. Photobiol. 3, 243–247
Hong, Y.-N., Schopfer, P. (1981) Control by phytochrome of urate oxidase and allantoinase activities during peroxisome development in the cotyledons of mustard (Sinapis alba L.) seedlings. Planta 152, 325–335
Jorgensen, R.A., Thompson, W.F. (1980) Observing patterns of gene expression at the RNA level: the greening response in Pisum. Carnegie Inst. Washington Yearb. 79, 116–119
Kafatos, F.C., Jones, C., Efstratiadis, A. (1979) Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 7, 1541–1552
Kirk, J.T.O., Tilney-Bassett, R.A.E. (1978) The plastids: their chemistry, structure, growth, and inheritance, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Klein, S., Schiff, J.A., Holowinsky, A.W. (1972) Events surrounding the early development of Euglena chloroplasts. II. Normal development of fine structure and the consequences of preillumination. Dev. Biol. 28, 253–273
Link, G. (1982) Phytochrome control of plastid mRNA in mustard (Sinapis alba L.). Planta 154, 81–86
Mandoli, D.F., Briggs, W.R. (1981) Phytochrome control of two low-irradiance responses in etiolated oat seedlings. Plant Physiol. 67, 733–739
Maniatis, T., Jeffrey, A., Kleid, D.G. (1975) Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage λ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72, 1184–1188
McIntosh, L., Poulsen, C., Bogorad, L. (1980) Chloroplast gene sequence for the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase of maize. Nature (London) 288, 556–560
Murray, M.G., Peters, D.L., Thompson, W.F. (1981) Ancient repeated sequences in the pea and mung bean genomes and implications for genome evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 17, 31–42
Myers, J.C., Spiegelman, S. (1978) Sodium pyrophosphate inhibition of RNA·DNA hybrid degradation by reverse transcriptase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 5329–5333
Palmer, J.D., Thompson, W.F. (1981) Clone banks of the mung bean, pea, and spinach chloroplast genomes. Gene 15, 21–26
Palmer, J.D., Thompson, W.F. (1982) Chloroplast DNA rearrangements are more frequent when a large inverted repeat sequence is lost. Cell 29, 537–550
Roychoudhury, R., Jay, E., Wu, R. (1976) Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acid Res. 3, 101–116
Sasaki, Y., Ishiye, M., Sakihama, T., Kamikubo, T. (1981) Light-induced increase of mRNA activity coding for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 2315–2320
Schiff, J.A. (1978) Photocontrol of chloroplast development in Euglena. In: Chloroplast development, pp. 747–767, Akoyunolgov, G., ed. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam
Schiff, J.A. (1980) Development, inheritance, and evolution of plastids and mitochondria. In: The biochemistry of plants, vol. 1, pp. 209–272, N.E. Tolbert, ed. Academic Press, New York London
Schopfer, P. (1977) Phytochrome control of enzymes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 28, 223–252
Shinozaki, K., Sasaki, Y., Sakihama, T., Kamikubo, T. (1982) Coordinate light-induction of two mRNAs, encoded in nuclei and chloroplasts, of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. FEBS Lett. 144, 73–76
Silflow, C.D., Hammett, J.R., Key, J.L. (1979) Sequence complexity of polyadenylated ribonucleic acid from soybean suspension culture cells. Biochemistry 18, 2725–2731
Sims, T., Hague, D. (1981) Light-stimulated increase of translatable mRNA for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in leaves of maize. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 8252–8255
Smith, H. (1975) Phytochrome and photomorphogenesis. McGraw-Hill, Maidenhead
Smith, H., Billett, E.E., Giles, A.B. (1977) The photocontrol of gene expression in higher plants. In: Regulation of enzyme synthesis and activity in plants, pp 93–127, Smith, H., ed. Academic Press, New York London
Smith, S., Ellis, R.J. (1981) Light-stimulated accumulation of transcripts of nuclear anc chloroplast genes for ribosebisphosphate carboxylase. J. Mol. Appl. Genet. 1, 127–137
Sullivan, D., Brisson, M., Verma, D.P. (1980) Reverse transcription of 25S soybean ribosomal RNA in the absence of exogenous primer. Biochim. Biophys. Res. Comm. 94, 144–150
Tobin, E.M. (1978) Light regulation of specific mRNA species in Lemna gibba L. G-3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 4749–4753
Tobin, E.M. (1981a) White light effects on the mRNA for the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein in Lemna gibba L. G-3. Plant Physiol. 67, 1078–1083
Tobin, E.M. (1981b) Phytochrome-mediated regulation of messenger RNAs for the small subunit of ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase and the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein in Lemna gibba. Plant Mol. Biol. 1, 35–51
Wahl, G.M., Stern, M., Stark, G.R. (1979) Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 3683–3687
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
C.I.W.-D.P.B. Publication No. 788
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, W.F., Everett, M., Polans, N.O. et al. Phytochrome control of RNA levels in developing pea and mung-bean leaves. Planta 158, 487–500 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397240
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397240